Architecture3
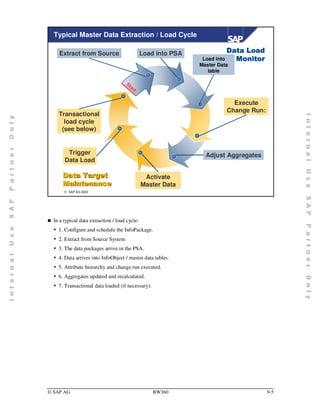
- 1. Typical Master Data Extraction / Load Cycle Extract from Source Load into PSA 'DWD /RDG Load into 0RQLWRU Master Data table St ar t Execute Change Run: Transactional load cycle (see below) Trigger Adjust Aggregates Data Load 'DWD 7DUJHW Activate 0DLQWHQDQFH Master Data ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ In a typical data extraction / load cycle: y 1. Configure and schedule the InfoPackage. y 2. Extract from Source System y 3. The data packages arrive in the PSA. y 4. Data arrives into InfoObject / master data tables. y 5. Attribute hierarchy and change run executed. y 6. Aggregates updated and recalculated. y 7. Transactional data loaded (if necessary). © SAP AG BW360 9-5
- 2. Typical Transaction Data Extraction / Load Cycle Load into PSA Load into ODS 'DWD /RDG Activate 0RQLWRU Data in ODS St ar t Drop Indices Roll up Aggregates Build DB Load into InfoCube Statistics 'DWD 7DUJHW 0DLQWHQDQFH Build Indices ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ In a typical data extraction / load cycle: y 1. Configure and schedule the InfoPackage. y 2. Extract the data from the source system. y 3. The data packages arrive in the PSA. y 4. Load the data into the ODS, where it is possible to verify the data. y 5. Load the InfoCube. y 6. Create Indexes y 7. Refresh DB Statistics y 8. Roll up © SAP AG BW360 9-6
- 3. Event Scheduling Pull Principle BW Source system Step 2 STAGING ENGINE InfoPackage EXTRACTOR Step 1 Push Principle BW Source system STAGING ENGINE Step 4 InfoPackage EXTRACTOR Step 2 Step 3 RSSM_EVENT_RAISE Z_BW_EVENT_RAISE Step 1 ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Two options for triggering the extraction are available: y SAP BW triggers the extraction directly by a defined InfoPackage (standard) y OLTP triggers SAP BW to start the extraction „ For more details, see SAP Note 135637. „ The push principle shows a workaround to start an extractor from the source system. © SAP AG BW360 9-7
- 4. Extraction and Dataload Loading Process Parallelization Technical Details Further Recommendations Performance Analysis / Monitoring ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-8
- 5. Dataflow Overview ODS Object Update Rules InfoSource InfoSource Communication Structure Communication Structure Communication Structure Communication Structure Transfer Rules Transfer Rules Transfer Rules Transfer Rules DataSource (Replicate) Transfer Structure Transfer Structure Transfer Structure Transfer Structure Transfer Structure Transfer Structure Transfer Structure Transfer Structure DataSource Extract Structure Extract Structure Extract Structure Extract Structure Source System 1 Source System 2 ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ All systems that provide BW with data are described as source systems. These can be: y SAP R/3, other SAP BW systems y Flat files, where metadata is maintained manually, and transferred into SAP BW through a file interface y External systems, where data and metadata is transferred using staging BAPIs. y Data Stage, XML, DB Connect „ Staging Master Data y Flexible Staging: using communication structure and update rules y Direct Staging: using communication structure without update rules „ The fields in the extract structure that have been assigned are made available in a template DataSource in SAP BW by a DataSource replication. „ The transfer structure is generated from the selected InfoObjects in the template „ In SAP BW, an InfoSource: y Describes the quantity of all the data available for a business transaction or a type of business transaction (for example, cost center accounting) y Is a quantity of information that logically belongs together, summarized into a single unit y Contains either transaction data or master data (attributes, texts, and hierarchies) y Is a set of InfoObjects stored in a structure called a communication structure © SAP AG BW360 9-9
- 6. Extractor Types Extractor Types Extractor Application Specific Application Application Independent BW Content Customer-Defined Customer- Generic Extractors Extractors Extractors Extractors FI LIS DB View PP SAP Query CO FI-SL HR Transparent SD CO-PA Table Database Database Database Table(s) Table(s) Table(s) ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Extractors belong to the data retrieval mechanisms in the SAP source system. An extractor can fill the extract structure of a DataSource with the data from the SAP source system datasets. „ There are application-specific extractors, each of which are hard-coded for the DataSource that was delivered with BW Business Content, and which fill the extract structure of the DataSource. BW- specific source system functions, extractors and DataSources are delivered by plug-ins. „ You can run Custom Extractors in R/3 application areas like: LIS, CO-PA, FI-SL, and HR. „ Independent of a particular application, you can generically extract master data or transaction data from any transparent table, database views or functional areas of the SAP query. For this, you can generate user-specific DataSources. In this case, we speak of generic DataSources. © SAP AG BW360 9-10
- 7. Dataflow in Source System Transfer Structure Extraction Structure Transparent Table, View, Function Module, ABAP Query Extractor Transparent Table Transparent Table ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ A DataSource is an object that, at the request of SAP BW, makes data available in a predetermined structure. The properties of a DataSource that are relevant to BW are copied into the BW system when you replicate DataSources. „ DataSources are used for extracting data from a source system and for transferring data into SAP BW. DataSources make the source system data available on request to SAP BW in the form of the extract structure. Data is passed through a transfer structure into SAP BW. „ The fields in the extract structure that have been assigned are made available in a template DataSource in SAP BW by replication of DataSources. „ The transfer structure is generated from the selected InfoObjects in the template DataSource in the SAP R/3 System for online transaction processing (OLTP). „ ROOSOURCE: Table of source system. Information about Datasources „ ROOSGEN: Table of source system. Information about name of the Transfer Structure © SAP AG BW360 9-11
- 8. Loading Process Transfer Structure PSA No PSA ALE Inbox Outbox (connection log) tRFC tRFC (connection log) Data packets Data IDOC Info IDOC Info Idoc SAP BW Source System Transfer Structure ALE Non-SAP Inbox Systems SAPI via third party Outbox tools Extract Structure Extractor ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ The user sets the transfer method (PSA or IDoc) and maintains the transfer rules. During the generation of the InfoSource, the method is transferred to the SAP source system (Repository). The data load process is released by a request IDoc to the source system. „ Info IDocs are used with both transfer methods. However, they are always transferred through ALE. Over the Info Idocs, the BW system generates the traffic light settings for monitoring the load processes. „ A data IDoc consists of a control record, a data record, and a status record. The control record contains administrative information about the recipient, the sender, the client, etc. The status record describes the status of the IDocs, such as processed. „ The stored data in the ALE input and output must be emptied or reorganized manually. „ In the tRFCs, the number of fields is limited to 255. For tRFCs, the data record length is limited to 1962 bytes. For IDocs, the limit is 1000 bytes. „ Non-SAP systems are not coupled directly to the appropriate transfer method. The data format is adapted to the internal BW format (such as removing separators in the flatfile, or capitalization). Non-SAP systems may be flat files or direct systems (coupled through BAPIs). © SAP AG BW360 9-12
