5.3 igneous rocks
•Transferir como PPT, PDF•
3 gostaram•4,102 visualizações
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Mais conteúdo relacionado
Mais procurados
Mais procurados (20)
Semelhante a 5.3 igneous rocks
Semelhante a 5.3 igneous rocks (20)
Different Types of Rocks and the processes involved in its formation,ppt

Different Types of Rocks and the processes involved in its formation,ppt
RCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRC.pptx

RCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRCRC.pptx
Rock Cycle 2Rock Cycle 2Rock Cycle 2Rock Cycle 2Rock Cycle 2.pptx

Rock Cycle 2Rock Cycle 2Rock Cycle 2Rock Cycle 2Rock Cycle 2.pptx
Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Rock Cycle 2.pptx

Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Rock Cycle Rock Cycle 2.pptx
Rock and the Rock cycle dsflkdsfkdskfl;dskfl;dskfldskflkds;f

Rock and the Rock cycle dsflkdsfkdskfl;dskfl;dskfldskflkds;f
Lecture # 02, 03 316 geology and earth quake engineering 5th

Lecture # 02, 03 316 geology and earth quake engineering 5th
Mais de mojavehack
Mais de mojavehack (20)
5.3 igneous rocks
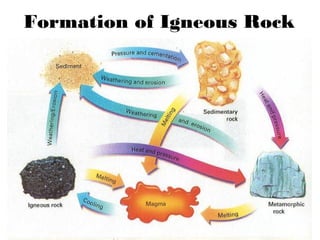
- 1. Formation of Igneous Rock
- 2. Formation of Igneous Rock • When lava cools and hardens it forms igneous rock. • The rock has two categories and is based on how the lava cools. – Intrusive igneous rock – Extrusive igneous rock
- 3. Intrusive Igneous • The cooling of magma deep below the earth’s surface. • Called intrusive because the lava that forms them intrudes other rocks. • The magma then slowly cools to form rock. • The slow cooling allows minerals to collect and form large crystals.
- 4. Extrusive Igneous • Formed when there is a rapid cooling of lava or melting of rocks on the earth’s surface. • The rapid cooling does not give crystals time to form. • The main difference between the two types of igneous rock is the size of the crystal when the rock is forming.
- 5. Texture of the Rocks • The larger the crystals, the more rough the rock will be. • When rapid cooling occurs and crystal are not allowed the opportunity to form, the rock will appear extremely smooth. • Crystal formation will be so small that they are not seen by the unaided eye.
- 6. Texture of the Rocks • An igneous rock with both large and small crystals is called porphyritic. • The porphyritic texture is created when lava cools slowly and is then sped up.
- 7. Texture of Rock • When thick lava cools rapidly no crystals form at all. • Usually thicker lava has an increased amount of trapped gases and this will cause the igneous rock to become full of holes.
- 8. Composition of Rock • The mineral make of the lava determines the chemical make-up of the rock. • There are 3 different types of families: – Felsic – Mafic – Intermediate