Mfrm
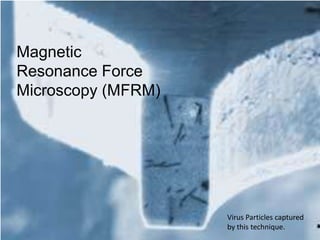
- 1. Magnetic Resonance Force Microscopy (MFRM) Virus Particles captured by this technique.
- 2. What is it? MRFM + = X 1,000,000
- 3. REALLY What is it? MRFM + = X 1,000,000
- 4. What is it? REALLY Borrows from MRI and Atomic Force Microscopy
- 5. What is it? REALLY MRI Magnetic Resonance Imaging Instead of ionizing radiation, it uses a magnetic field and powerful radiation
- 6. What is it? REALLY What MRFM Takes from MRI The magnetic Field
- 7. What is it? REALLY Atomic Force Microscopy A laser shines onto moving cantilever The laser is reflected onto a position-sensitive detector.
- 8. What is it? REALLY What MRFM Takes from AFM The laser The cantilever
- 9. History Began development in 1991 Dr. John A. Sidles “Measured minute magnetic fields to construct images of biological structures.”
- 10. How it Works
- 11. How it Works Specimen placed on cantilever Passed over Magnet Laser scans specimen on cantilever Image created by the vibrating of cantilever
- 12. It’s SCIENCE! F = m● B ∆
- 13. What can it Be Used for?
- 14. What can it Be Used for? Sub surface images Atomic level Resolution
- 15. Content Works Cited http://www.its.caltech.edu/~hammel/mrfmpch.html http://www.nytimes.com/2009/01/13/science/13mri.html http://micromachine.stanford.edu/smssl/projects/NovelMicrostructures/MRFMDetails.html http://www.worldscibooks.com/physics/6051.html http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=bodymr http://www.nanoscience.com/education/AFM.html
- 16. Photo Works Cited http://www.sutterbuttesimaging.com/images/mri_scannerlg.jpg http://www.photoshopcstutorial.com/tutorials/magnify/images/magnifyingglass.gif]br />http://physics.illinois.edu/people/budakian/MRFM_hi-res.jpg http://www-tc.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/sciencenow/3214/images/01-coll-dna-knoll-l.jpg http://www.mun.ca/biochem/courses/3107/images/50Sribosome3.jpg http://www.interweb.in/attachments/pc-wallpapers/16375d1223299224-abstract-wallpapers-images-photos-picture-gallery-blue-abstract-vista-wallpaper.jpg
Notas do Editor
- Introduction Name: Samuel Karas Topic: Magnetic Resonance Force Microscopy (MFRM)Image take with MRFM
- What is it in a nutshell?MRI + Magnification times one million = MFRM
- This is a very barebones explanationSo what really is it?
- It is actual a combination of two modern technologiesThe MRIAnd Atomic Force MicroscopyTo better understand MRFM, we must first look at these two technologies
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)Non-invasive imaging systemUnlike X-ray it utilizes a magnetic field to produce the picturesIt tracks the oscillations of the protons in order to create a picture.
- Atomic Force MicroscopyThe laser shines on the object that the image is being created of.The light reflects off the object and cantilever to a position detector.This is what creates the image
- The concept was created by Dr. John A. Sidles in 1991.He wanted a machine to create images of tiny particlesQuote
- How it worksEach of these parts plays a integral part in the machine.I’ll go into more detail in a second.
- The specimen is placed on the cantilever, because of the way this machine works, it does not need to be crystallized in any way.This magnet is used as a constant.The vibrations are picked up by the laser which is what creates the image.This final magnet spins which which causes the vibration of the cantilever
- The equationF= Forcem = spin magnetization – The coiled magnetB= permanent magnet – The spinning magnet
- It can view the structure of dnaIt can view proteins previously unable to be viewedIt can also view biological items that for some reason cannot be crystalized
- It has the ability to view subsurface images, unlike a Scanning Electron Microscope.It also has the ability view things at the atomic level.THE END!!