- 9. Transfer Rules :ith the help of the transfer rules, you can determine how the fields for the transfer structure are assigned to the InfoObjects of the communication structure. ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ You can begin to perform maintenance of the transfer structure and transfer rules using the InfoSource tree of the Administrator Workbench. The context menu of the source system for an InfoSource provides you with the maintenance marker using the function Maintain Transfer Rules. „ The transfer structure provides BW with all the source system information available for a business process. „ An InfoSource in BW requires at least one DataSource for data extraction. DataSource data that logically belongs together is staged in an extract structure in an SAP source system. „ In transfer structure maintenance, you determine which extract structure fields are transferred to BW. When you activate the transfer rules in BW, an identical transfer structure for BW is created in the source system from the extractor structure. „ This data is transferred 1:1 from the transfer structure of the source system into the BW transfer structure, and is then transferred into the BW communication structure using the transfer rules. „ A transfer structure always refers to a DataSource from a source system and an InfoSource in BW. © SAP AG BW360 9-13
- 10. Update Rules Update rules Edit Goto Extras Environment System Help Update Rules change: Rules Version comparison Business Content Administrator Workbench InfoCube CSS_FLOW Time flow Used packet InfoSource CSS_TRANC Transact. Data (Customer messages) by packet not Version Active Saved per single insert Object status Active,executable Last changed by POLENZ 24.05.2000 14:49:56 Person responsable WALTHER Startroutine Update rules Status Key figures Source Aktiv Customers Number ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ You begin to perform maintenance of the update rules using the InfoProviders tree of the Administrator Workbench. The context menu of the data target belonging to an InfoCube or ODS provides you with the maintenance marker using the function Maintain Update Rules. „ The start routine operates on data packet level. Use the start routine to prevent expensive processing for each record. y Control the size of internal tables carefully within the Start routine. Otherwise, you may see growing ABAP objects during the load that increase the runtime of the update rules. y Avoid redundant database accesses at the packet level. Try to buffer the information. © SAP AG BW360 9-14
- 11. Transfer / Update Rules 6tart routines can be used to work on an entire data package $fter the start routine in the transfer rules, the package is processed record by record $fter the start routine in the update rules, the package is processed record by record for each keyfigure ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-15
- 12. Updating InfoCubes )or each new characteristic value, a SID will be created )or each characteristic value, a DIM ID for new SID combinations will be created if necessary 7hen insert into the fact table SID ,QIRXEH Tables Tables FACT Table Dimension Tables ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Read the SID Tables for each characteristic value. If no SID is available, create a record in the SID table. „ Read the Dimension tables, if no dimension table entry is available for the SIDs retrieved in step 1, create a record in the dimension table. „ Insert the package into the fact table after completing 1 and 2 for the entire package. © SAP AG BW360 9-16
- 13. Activation of Masterdata Data load via Infopackage = updates just in master data tables New master data not Attributes Hierarchies available for (modified version) (modified version) reporting !! Activation = update/recalculation in aggregates, update version from M to A in master data tables Attributes Hierarchies New master (active version) (active version) data available for reporting !! Updated attribute Hardware not visible for reporting ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ After updating master data (step 1) you have to activate this data (step 2), in order to make it available for reporting. „ After update, the version of the values is set to M(=modified). Modified data is not visible for reporting. „ Difference between attributes and hierarchies: y After update of attributes the affected infoobjects are automatically proposed in RSATTR Æ infoobject list for changerun. y After update of hierarchies the affected hierarchies are NOT automatically proposed in RSATTR Æ hierarchy list for changerun. (note 196812: activation of hierarchies) © SAP AG BW360 9-17
- 14. Activation of Attributes Method 1: Manual activation Method 2: Automatic activation (only possible if no by changerun possible aggregates are existing, otherwise: method 2) Modified attributes in master data tables Info objects are automatically Activation of proposed by modified attributes the system Active data in Active data in master data master data tables and tables and aggregates aggregates ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ After update of attributes or navigational attributes, you have to manage the activation of this modified data „ 2 methods: y Method 1: manual activation (RSA1 Æ Modeling Æ Infoobject Æ context: activate masterdata (only if no aggregates are existing) y Method 2: infoobjects with updated attributes are automatically detected by Changerun Monitor (RSATTR) and proposed for activation © SAP AG BW360 9-18
- 15. Activation of Hierarchies Modified hierarchy data 67(3 Method 1: Manual Method 2: Method 3: Report activation InfoPackage RRHI_HIERARCHY_ACTIVATE 67(3 „ No aggregates existing: Data is active after performing one of these three methods „ Aggregates existing: The hierarchies are just noted for activation. Activation and update in aggregates have to be done by Changerun. Note: Hierarchies are not automatically suggested for changerun. You must note the hierarchy by one of the three methods mentioned above for activation! ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ STEP 1: direct activation (only if no aggregates existing) or note for changerun (if aggregates are existing) with 3 methods possible: y Method 1: manual activation via context menu for hierarchy (rsa1 Æ Modeling Æ Infoobject Æ choose hierarchy: context: Activate) y Method 2: apply flag in infopackage for hierarchy load: flag for activation or activate y Meaning: if aggregates are existing just note for changerun (= flag for activation), if no aggregates are existing do a direct activation. y Method 3: execute report ‘RRHI_HIERARCHY_ACTIVATE’ - Meaning: if aggregates are existing just note for changerun; if no aggregates are existing, direct activation possible (= activate) - ‘delete affected aggregates’ means aggregates deactivated and hierarchy is activated afterwards. No recalculation of aggregate is done. © SAP AG BW360 9-19
- 16. Extraction and Dataload Loading Process Parallelization Technical Details Further Recommendations Performance Analysis / Monitoring ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-20
- 17. Analysis / Monitoring Tools – Overview $pplication Monitors (BW) „ BW Monitor (transaction RSMO) „ BW Statistics / ST03 / RSDDSTATWHM %asis Perspective (BW and source system) „ Database trace (ST05) „ ABAP trace (SE30) „ System trace (ST01) ... 6ource system „ Extractor checker (RSA3) ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-21
- 18. RSMO Monitor for Extraction and Data Load Use the Goto menu Monitor – Administrator Workbench or the Monitor icon Monitor: Selection Data Request Choose appropriate selection criteria to view extraction / load status of InfoPackages ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Features of the monitor in SAP BW: y Selection screen has user-dependent selection variants y The Monitor Assistant can run in the background. Using the IMG, data requests for analysis can now be scheduled to run in the background. - If the wizard is scheduled to start periodically, all requests that have not yet been assessed are analyzed regularly. - E-mail can be sent automatically to appropriate persons © SAP AG BW360 9-22
