Light presentation
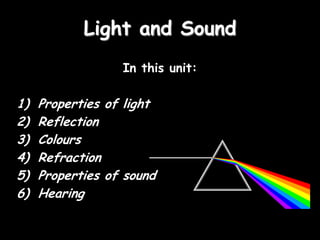
- 1. Light and Sound In this unit: 1) Properties of light 2) Reflection 3) Colours 4) Refraction 5) Properties of sound 6) Hearing
- 2. Part 1 – Properties of Light Light travels in straight lines: Laser
- 3. Light travels VERY FAST – around 300,000 kilometres per second. At this speed it can go around the world 8 times in one second.
- 4. Light travels much faster than sound. For example: 1) Thunder and lightning start at the same time, but we will see the lightning first. 2) When a starting pistol is fired we see the smoke first and then hear the bang.
- 5. We see things because they reflect light into our eyes: Homework
- 6. Luminous and non-luminous objects A luminous object is one that produces light. A non-luminous object is one that reflects light. Luminous objects Reflectors
- 7. Shadows Shadows are places where light is “blocked”: Rays of light
- 8. Properties of Light summary 1) Light travels in straight lines 2) Light travels much faster than sound 3) We see things because they reflect light into our eyes 4) Shadows are formed when light is blocked by an object
- 9. Part 2 - Reflection Reflection from a mirror: Normal Incident ray Reflected ray Angle of Angle of incidence reflection Mirror
- 10. The Law of Reflection Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection In other words, light gets reflected from a surface at ____ _____ angle it hits it. The same !!!
- 11. Clear vs. Diffuse Reflection Smooth, shiny surfaces have a clear reflection: Rough, dull surfaces have a diffuse reflection. Diffuse reflection is when light is scattered in different directions
- 12. Using mirrors Two examples: 2) A car headlight 1) A periscope
- 13. Colour White light is not a single colour; it is made up of a mixture of the seven colours of the rainbow. We can demonstrate this by splitting white light with a prism: This is how rainbows are formed: sunlight is “split up” by raindrops.
- 14. The colours of the rainbow: Red Orange Yellow Green Blue Indigo Violet
- 15. Adding colours White light can be split up to make separate colours. These colours can be added together again. The primary colours of light are red, blue and green: Adding blue and red Adding blue and makes magenta green makes cyan (purple) (light blue) Adding red Adding all and green three makes makes yellow white again
- 16. Seeing colour The colour an object appears depends on the colours of light it reflects. For example, a red book only reflects red light: White Only red light light is reflected
- 17. A pair of purple trousers would reflect purple light (and red and blue, as purple is made up of red and blue): Purple light A white hat would reflect all seven colours: White light
- 18. Using coloured light If we look at a coloured object in coloured light we see something different. For example, consider a football kit: Shirt looks red White light Shorts look blue
- 19. In different colours of light this kit would look different: Red Shirt looks red light Shorts look black Shirt looks black Blue light Shorts look blue
- 20. Some further examples: Colour object Object Colour of light seems to be Red Red Red socks Blue Black Green Black Red Black Blue teddy Blue Green Red Green camel Blue Green Red Magenta book Blue Green
- 21. Using filters Filters can be used to “block” out different colours of light: Red Filter Magenta Filter
- 22. Investigating filters Colour of filter Colours that could be “seen” Red Green Blue Cyan Magenta Yellow
- 23. Red Blue Green White Yellow Cyan Magenta
- 24. Refraction Refraction is when waves ____ __ or slow down due to travelling in a different _________. A medium is something that waves will travel through. When a pen is placed in water it looks like this: In this case the light rays are slowed down by the water and are _____, causing the pen to look odd. The two mediums in this example are ______ and _______. Words – speed up, water, air, bent
- 27. Sound – The basics We hear things when they vibrate. If something vibrates with a high frequency (vibrates very ______) we say it has a _____ pitch. If something vibrates with a low frequency (vibrates ______) we say it has a ____ pitch. The lowest frequency I could hear was… Words – slowly, low, high, quickly
- 28. Drawing sounds… This sound wave has a _____ frequency: This sound wave has a ___ _frequency:
- 29. Drawing sounds… This sound wave has a _____ amplitude (loud): This sound wave has a _____ amplitude (quiet):
- 30. Hearing problems Our hearing range can be damaged by several things: 1) Too much ear wax! 2) Damage to the auditory nerve 3) Illness or infections 4) Old age (not like Mr Richards)
- 31. Other sound effects… Like light, sound can be… 1) Reflected – sound reflections are called ______. 2) Refracted – this is why you might sound strange if you try talking underwater
- 32. The Ear Label your diagram with the following: These bones are vibrated by the eardrum This tube carries the sound towards the eardrum This part is used to help us keep our balance This part “picks up” the vibrations This part of the ear contains many small hairs with turn vibrations into an electrical signal This part connects the ear to the mouth This part “channels” the sound towards the ear drum
- 33. The Ear