Phsiology of fractures
- 1. PRESENTER : Dr ANKUR MITTAL
- 2. What is fracture? Any break in continuty of bone is fracture BUT An injury that fractures bone not only damages its cells , blood vessels and bone matrix but also surrounding tissues, including periosteum and muscles.
- 3. Components of Bone Formation •Bone marrow •Cortex •Periosteum •Soft tissue Note: Periosteum has 2 layers: •an outer fibrous layer • inner more cellular and vascular cambium layer It covers the external surface of bone and participates in healing of many types of fractures. The thicker more cellular periostium of infants and children has more extensive vascular supply therefore more active in fracture healing than adults.
- 4. Blood Supply Long bones have three blood supplies Periosteal vessels 1. Nutrient artery (intramedullary) Nutrient 2. Periosteal vessels artery 3. Metaphyseal vessels Metaphysea vessels
- 5. Nutrient ARTERY •Normally the major blood supply for the diaphyseal cortex (80 to 85%) •Enters the long bone via a nutrient foramen •Forms medullary arteries up and down the bone PERIOSTEAL VESSELS •Arise from the capillary-rich periosteum •Supply outer 15 to 20% of cortex normally •Capable of supplying a much greater proportion of the cortex in the event of injury to the medullary blood supply
- 6. METAPHSEAL VESSELS •Arise from periarticular vessels •Penetrate the thin cortex in the metaphyseal region and anastomose with the medullary blood supply Vascular Response in Fracture Repair •Initially decreased flow due to disrupted vessels •In several days the blood flow greatly increases, peaking at 2 weeks •Gradually returns to normal by 12 weeks
- 7. MECHANISM OF BONE FORMATION 1. Cutting Cones 2. Intramembranous Bone Formation 3. Endochondral Bone Formation CUTTING CONES Primarily a mechanism to remodel bone Osteoclasts at the front of the cutting cone remove bone Trailing osteoblasts lay down new bone
- 8. Intramembranous (Periosteal) Bone Formation Mechanism by which a long bone grows in width Osteoblasts differentiate directly from preosteoblasts and lay down seams of osteoid Does NOT involve cartilage anlage Endochondral Bone Formation Mechanism by which a long bone grows in length Osteoblasts line a cartilage precursor The chondrocytes hypertrophy, degenerate and calcify (area of low oxygen tension) Vascular invasion of the cartilage occurs followed by ossification (increasing oxygen tension)
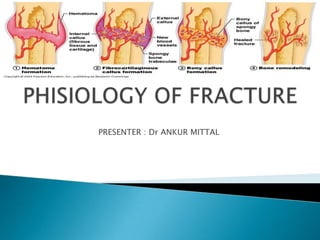
- 10. Hematoma Formation (1st) Last for less than 7 days Tissue disruption results in hematoma at the fracture site Local vessels thrombose causing bony necrosis at the edges of the fracture Increased capillary permeability results in a local inflammatory milieu Osteoinductive growth factors stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
- 11. Cellular Formation Phase(2nd) • 2-3 weeks • Acidic environment but turning neutral • Influx of endosteal cells from cambium layer produce a fibrous callus (environment has high oxygen tension) then cartilage (has a low oxygen tension environment)
- 12. Callus Formation Phase (3rd) 4-12 weeks Fibroblast deposit collagen in the granulation tissue Soft Callus is formed (Unorganized network of woven bone); Internal callus (grows quickly to create rigid immobilization) The hard callus lasts 3-4 months. Hard callus – a gradual connection of bone filament to the woven bone (Acts like a temporary splint) Bone is beginning to strengthen and immobilize If proper immobilization does not occur; cartilage will form instead of bone
- 13. Periosteal callus forms along the periphery of the fracture site Intramembranous ossification initiated by preosteoblasts Intramedullary callus forms in the center of the fracture site Endochondral ossification at the site of the fracture hematoma Chemical and mechanical factors stimulate callus formation and mineralization
- 14. Schematic drawing of the callus healing process. Early intramembranous bone formation (a), growing callus volume and diameter mainly by enchondral ossification (b), and bridging of the fragments (c).
- 15. A: Roentgenogram of a callus healing in a tibia with the osteotomy line still visible (6 weeks p.o.). B: Histological picture of a tibia osteotomy (fracture model) after bone bridging by external and intramedullary callus formation. A few areas of fibrocartilage remain at the level of the former fracture line (dark areas).