- 19. Features of the Detail Monitor Info IDoc 2: Application document posted When a step is highlighted, its status information is shown below Date Time ... BW Ido... B... T...OLTP I... ... 05/09/2000 11:22:43 1 75973 53 54228 03 ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Date and time stamps are available for each phase of the extraction/load request. „ Idoc numbers for the SAP BW system and the OLTP system are provided. „ These status numbers specify the type of information delivered from the Service API source system. 1: Info Idoc Status 2: Number of IDoc BW/OLTP 3: Status of Idoc 4: connect to the source system „ A two-digit status is assigned to an IDoc to allow the processing to be monitored. Both the SAP application and the the external system (during status confirmation ) must maintain the field with the correct value. „ For more information about these values, select Environment Æ ALE management Æ In the Data Warehouse/In the Source System in the transaktion RSMO or use transaction WE05. Use transaction BD87 for IDoc monitoring. „ The statuses for outbound IDocs are between '01' and '49', while the statuses for inbound IDocs begin with '50'. © SAP AG BW360 9-23
- 20. Options in RSMO 2SWLRQV IRU PDVWHU GDWD „ Lock on Master Data Table (must be deleted if upload fails) „ Transaction RS12 / SM12 2SWLRQV IRU WUDQVDFWLRQDO GDWD „ Request will be reversed in data target „ Data must be in PSA „ System will add a new request with reversed sign, data will not be deleted ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ When using InfoPackages in the Monitor, there is complete proof of the origin and consistency of the data of an InfoCube on all processing levels. „ The Monitor consists of 3 interfaces: y Request overview y Detail screen y Selection screen „ The overview of the data requests that are to be analyzed in the Monitor is displayed by default in a tree. Under New Selections, you can set which type of request overview you want displayed in the future when you go to the Monitor. „ In the selection screen of the Monitor, you use the relevant radio button to determine how you want the request overview displayed.You can also use the various selection options to determine the data requests that you want to check. „ To get to the selection screen, choose Monitor → New Selections. After you have made your selections, choose Execute to go back to the Monitor Request Overview. © SAP AG BW360 9-24
- 21. Traces in RSMO „ Simulation can be used for debugging of transfer / update rules „ Experience needed to find the right ABAP Coding in debug mode ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Sometimes it is hard to find the transfer / update rule in the debugger. In these cases it might be better to introduce an endless loop in the transfer / update rule. As soon as the process run inside this loop go to SM50 Æ Program/Mode Æ Program Æ Debugging and debug this workprocess. „ Advantage: Easy to find the correct program part. „ Disadvantage: Only complete data package can be debugged; need to know where to introduce the endless loop. © SAP AG BW360 9-25
- 22. Request Level: Schedule / Extract / Transfer TRFC Loading Process Service API Extractor Scheduler ALE ALE Data Targets ALE ALE Upload Monitor – RSMO Update Transfer PSA Rules Rules Business Source Information System Warehouse ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Monitoring information for Scheduling, Extraction, and Transfer of the data can be seen in the first three sections of the Details tab in the BW Monitor. This information refers to the entire loading process (request). „ Problems with extraction need to analyzed directly in the source system with trace tools / extractor checker (RSA3). „ Data transfer time is the time needed to send the data packages from the source system to the target system. © SAP AG BW360 9-26
- 23. Package Level: PSA / Rules / Update TRFC Loading Process Service API Extractor Scheduler ALE ALE Data Targets ALE ALE Upload Monitor – RSMO Update Transfer PSA Rules Rules Business Source Information System Warehouse ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ When you have maintained the transfer structure and the communication structure, you can use the transfer rules to determine how the transfer structure fields are to be assigned to the communication structure InfoObjects. You can arrange for a 1:1 assignment. You can also fill InfoObjects using routines or constants. „ The time spent in the transfer rules is displayed in the upload monitor: choose Processing → DataPacket → Transfer Rules. „ The update rules specify how the data (key figures, time characteristics, characteristics) are updated in the data targets from the communication structure of an InfoSource. You are therefore connecting an InfoSource with an InfoCube/ODS object. „ A data target can be supplied with data from several InfoSources. A record of update rules must be maintained for each of these InfoSources, describing how the data is written from the communication structure belonging to the InfoSource into the data target. „ The InfoObjects of the communication structure belonging to the InfoSource are described in the update as source InfoObjects (meaning source key figure or source characteristic). „ There is an update rule for each key figure of the InfoSource. This is put together from the rule for the key figure itself and the current rules for characteristics, time characteristics, and units assigned to it. „ The time spent in the transfer rules is displayed in the upload monitor: choose Processing → DataPacket → Update Rules. © SAP AG BW360 9-27
- 24. ODS Activation TRFC Loading Process Service API Extractor Scheduler ALE ALE Data Targets ALE ALE Upload Monitor – RSMO Update Transfer PSA Rules Rules Business Source Information System Warehouse Activation from M into A Version Update of InfoCube ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ An ODS object serves as a storage location for consolidated and cleansed transaction data on a document (atomic) level. Unlike multi-dimensional data storage using InfoCubes, the data in ODS objects is stored in transparent, flat database tables. „ Every ODS object is represented on the database by three transparent tables: y Active data: table containing the active data (A table). y Activation Queue: table containing new data or data that has been modified since the last activation. y Change log: for delta updates from the ODS object into other ODS objects or InfoCubes. „ When you update ODS object data, the records are stored initially in the table with the new data. For data that is loaded into BW more frequently than once a day, for example, it is possible to update several requests, one after the other. „ The data from one or more requests is transferred in a single activation step out of the table containing the new data and into the table containing the active data. The new data is deleted from the corresponding table. The table with the active data is, therefore, the main table for ODS objects. It contains the data for reporting. When you activate the data, the changes are sent to the change log so that the data in the related ODS objects or InfoCubes is updated accordingly. „ To transfer the data from the M table to the A table, choose Processing → ODS Activation. © SAP AG BW360 9-28
- 25. Extraction and Dataload Loading Process Parallelization Technical Details Further Recommendations Performance Analyis / Monitoring ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-29
- 26. Source Systems SAP-BW Restricted amount of main memory Data- package 1 Data- package 2 Data- package 3 SAP System Non-SAP System Huge tables for extraction Restricted amount of main memory ¤ SAP AG 2003 Extraction from SAP system: „ Typical situation: y Huge extraction (millions of records) „ Problem: y It makes no sense to transfer all data in one step, because of restricted network capacity and restricted main memory on source and target system y Parallelism for processing in BW is welcomed. „ Solution: Splitting data up in several (small) packages, that can be held in main memory while processing in BW Æ less memory consumption and parallelism in processing possible. „ Maintain predefined table ROIDOCPRMS for restricting package size (see next slide) Extraction from non- SAP systems: „ Care for optimal network connection to source system. „ Follow recommendations for the source system or for the ETL Tool. © SAP AG BW360 9-30
- 27. Parallelization Options 5equests in parallel „ Split up large request with selection criteria „ Split up large file into smaller ones and load in parallel „ Run loads from different DataSources / Source Systems in parallel 3arallelization within Request „ Packaging (size and degree of parallelism customizing) „ Parallelization options in InfoPackage „ Several data targets in one load ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-31
- 28. Settings on the Source System VHWWLQJV 0HPRU VHWWLQJV „ BW extractors need a lot of extended memory (depending very strong to the data package size) „ Large memory consumption for extraction processes in parallel (= parallel scheduled InfoPackages) 38 „ Extraction runs with background processes. Extractors running in parallel are able to slowdown the source system. Extract data in times when there is just less load on the system ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Avoid extractions from OLTP during dialog time. At least don‘t extract in dialog time with InfoPackages in parallel. „ Try to extract during ‘off times‘ of the the source system „ Typical memory consumption for CO extractors: 200 – 400 MB, thus total available memory should be about 2 GB (memory for SAP system, user, extraction, ...) © SAP AG BW360 9-32
- 29. Extraction from SAP Source System (1) )or dataload from SAP R/3 you have to maintain these parameters directly in the SAP R/3 (not in BW!) )or datamart (e.g. export datasource scenarios) you have to maintain these parameters in BW (that one, which is used for extraction) Maintain Control Parameters for Data Transfer 7A: sbiw Æ general settings Æ maintain control parameters for data transfer *oals: „ Reduce consumption of memory ressources „ Allocate data processing to different work processes in BW Src.system Max. (kB) Max. lines Frequency Max. proc. Target system for batch job WMS ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Most important parameter: y Max. (kB) (= maximal package size in kB): When you transfer data into BW, the individual data records are sent in packets of limited size. You can use these parameters to control data packets. If no entry was maintained, then the data is transferred with a default setting of 10,000 kBytes per data packet. The memory requirement not only depends on the settings of the data packet, but also on the size of the transfer structure and the memory requirement of the relevant extractor. y Max. lines (= maximum package size in number of records) With large data packages, the memory consumption strongly depends to the number of records which are transfered by one package. Default value for max lines is 100,000 per data package. Maximum memory consumption per data package is around 2*Max. lines*1000 Byte. y Frequency: Frequency of Info IDocs. Default: 1. Recommended: 5 - 10 y Max proc. (= maximum number of dialog workprocesses which were allocated for this dataload for processing extracted data in BW) An entry in this field is only relevant from release 3.1I onwards. Enter a number larger than 0. The maximum number of parallel processes is set by default at 2. The ideal parameter selection depends on the configuration of the application server, which you use for transferring data. „ Goals: y Reduce consumption of memory ressources (especially extended memory). y Allocate data processing to different work processes in BW. © SAP AG BW360 9-33
- 30. Extraction from SAP Source System – Recommended Values (2) $ction: SBIW Æ General settings Æ Maintain control parameter for data transfer 5ecommended values: max size: 20,000 – 50,000 (kbyte) max lines: 50,000 – 100,000 (Data lines) frequency: 10 max proc.: 2–5 0aintain control parameter for data transfer also on the BW System, because export datasources and datamart scenarios (MYSELF source system) are using these settings as well. ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-34
- 31. Override Standard Setting in InfoPackage DataS. Default Data Transfer Shift+F8 Default Settings in Source System Maximum size of a data package in kByte 30.000 Maximum number of dialog processing for sending data 3 Number of data packets per Info-IDoc 10 ou can reduce individually in the InfoPackage frequency and max. size for the extraction process ,t is not possible to override max. lines (except for flat file uploads) ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-35
- 32. Data Load with Flat Files (RSCUSTV6) BW: Threshold Value for Data Load FrequencyStatus-IDOC 10 Packet size 30.000 Partition size 1.000.000 Business Information Warehouse Links to Other ... Maintain Control Parameters for the data transfer )requency Status-IDOC and packet size refer to dataload from flat files 3artition size refers to partitioning of PSA tables ¤ SAP AG 2003 FrequencyStatus-IDOC: „ With the specified frequency, you detemine after how many data packages an Info IDoc is sent, or how many data packages are described by an Info IDoc. „ Recommended value: 10 Packet size: „ The number of data records that are delivered with every upload from a flat file within a datapackage. There is a default value of 1000. If you want to upload a large quantity of transaction data, change the 'number of data records per packet' from the default value of 1000 to between 10000 (Informix) and 50000 (Oracle, MS SQL Server). „ For data transfer from flat file into BW, the individual data records are sent in packages. With these parameters you restrict the size of such a data package. „ The memory requirement depends not only on the setting for data packet size, but also on the width of the transfer structure, and the memory requirement of the relevant extractor. Partition size: „ PSA tables are partitioned at the DB-level. You can determine the max. number of records per DB- partition of a PSA table. By default, this value is set to 1,000,000 records. © SAP AG BW360 9-36
- 33. Processing Options in the InfoPackage ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ This is an overview of all processing options you can choose in the InfoPackage (with transfer method PSA). © SAP AG BW360 9-37
- 34. PSA and then into Data Targets $s many (dialog) processes into PSA as configured in the SAP source system $s many (dialog) processes into the Data Targets as configured in the source system 3SA and Data Targets are processed sequentially for each package ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ PSA and then into Data Targets (Package by Package): y Select this field if you first want to update the data in the PSA and then in the InfoCubes or in the master data table of the InfoObject. y If the update in the InfoCubes or in the master data table of an InfoObject fails, then the data is in the PSA. You can update the data from there again. Different packages are loaded in parallel. y Upload from flat file will be done in one batch process, the statement on the slide is only valid for SAP source systems. © SAP AG BW360 9-38
- 35. PSA and Data Targets in Parallel 0ore (dialog) work processes can be used than configured in the source system $s many processes into PSA as configured in the source system )or each package the data is written to the PSA and in another parallel work process into the Data Targets ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ PSA and Data Targets in Parallel: y Select this field if you want to update the data in the PSA and in the InfoCubes or master data table of an InfoObject in parallel. y When updating in parallel, as soon as sufficient dialog processes are free, an additional process for updating is opened. y The maximum number of processes customized in the source system is only valid for updating the PSA. y Since writing into data targets is usually slower than writing into the PSA, there are more processes updating the data targets (older packages still running) than writing into the PSA. That’s why there is no fixed limit of number of processes used for the load. y If the update in the InfoCubes or master data table of an InfoObject fails, you can update the data from the PSA once again. © SAP AG BW360 9-39