- 16. Callus is the first sign of union visible on x-ray after 3 weeks of #
- 17. Ossification Phase (4 th) •1- 4 Years •It will occur with adequate immobilization •Bone ends become crossed with a new Haversian system that will eventually lead to the laying down of primary bone Fracture is bridged and united
- 18. Remodeling Phase (5th) •Remodeling hard callus to compact bone or woven bone is gradually converted to lamellar bone. •May take a few years •Medullary cavity is reconstituted •Bone is restructured in response to stress and strain (Wolff’s Law)
- 20. Differences in healing between cortical and cancellous bone: Healing in cancellous bone occurs without the formation of significant external callus. After the inflammatory stage bone formation is dominated by intramembranous ossification This is due to tremendous angiogenic potential of trabecular bone as well as fixation used for metaphyseal fractures which is often more stable.
- 21. Prerequisites for Bone Healing •Adequate blood supply •Adequate mechanical stability Mechanisms for Bone Healing •Direct (primary) bone healing •Indirect (secondary) bone healing
- 22. DIRECT BONE HEALING Mechanism of bone healing seen when there is no motion at the fracture site (i.e. rigid internal fixation) Does not involve formation of fracture callus Osteoblasts originate from endothelial and perivascular cells A cutting cone is formed that crosses the fracture site Osteoblasts lay down lamellar bone behind the osteoclasts forming a secondary osteon Gradually the fracture is healed by the formation of numerous secondary osteons A slow process – months to years
- 23. Components of Direct Bone Healing Contact Healing Direct contact between the fracture ends allows healing to be with lamellar bone immediately Gap Healing Gaps less than 200-500 microns are primarily filled with woven bone that is subsequently remodeled into lamellar bone Larger gaps are healed by indirect bone healing (partially filled with fibrous tissue that undergoes secondary ossification)
- 24. INDIRECT BONE HEALING •Mechanism for healing in fractures that are not rigidly fixed. •Bridging periosteal (soft) callus and medullary (hard) callus re-establish structural continuity •Callus subsequently undergoes endochondral ossification •Process fairly rapid - weeks
- 25. Local Regulators of Bone Healing •Growth factors •Cytokines •Prostaglandins/Leukotrienes •Hormones •Growth factor antagonists
- 26. GROWTH FACTORS •Transforming growth factor[TGF] •Bone morphogenetic proteins[BMP] •Fibroblast growth factors[FGF] •Platelet-derived growth factors[PDGF] •Insulin-like growth factors[IGF]
- 27. TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTORS •Superfamily of growth factors (~34 members) •Act on serine/threonine kinase cell wall receptors •Promotes proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal precursors for osteoblasts, osteoclasts and chondrocytes •Stimulates both endochondral and intramembranous bone formation •Induces synthesis of cartilage-specific proteoglycans and type II collagen •Stimulates collagen synthesis by osteoblasts
- 28. BONE MORPHOGENETIC PROTIENS Osteoinductive proteins initially isolated from demineralized bone matrix Proven by bone formation in heterotopic muscle pouch Induce cell differentiation BMP-3 (osteogenin) is an extremely potent inducer of mesenchymal tissue differentiation into bone Promote endochondral ossification BMP-2 and BMP-7 induce endochondral bone formation in segmental defects Regulate extracellular matrix production BMP-1 is an enzyme that cleaves the carboxy termini of procollagens I, II and III
- 29. These are included in the TGF-β family Except BMP-1 BMP2-7,9 are osteoinductive BMP2,6, & 9 may be the most potent in osteoblastic differentiation Work through the intracellular Smad pathway Follow a dose/response ratio BMP ANTAGONISTS May have important role in bone formation Noggin Extra-cellular inhibitor Competes with BMP-2 for receptors
- 30. BMP FUTURE DIRECTIONS •BMP-2 •Increased fusion rate in spinal fusion •Must be applied locally because of rapid systemic clearance • •? Effectiveness in acute fractures •? Increased wound healing in open injuries •Protein therapy vs. gene therapy
- 31. FIBROBLAST GROWTH FACTORS •Both acidic (FGF-1) and basic (FGF-2) forms •Increase proliferation of chondrocytes and osteoblasts •Enhance callus formation •FGF-2 stimulates angiogenesis