- 36. Only PSA $s many (dialog) processes into PSA as configured in the source system 'ata will not be transferred into the data targets ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Only PSA: y Select this field if you want to update the data only into the PSA. You can start the update manually in the PSA tree as soon as the data request is technically okay. You know this by the green overall status of the data request in the monitor. The update of the data targets will happen in one background process. © SAP AG BW360 9-40
- 37. Only PSA – Update Subsequently in Data Targets $s many (dialog) processes into PSA as configured in the source system 2ne (background) process from PSA into data target ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Only PSA with indicator Update Subsequently in Data Targets y If you set this indicator, the data will be updated in the data targets, after being completely successfully loaded in the PSA. © SAP AG BW360 9-41
- 38. Data Targets only $s many (dialog) processes into data target as configured in the source system 'ata will not be available in PSA ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Data Targets Only: y Select this field if you do not want to update the data in the PSA, but automatically into the InfoCubes or into the master data table of an InfoObject. Packages are loaded in parallel. y If the update fails, depending on the error, the data can be sent to BW again by the TRFC overview in the source system. It is possible, however, that they must also be requested again. This method has its advantages for performance, but there is the danger that data may be lost. © SAP AG BW360 9-42
- 39. Extraction and Dataload Loading Process Parallelization Technical Details Further Recommendations Performance Analyis / Monitoring ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-43
- 40. Transfer Method Recommended 7UDQVIHU PHWKRG 36$ LV UHFRPPHQGHG IRU SHUIRUPDQFH UHDVRQV ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ For hierachy uploads, IDOC sometimes has to be used (depending on the DataSource), for all other data loads the method PSA is recommended. © SAP AG BW360 9-44
- 41. Recommendations for Self-Coded Rules 5educe database accesses „ Avoid single database access in loops „ Use internal ABAP tables to buffer data when possible 5educe ABAP processing time „ Control the size of the internal tables carefully (don't forget to refresh when neccessary) „ Access internal ABAP tables using hash keys or via index 5euse existing function modules „ If you reuse existing function modules or copy parts of them, ensure that the data buffering used works properly again in your ABAP code 8se start routines whenever possible 7ransfer rules vs. Update rules „ Transformations in the transfer rules are cheaper because transfer rules are not processed for each key figure but update rules are ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-45
- 42. Using InfoCube Data Load Performance Tools Administrator Workbench → Modeling → InfoCube Manage → Tab Performance Create Index button: set automatic index drop / rebuild Statistics Structure button: set automatic DB statistics run after a data load ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ BW provides this tool to assist users in checking, deleting, and recreating the indexes on InfoCube fact tables and aggregate fact tables. It also enables users to check whether statistics are available on InfoCube fact tables and aggregate fact tables. These statistics can be calculated from this screen. „ If a large volume data load is expected, load performance can be improved by dropping the fact table’s secondary indexes and recreating them after the load. y Performing insert operations into secondary indexes can cause a performance loss. y Dropping/recreating indexes before/after a data load avoids index degeneration. „ If a large volume data load is expected, database optimizer statistics can be recalculated automatically following the data load. y When data is added to a fact table, query performance and data load performance can be improved by maintaining database statistics for the InfoCube fact table. y The percentage box determines whether statistical sampling techniques can be used to estimate the properties of a table. A 10% sample is usually sufficient for obtaining effective statistics. „ The lower part of the screen on statistics does not appear for all database platforms. y Example: it does not appear on the Microsoft SQL Server platform, because SQL Server generates database statistics automatically. „ Those setting are only used if the load is not executed within a process chain! © SAP AG BW360 9-46
- 43. Automating Index and DB Statistics Operations Index creation for InfoCube RONSCUBE Delete InfoCube indices before each data load and then recreate Also delete and then recreate indices with each delta upload Start in the background Selection SubseqProcessing Job Name BI_INDX Statistics creation for InfoCube OFIAR_CO2 Recalculate DB statistics after each data load Start Also recalculate statistics after delta upload Start in the background Selection SubseqProcessing Job Name BI_INDX Start ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ The graphic shows the options available for dropping and recreating indexes for the fact table, and the options for recalculating the database statistics. These settings are optimal for most systems. „ Those setting are only used if the load is not executed within a process chain! © SAP AG BW360 9-47
- 44. Loading Tips /oading Data „ For performance reasons, always upload master data first „ Uploading master data in the sequence attributes, texts, and then hierarchies gives best performance ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ We recommend that you load the master data for the characteristics before the transaction data. „ If you load data using automatic SID creation, this causes a large overhead. © SAP AG BW360 9-48
- 45. Extractor Checker ([WUDFWRU FKHFNHU (delivered with S-API) Activation Package of debug ,Q %: mode size „ Check and debug possible archive file Settings Execution Mode Request number TEST „ check and debug Data Records / Calls 100 Debug Mode DataSources (also Display Extr. Calls 10 Auth. Trace Update mode F Export DataSources) Target sys ,Q 5 50 „ Check and debug DataSources (also Export DataSources ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Some extractors and customer exits return different data, depending on which package size is requested. „ For realistic testing, set the number of data records in RSA3 to a realistic value (derived from table ROIDOCPRMS). Some extractors and customer exits return different data, depending on which package size is requested. „ The extractor checker must never be called in the delta mode. There is no permission to do this, because otherwise it would be possible to get delta information, which afterwards is no longer available for the real extraction process. „ Using extractor checker in DEBUG MODE means: extraction stops immediately in DEBUG Mode because of a predefined break-point. Then you are able to debug the extractor report step by step. „ Using extractor checker in AUTH. TRACE Mode means: after execution of extractor checker you get a new ‘Display Trace‘ at the bottom of your screen. You can analyze failed authorization checks with this trace information. © SAP AG BW360 9-49
- 46. Buffer Number Range Objects (1) ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ To identify other potential DIMID’s for number range buffering, enter bid* and drop down will provide a list of DIMID’s. Now search for the technical name of your dimension. For master data the prefix is BIM* for the number range object. „ Instead of having to retrieve a number from the number range table on the database for each row to be inserted, you can set for example, 500 numbers into memory for each dimension table. „ It is ONLY the number themselves that are held in memory. „ During the insert of a new record, it will retrieve the next number in the sequence from memory. This is much faster. „ However, if the database should go down the buffered number range is also gone. „ If the database goes down there may be missing sequence numbers when the database is brought back up and the process is resumed. © SAP AG BW360 9-50
- 47. Buffer Number Range Objects (2) hange the Buffering of the Number Range Objects Number range object Edit Display text specs Maintain text Delete group ref. No. Range Object: Change documents Numbe Set-up buffering No buffering Cancel Main memory Object BIM0001196 No. range object has no Local file Short text SIFs char. OASSET Long text SIFs char. OASSET Interval characteristics Subobj. data element To-year flag No.len domain NUMC10 No interval rolling Customizing specifications No.r.transation Warning % Buffering in local file No. of numbers in buffer ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Use transaction SNRO (maintenance of number range objects) in order to buffer the number range for a particular object. „ After executing the transaction, enter the name of the number range object and then press the change button. EDIT Æ SET-UP BUFFERING Æ MAIN MEMORY „ Now you can enter the number to be buffered. Normally a value between 50 and 500 is appropriate. © SAP AG BW360 9-51
- 48. Load Balancing (1) /RJRQ JURXSV 60/*
- 49. „ For distribution of users (un)equally on the SAP instances „ Useable for SAPGUI login, RFC login, BEx and Web reporting „ Calculation of quality factor ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Calculation of quality factor: reponse time is weighted considerably higher compared to the number of users (5:1) (default setting) „ Calculation of quality factor is executed: y Each 300 s (default value for rdisp/auto abap time) y After a certain number of logons © SAP AG BW360 9-52
- 50. Load Balancing (2) Define logon group for BW application servers (SMLG) and apply it to the RFC connection from source L Application system to BW o server a d Data packet new task / commit work B Application a server l Data packet new task / commit work a n c Data packet new task / commit work i Application n server g BW OLTP Source System ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ You can only use dialog work processes across different servers if the extraction program has the option of using server groups. Otherwise, you are limited to the dialog work processes of one server. „ Even if you mark the flag in transaction SM59 for load balancing, you are still logged on to a single server. The message server determines which server this is. „ To further improve load balancing, in transaction SM59 set the system settings for asynchronous RFC (aRFC option) to: After Call = 1. „ Connection attemps before cancellation connection: SM59 Æ R/3 Destination Æ Destination Æ tRFC options. © SAP AG BW360 9-53
- 51. Extraction and Dataload: Unit Summary 1RZ RX ZLOO EH DEOH WR „ Explain the dataload process „ Identify some possible resource bottlenecks ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 9-54
- 52. Exercises Unit: Extraction and Dataload Topic: Monitoring and analysis of extraction and data load process At the conclusion of this exercise, you will be able to: • work with the load monitor A possible business scenario would be master and transactional data load in infoobjects and infocubes. Use for the subsequental exercises the BW workload monitor, SM50, ST04 and ST05. 1-1 The instructor starts load process 1: 1-1-1 What kind of load process is running? (Master or transactional data load) 1-1-2 What are the settings for processing in the infopackage (tabstrip processing)? 1-1-3 What source system is used? 1-1-4 How many records have been loaded? 1-1-5 How long does the load process take? 1-1-6 Analyse the starschema of the infocube after the workload. How can you optimize the star schema? 1-1-7 How can you speed up the initial load process from 1-1? (Describe at least 2 possibilities) 2-1 The instructor starts load process 2: It is the same data source as for load process 2, but a different infocube (optimized structure!) 2-1-1 What is the difference to 1-1? 2-1-2 Monitor the load process in SM50 again and try to find further optimization opportunities. Take a look at the transfer rule! What happens in the transfer rule? 2-1-3 Do you have any further ideas how to optimize the load process? 2-1-4 How long does the load process take? © SAP AG BW360 9-55
- 53. 3-1 Then instructor starts load process 3: It is the same data source and the same data as before (load process 2), but with an optimized transfer rule. 3-1-1 Compare the self defined ABAP coding in the transfer rule from load process 2 with the coding used for load process 3. What is the main difference? 3-1-2 How long does the load process take? © SAP AG BW360 9-56
- 54. Solutions Unit: Extraction and Dataload Topic: Monitoring and analysis of extraction and data load process 1-1 The instructor starts load process 1: 1-1-1 What kind of load process is running? (Master or transactional data load) Goto transaction RSA1, choose Monitoring Æ Monitor Æ set filter: today. Tabstrip: Header shows transactional data load 1-1-2 What are the settings for processing in the infopackage (tabstrip processing)? Goto tabstrip ‘Header’ in the dataload monitor and doubleclick on the infopackage. Check tabstrip ‘Processing’ in the infopackage. ’Only data target’ is used. 1-1-3 What is the name of the BW object which is filled? Goto tabstrip ‘Header’ in the dataload monitor: Infcube T_SFLOAD is filled 1-1-4 What source system is used? Goto tabstrip ‘Header’ in the dataload monitot: T90CLNT090: IDES R/3 1-1-5 How many records have been loaded? 262135 records have been loaded 1-1-6 How long takes the load process? Goto tabstrip ‘Header’ in the dataload monitor 1-1-7 Analyse the starschema of the infocube after the workload. How can you optimize the star schema? Goto RSA1 Æ Modeling Æ InfoproviderÆ Infoarea: BW Training → BW Customer Training Æ BW360 Performance and Administration → Unit09: Right mouse on infocube ‘T_SLOAD’: choose ‘MANAGE’. Then open menu ‘Goto’ and choose ‘Data target analysis’. Open Folder ‘All elementary tests’Æ Database. Drag and drop ‘Database information about infoprovider table’ . Select infoprovider ‘T_SLOAD’ and ‘Execute’ test.’Display’ test. Dimension 8 is very big. 1-1-8 How can you speed up the initial load process from 1-1? (Describe at least 2 possibilities) possibility 1: buffer DIM Ids (snro Æ objecttype: BID*) possibility 2: change dimension 8 to line item possibility 3: increase maxproc (currently 3) © SAP AG BW360 9-57
- 55. 2-1 The instructor starts load process 2: It is the same data source as for load process 2, but a different infocube (optimized structure!) 2-1-1 What is the difference from 1-1? Infocube T_FLOAD has 3 line item dimensions. Less generation of DIM Ids during data load. 2-1-2 Monitor the load process in SM50 again and try to find further optimization potential. Take a look at the transfer rule! What happens in the transfer rule? Goto RSA1 Æ Modeling Æ Infosource: Goto BW Training Æ ZT_BW360. Doubleclick on ‘T_SLOAD’. Open the transfer structure and display transfer rule for infoobject ‘T_MATNO2’. you find ‘VHOHFW IURP ELFS7B0$7 «««· Masterdata is read from the database for each record which passes the transfer structure. Result: Many database accesses with this transfer rule. 2-1-3 Do you have any further ideas on how to optimize the load process? Use internal table which buffers the master data table. Then master data need not to be read again from the database, but from the main memory. 2-1-4 How long takes the load process? Goto tabstrip ‘Header’ in the dataload monitor 3-1 Then instructor starts load process 3: It is the same data source and the same data as before (load process 2), but with an optimized transfer rule. 3-1-1 Compare the self defined ABAP coding in the transfer rule from load process 2 with the coding used for load process 3. What is the main difference? Internal hash table is used for buffering the master data table. 3-1-2 How long takes the load process? Goto tabstrip ‘Header’ in the dataload monitor © SAP AG BW360 9-58