- 32. PLATELET DERIVED GROWTH FACTORS •A dimer of the products of two genes, PDGF-A and PDGF-B •PDGF-BB and PDGF-AB are the predominant forms found in the circulation •Stimulates bone cell growth •PDGF-AB Increases type I collagen synthesis by increasing the number of osteoblasts •PDGF-BB stimulates bone resorption by increasing the number of osteoclasts
- 33. INSULIN LIKE GROWTH FACTORS Two types: IGF-I and IGF-II Synthesized by multiple tissues IGF-I production in the liver is stimulated by Growth Hormone Stimulates bone collagen and matrix synthesis Stimulates replication of osteoblasts Inhibits bone collagen degradation
- 34. CYTOKINES •Interleukin-1,-4,-6,-11, macrophage and granulocyte/macrophage (GM) colony-stimulating factors (CSFs) and Tumor Necrosis Factor Stimulate bone resorption •IL-1 is the most potent •IL-1 and IL-6 synthesis is decreased by estrogen May be mechanism for post-menopausal bone resorption Peak during 1st 24 hours then again during remodeling •Regulate endochondral bone formation
- 35. PROSTAGLANDINS/LEUKOTRIENS Effect on bone resorption is species dependent and their overall effects in humans unknown Prostaglandins of the E series •Stimulate osteoblastic bone formation •Inhibit activity of isolated osteoclasts Leukotrienes Stimulate osteoblastic bone formation Enhance the capacity of isolated osteoclasts to form resorption pits
- 36. HORMONES •Estrogen Stimulates fracture healing through receptor mediated mechanism Modulates release of a specific inhibitor of IL-1 •Thyroid hormones Thyroxine and triiodothyronine stimulate osteoclastic bone resorption •Glucocorticoids Inhibit calcium absorption from the gut causing increased PTH and therefore increased osteoclastic bone resorption
- 37. Parathyroid Hormone Intermittent exposure stimulates •Osteoblasts •Increased bone formation Growth Hormone •Mediated through IGF-1 (Somatomedin-C) •Increases callus formation and fracture strength •VASCULAR FACTORS Metalloproteinases Degrade cartilage and bones to allow invasion of vessels Angiogenic factors Vascular-endothelial growth factors Mediate neo-angiogenesis & endothelial-cell specific mitogens Angiopoietin (1&2) Regulate formation of larger vessels and branches
- 38. Bone Healing under Interfragmentary Movement Fracture healing under interfragmentary movement occurs by callus formation that mechanically unites the bony fragments. •The flexural and torsional rigidity of a fracture depends on the material properties and the second moment of inertia (rigidity = EI) of the callus. •Particularly the increase in callus diameter has a significant effect on the stabilization of the fracture. • Linear relation to the mechanical quality of the callus tissue (E), •The rigidity is proportional to the fourth power of the diameter (IBending = πd4/64, ITorsion = π d4/32)
- 39. The interfragmentary movement under external loading decreases with healing time in relation to the rigidity of the callus. Finally, the hard callus bridges the bony fragments and reduces the interfragmentary movement to such a low level that a healing of the fracture in the cortex can take place When this has happened, the callus tissue is no longer required and is resorbed by osteoclasts. Finally, after a remodeling process, the shape and strength of the normal bone are reconstituted
- 40. Healed osteotomy of a metatarsal with bony bridging of the cortical osteotomy gap and only small remaining callus volume.
- 41. Fracture Healing under Interfragmentary Compression •Implants and external loads Compression forces compression and close contact ( the external traction forces => the internal compression preload ) •compression preload +friction between the fragmentsrelative movement between the fragments is avoided. •Under this absolutely stable fixation, bone healing can occur by direct osteonal bridging of the fracture line with minimally or no callus formation . •In areas with direct contact, remodeling starts a few weeks after fracture fixation, which leads to bridging of the fragments by newly formed osteons .
- 42. Haversian osteons with osteoclasts in their cutter heads resorb bone, create a tunnel that crosses the fracture line, and fill the tunnel with new bone in a process of osteoblastic activity. In areas with a gap between the fragments, a filling of the gap by woven bone occurs as a first step before the Haversian osteons can cross the fracture area . In reality a mixture of contact and gap healing will occur.