- 56. Process Chains RQWHQWV „ Design of process chains „ Properties of process chains ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 10-1
- 57. Process Chains: Unit Objectives $W WKH FRQFOXVLRQ RI WKLV XQLW RX ZLOO EH DEOH WR „ Use process chains ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 10-2
- 58. Process Chains: Overview Diagram Architecture and Customizing InfoCube Data Model Transactional Data Targets Transport Management ODS Objects Indexing Process Chains BW Statistics Extraction and Dataload Reporting Performance Partitioning Aggregates ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 10-3
- 59. Introduction: Typical Data Load Cycle Load into PSA Load into ODS 'DWD /RDG Activate 0RQLWRU Data in ODS St ar t Drop Indices Roll up Aggregates Build DB Load into Cube Statistics 'DWD 7DUJHW 0DLQWHQDQFH Build Indices ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 10-4
- 60. Job Scheduling and Monitoring with BW 2.0B/2.1C 0onitoring of entire load process not possible (different logs for InfoCubes, attribute changerun, drop index, …) omplex event chain scenarios necessary omplicate restart of terminated processes ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ There were certain limitations of event chains (BW 2.x), which have been solved with the introduction of process chains. „ PC monitoring extends beyond the data load process itself. „ Moving responsibility means that the predecessor process is not responsible to start the successor process(es). When a process is complete, an event is raised to indicate the completion of the process. „ This event triggers the successor process to receive the status of the predecessor, request any needed additional information, and then execute. The successor process is responsible to gather information and run correctly. © SAP AG BW360 10-5
- 61. Transaction RSPC: Process Chains Maintenence General Services Start Process Start AND (Last) PC Immediate OR (Each) EXOR (First) ABAP Program Operating System Command Load Data Local Process Chain PC Customer Attributes Remote Process Chain Load Process and Subsequent Processing Data Loading Process Read PSA and update data target Attrib. Change Save Hierarchy PC Change Run Further Processing of ODS Object Data Data Export into External Systems Delete Overlapping Requests from InfoCube Data Target Contents Load Data Data Target Administration PC Cube Deletion PC Transaction Data Delete Index Generate Index Construct Database Statistics Initial Fill of New Aggregates ODSO Data Roll Up of Filled Aggregates PC Activate just loaded request Compression of the InfoCube Activate ODS Object Data Complete Deletion of Data Target Contents Other BW Processes AND Attribute Change Run PC Cube deleted and ODS data activated Adjustment of Time-Dependent Aggregates Deletion of Requests from PSA ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Easy creation of process chains via Drag Drop. „ Creation of items possible. © SAP AG BW360 10-6
- 62. RSPC User Interface: Building a Process Chain Load Process and Subsequent Processing Data Loading Process Read PSA and update data target Start Save Hierarchy Further Processing of ODS Object Data TR Data Export into External Systems Delete Overlapping Requests from InfoCube Data Target Administration Delete Index Generate Index Construct Database Statistics Load Data Draw line to Initial Fill of New Aggregates connect Roll Up of Filled Aggregates TR Texts Compression of the InfoCube Drag and drop processes Activate ODS Object Data Complete Deletion of Data Target Contents Other BW Processes Attribute Change Run Adjustment of Time-Dependent Aggregates Deletion of Requests from PSA Attrib. Change General Services Start Process TR Characteristics AND (Last) OR (Each) EXOR (First) ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ When you draw a line to connect processes, you are prompted to indicate whether the subsequent process should execute based on the success or the failure of the predecessor process. In other words, it is possible to schedule a process to run only if the predecessor process fails. © SAP AG BW360 10-7
- 63. Automatic Insertion of Corresponding Process Types ,f a process is inserted into the process chain the corresponding process variants are inserted into the process chain automatically: ([DPSOH: ([DPSOH You drag and drop a data load process to your process chain, the Index drop and the Index create process are automatically inserted. ,f you want no corresponding processes to be inserted automatically, flag the (user specific) setting in the menu under Settings Æ Default Chains ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 10-8
- 64. Collector Processes ollectors are used to manage multiple processes that feed into the same subsequent process. The collectors available for BW are: „ AND: All of the processes that are direct predecessors must send an event in order for subsequent processes to be executed „ OR: A least one predecessor process must send an event ‹ The first predecessor process that sends an event triggers the subsequent process „ EXOR: Exclusive “OR” ‹ Similar to regular “OR”, but there is only ONE execution of the successor processes, even if several predecessor processes raise an event ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Collector processes allow the designer of a process chain to trigger a subsequent process based on whether certain conditions are met by multiple predecessor processes. „ Application processes are the other type of processes – these represent BW activities such as aggregate rollup, etc. „ Although the “AND” condition is implemented for process chains using the event chain functionality from 2.x, this event chain is internal and cannot be edited. © SAP AG BW360 10-9
- 65. Application Processes $pplication processes represent BW activities that are typically performed as part of BW operations. Examples include: „ Data load „ Attribute/Hierarchy Change run „ Aggregate rollup „ Reporting Agent Settings 2ther special types of application processes exist: „ Starter – process that exists to trigger process chain execution „ ABAP program „ Another process chain „ Remote process chains „ Operating System command „ Customer built process ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ A starter process is part of every process chain. © SAP AG BW360 10-10
- 66. Start Process Variant name and description Direct scheduling: Job BI_PROCESS_TRIGGER will be scheduled when the process chain is acitvated. Scheduling Options for SAP Basis – Job Scheduler Start using Meta Chain of API: (only used when ‘direct No BI_PROCESS_TRIGGER will be scheduled. scheduling’ is chosen) Start of the process chain have to be done via FM ‚RSPC_API_CHAIN_START‘ or with another process chain ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ The process variant could be used just by one process chain. „ Each process chain could be started manually or via RFC connection with the function module ‚RSPC_API_CHAIN_START‘. © SAP AG BW360 10-11
- 67. Basic Principles 2penness Ÿ abstract meaning of “process“: “Any activity with defined start and defined ending” 6ecurity Ÿ founding on the batch administration: „ Processes get planned before they run and can be viewed with standard batch-monitor „ Dumps and Aborts are caught and thus can be treated as failures 5esponsibility: „ Each process have to care for all necessary information and dependencies for its own, when it is added to the process chain. „ Predecessor process is not responsible to start the correct successors and provide them with necessary information … ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Functions of the predecessor and successor processes: y Predecessor process runs then signals when it has completed, writing information about the completed task to a database table (RSPCPROCESSLOG). y Successor process reacts to the event which is triggered by the predecessor, reads the database table (RSPCVARIANT, RSPCVARIANTATTR) to obtain any needed information, then executes. y Additional administrative process is to check the sequence of the processes. © SAP AG BW360 10-12
- 68. Structure of a Process Attribute Change Run Type – Kind of task ps_attrib2_long PA_ATTRIB2 Execute InfoPackage: ZPAK_4QVBBF65GZONPAP96APH2P3KQ Variant – Configuration Process = process type + variant $GGLWLRQDOO „ Sequence at Runtime: ‹ Get the variant and predecessor list ‹ Check status information from predecessors ‹ Execution of the process ‹ Report ending with status „ Instance: Messages and information written to table RSPCINSTANCE and RSPCPROCESSLOG at runtime ‹ RSPCINSTANCE are storing meta data for the successor process (process type, variant ...) ‹ RSPCPROCESSLOG: log information about the different processes collected at runtime ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ A process type is an ABAP OO object. „ The object is initiated when it is time for a process to run. „ The variant holds the specific configuration information for a process. „ Variant – Configuration y Each process can have one or several variants y Maintenance of variant is specific for every process type „ Instance: (‚instance for process is like request for infopackage‘) y snapshot of the variant configuration (table RSPCVARIANT*) at runtime and written to table RSPCINSTANCE y Log information about the different processes collected at runtime and written to table RSPCPROCESSLOG © SAP AG BW360 10-13
- 69. Example: Structure of a Process – Process Type Other BW Processes Attribute Change Run 7SH – Attribute Change Run „ Execute the hierarchy and attribute change run „ Process types can be maintained via Settings – Process Types ‹ Do not change standard process types (if allowed) Change View Possible Process Types: Details ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ If standard process types can be changed depending on its name range (transaction SE06). „ Don‘t modify standard process types, but you can create your own process types (see HOW TO – Guides on service.sap.com/bw Æ serviceimplemation Æ How To ... Guide). „ RSPC Æ Settings Æ Maintain Process type (= Table/maintenance view RSPROCESSTYPES) (SM30)) contains all information about the defined process types. © SAP AG BW360 10-14
- 70. Example: Structure of a Process – Variant 9DULDQW – Configure the Hierarchy and Attribute Change run „ Execute the specific hierarchy and attribute change run for which hierarchy, which InfoObject or which data loading process Process Maintenance: Attribute Change Run Variant Selection (1) 4 Entries found ASUG_COST_HIER_CHANGE Restrictions ASUG cost center hierarchy attrib... To Select, Press F4 On The Object Typ Object Object Execute Typ Object Na HIERARCHY Hierarchy Execute InfoPackage INFOOBJECT InfoObject LOADING Execute InfoPacka. REPORTVARI Report Variants 4 Entries found ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Variants have to be created for the process types. With variant settings the process type gets necessary information for execution. „ For example: y If you assign the process type Attribute Change run to a process chain you must define a variant. With this variant you have to define the InfoObjects for which you want to activate the master data. There are four different possibilities: - HIERARCHY: direct selection of the hierarchy which need to be activated - INFOOBJECT: direct selection of the infoobjects which need to be activated - LOADING: indirect selection: reference to an InfoPackage, which must be loaded before in the process chain. Combined with the meta data of these objects and the instance information the system derives the affected InfoObjects and hierarchies. If the chosen LOADING object is not in the process chain, the system automatically inserts the chosen infopackage in process chain. - REPORTVARIANT: indirect selection: reference to a change run variant which you can define with RSDDS_AGGREGATES_MAINTAIN (SE38) or TCode RSATTR Æ Executing the Attribute/hierarchy change run with Variant: Instead of applying the InfoObjects or hierarachies directly to the process variant in RSPC you can create a central variant for the report RSDDS_AGGREGATES_MAINTAIN. You can assign InfoObjects and hierarchies to this report variant. This central variant could be used by several process variants in RSPC. The benefits are central maintenance, .. „ Using a reference object like LOADING or REPORTVARIANT is sometimes more flexible. © SAP AG BW360 10-15
- 71. 3 Different Views to Process Chains Planning view for Checking view for Log View for checking the plan check consistency monitoring status of the of the process maintenance activities process chain chain and executions working Views related to the working area area Different views to the the activities which are possible: z Process chains z Process types z Data targets z InfoSources z Logs ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ There are three main views in the icon bar with different views: y Planning view (shows if the process chain is active) - Grey: unplanned processes (e.g. not activated process chain) - Green: planned processes (process chain is active and start process is released) - Yellow: planned but unknown processes - Red: multiple planned processes y Checking view (consistency check like double used start variants, missing index deletion and recreation, wrong references in variants, ...) - Green: Error-free processes - Yellow: Process with warnings - Red: Process with errors y Log view - Grey: Not yet run - Green: Finished without error - Yellow: running - Red: aborted or failed - note that the log information is a usually mixture of - log information of maintenance activites (e.g. new process, change of design, activation) - log information of WHM activites (like previous executions of process chains) © SAP AG BW360 10-16
- 72. Different Object Trees for Process Chain Administration (1) )or easy administration on process chains different object trees can be displayed. Display component Process Types Available process types Process chain Process types can be created via Settings – Process Types Further information included in section Implementing a process Creation and assignment of ‘Display Components’ via menu or via button ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Folders in the process chain are called display components. „ For mainentance of display components you have to use process chains Æ attributes Æ display components. y For reassignment of process chain to different display component y For creation of new display component © SAP AG BW360 10-17
- 73. Different Object Trees for Process Chain Administration (2) )or easy administration on process chains, different object trees can be displayed. Log Display the log tree InfoAreas InfoSources Search in Search in InfoSources InfoProvider tree tree for InfoPackages Possible processes on data In InfoPackage reference to target are displayed process chain is displayed ¤ SAP AG 2003 © SAP AG BW360 10-18
- 74. Maintain Process Chains – Detail View RSPC View Detail View: „ Technical names „ Ability to move boxes to re-design the process chain „ Hidden collector 1RWH In detail view, a collector processes are process is displayed as multiple displayed collector processes (needed for conditions) ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ When collector processes are built into a process chain, there are actually several background jobs scheduled with events in order to construct the conditional nature of collector processes. „ The simple view displays the processing chain as it exists logically. The detail view displays the processing chain with the extra collector processes. © SAP AG BW360 10-19
- 75. Maintain Message Write a message and fill in recipient and type. Info saved within process variant. Send with Note Planning view context menu Bwadmin@sap.com BWADMIN@sap.com ¤ SAP AG 2003 „ Email can be sent to indicate successful or completion of a process too. © SAP AG BW360 10-20