- 43. Osteon with bone-resorbing osteoclasts (left) that drill a tunnel into the bone and osteoblasts that lay down new bone (osteoid) and fill the tunnel with a new bone layer (original magnification 100×) New Osteoclast Osteoblast bone
- 44. Contact healing with osteons crossing the fracture line (left). Healing of a fracture gap (right). Woven bone fills the gap before the osteons can bridge the fracture area.
- 45. An advantage of absolute stability is that the blood vessels may cross the fracture site more easily and lead to faster revascularization . In contrast to callus healing, there is no increased bone diameter under direct osteonal healing. This limits the load-bearing capacity of the healing bone, which consequently requires a longer period of protection by the implant.
- 46. Delayed Healing and Nonhealing under Unstable Fixation When the interfragmentary movement is too large, the bony bridging of the fragments is delayed or even prevented. Large interfragmentary movements cause large tissue strains and hydrostatic pressures in the fracture that prevent the vascularization of the fracture zone. Without this vascularization bone cells cannot survive, bone cannot be built, and only fibrocartilage can be formed . Because the resisting fibrocartilage layer in between the two bony fragments looks like the image of a joint, the nonunion is also called pseudarthrosis (false joint).
- 47. Variables that influence fracture healing: 1. Injury variables : • Open fractures • Severity of injury : The more impact the injury has made on bone and on the tissues surrounding it, the worse the healing will become. Slight injury will only likely cause mild contusions and will thus heal so easily. However, comminuted injuries which also damaged the surrounding tissues will not heal that quickly. • Intra articular fractures : Collagenasses can break the healing process of the bone as these fractures continue to be in contact with synovial fluid. The more that collegenasses partner with synovial fluid, the slower the healing process will even become.
- 48. • Segmental fractures • Soft tissues interposition • Damage to the blood supply : Regulate blood supply well for lack of it will drag down the healing process. This is one of the factors affecting bone healing especially in parts such a scaphoid bones, talus, and femoral head. 2. Patient variables • Diseases/Disorders : Diseases which are discovered to slow down the healing of fractures are diabetes, osteoporosis, and others which result to immunocompromised state. Abnormal healing is also caused by diseases such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and Marfan’s syndrome.
- 49. • Age : The younger the patients and the bones are, the faster the healing process works. Young patients have bones with the ability to recover from deformities soon enough and remodel them. However, the remodeling and recovering abilities of the bones decrease as they reach maturity. • Nutrition : For healing to occur, energy is necessary in the form of protein and carbohydrates. • Systemic hormones : These hormones that affect bone healing include the growth hormone, thyroid hormone, calcitonin, and corticosteroids. The last hormone mentioned can slow down the healing process. • Nicotine and other agents
- 50. 3. Tissue variables • Form of bone (cancellous or cortical) : Two types of bones – calcellous or spongy and cortical or compact bones – can be compared with the differences in the rate of their healing duration. The spongy bones have greater surface areas, more stable, and have better foods when put side by side with compact bones. • Bone necrosis • Bone disease : Any disease process that weakens the musculoskeletal tissue, like osteoporosis or osteomalacia, may impair union. • Infection : Infections cause necrosis and edema, take energy away from the healing process, and may increase the mobility of the fracture site.
- 51. 4. Treatement variables • Apposition of fracture fragments : Normal apposition of fracture fragments is needed for union to occur. Inadequate reduction, excessive traction, or interposition of soft tissue will prevent healing • Loading and micromotion Inter Fragmentary Movement- Axial Movement Small interfragmentary(IFM) movements stimulate callus formation Small fracture gaps Cyclic axial movement stimulated callus volume to be advantageous
- 52. Large fracture gaps Callus formation seems to be limited and bridging of the fracture gap is delayed Very stiff fixation of a fracture can suppress the callus formation and delay healing. In such cases, an externally applied interfragmentary movement can be used to stimulate callus healing. However, when the fracture fixation itself allows axial movements to a sufficient extent to stimulate callus formation, an additional external application of interfragmentary movements does not lead to further improvement of the healing process.
- 53. Shear Movement Shear movement delays the fracture healing ? Impede vascularization and promote fibrous tissue differentiation Oblique tibial fracture (shear movements : 4 mm) -- treated with functional bracing show rapid natural healing Shear movement to induce delayed unions and nonunions ? Control Shear movement Osteotomies of oblique or transverse type
