Cell theory membrane structure cell transport and important organelles
•Transferir como PPTX, PDF•
19 gostaram•11,929 visualizações
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Denunciar
Compartilhar
Recomendados
Mais conteúdo relacionado
Mais procurados
Mais procurados (20)
The Structures & Functions of Plant and Animal Cell 

The Structures & Functions of Plant and Animal Cell
Destaque
Destaque (20)
Dissolution testing conventional and controlled release products

Dissolution testing conventional and controlled release products
Semelhante a Cell theory membrane structure cell transport and important organelles
Semelhante a Cell theory membrane structure cell transport and important organelles (20)
fundamentalunitoflifeclassix-220731093151-24fe9dbf (1).pptx

fundamentalunitoflifeclassix-220731093151-24fe9dbf (1).pptx
fundamentalunitoflifeclassix-220731093151-24fe9dbf (1).pptx

fundamentalunitoflifeclassix-220731093151-24fe9dbf (1).pptx
Cell structure and function (Miller and Levine Biology chapter 7)

Cell structure and function (Miller and Levine Biology chapter 7)
Mais de James H. Workman
Mais de James H. Workman (20)
Oogenesis female reproductive system hormone signaling in female

Oogenesis female reproductive system hormone signaling in female
Último
A Principled Technologies deployment guide
Conclusion
Deploying VMware Cloud Foundation 5.1 on next gen Dell PowerEdge servers brings together critical virtualization capabilities and high-performing hardware infrastructure. Relying on our hands-on experience, this deployment guide offers a comprehensive roadmap that can guide your organization through the seamless integration of advanced VMware cloud solutions with the performance and reliability of Dell PowerEdge servers. In addition to the deployment efficiency, the Cloud Foundation 5.1 and PowerEdge solution delivered strong performance while running a MySQL database workload. By leveraging VMware Cloud Foundation 5.1 and PowerEdge servers, you could help your organization embrace cloud computing with confidence, potentially unlocking a new level of agility, scalability, and efficiency in your data center operations.Deploy with confidence: VMware Cloud Foundation 5.1 on next gen Dell PowerEdg...

Deploy with confidence: VMware Cloud Foundation 5.1 on next gen Dell PowerEdg...Principled Technologies
Último (20)
How to Troubleshoot Apps for the Modern Connected Worker

How to Troubleshoot Apps for the Modern Connected Worker
Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business

Why Teams call analytics are critical to your entire business
TrustArc Webinar - Unlock the Power of AI-Driven Data Discovery

TrustArc Webinar - Unlock the Power of AI-Driven Data Discovery
Scaling API-first – The story of a global engineering organization

Scaling API-first – The story of a global engineering organization
Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf

Boost Fertility New Invention Ups Success Rates.pdf
Tata AIG General Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024

Tata AIG General Insurance Company - Insurer Innovation Award 2024
Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)

Powerful Google developer tools for immediate impact! (2023-24 C)
Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher

Strategies for Landing an Oracle DBA Job as a Fresher
HTML Injection Attacks: Impact and Mitigation Strategies

HTML Injection Attacks: Impact and Mitigation Strategies
From Event to Action: Accelerate Your Decision Making with Real-Time Automation

From Event to Action: Accelerate Your Decision Making with Real-Time Automation
Polkadot JAM Slides - Token2049 - By Dr. Gavin Wood

Polkadot JAM Slides - Token2049 - By Dr. Gavin Wood
Deploy with confidence: VMware Cloud Foundation 5.1 on next gen Dell PowerEdg...

Deploy with confidence: VMware Cloud Foundation 5.1 on next gen Dell PowerEdg...
Top 5 Benefits OF Using Muvi Live Paywall For Live Streams

Top 5 Benefits OF Using Muvi Live Paywall For Live Streams
Cell theory membrane structure cell transport and important organelles
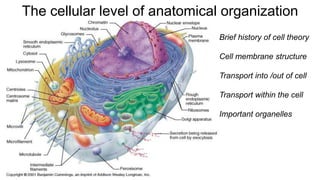
- 1. The cellular level of anatomical organization Anatomy and Physiology Brief history of cell theory Cell membrane structure Transport into /out of cell Transport within the cell Important organelles
- 2. Cell Theory: 1. All living things are made of one or more cells 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms 3. All cells arise from existing cells
- 3. Development of the cell theory: Robert Hooke in 1663, observed cork (plant): named the cell Robert Brown observed and named nucleus Theodor Schwann in 1800’s states: all animals are made of cells
- 4. Development of the Cell Theory Matthias Schleiden in 1800’s states: all plants are made of cells Louis Pasteur’s work with bacteria ~ 1860 disproved idea of spontaneous generation (living things from nonliving) Rudolf Virchow observes cells dividing and states all cells come from preexisting cells
- 5. A cell is the simplest structural and functional unit of life. There are no smaller subdivisions of a cell or organism that, in themselves, are alive. An organism’s structure and all of its functions are ultimately due to the activities of its cells. Importance of Cell Theory
- 6. Importance of Cell Theory Cells come only from preexisting cells, not from nonliving matter. All life, therefore, traces its ancestry to the same original cells. Because of this common ancestry, the cells of all species have many fundamental similarities in their chemical composition, and metabolic and physiological mechanisms.
- 7. Why Cells are Small
- 8. Small cells are more efficient Surface area to volume ratio must remain high for materials to easily reach all parts of the cell
- 10. Cell Membrane Structure and Transport
- 11. Cell Membrane •Defines cell boundaries •Controls interactions with other cells •Controls passage of materials in and out of cell (contributes to homeostasis) • Fluid-Mosaic model
- 13. Fluid Mosaic Model of Membranes
- 16. Membrane Permeability •Cell membranes are selectively permeable (semi-permeable) •Some solutes cross the membrane freely, some cross with assistance, and others do not cross at all.
- 19. The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane Osmosis will continue as long as there are more water molecules on one side of the membrane (“osmotic pressure”) Water will continue to diffuse until there are equal numbers of molecules inside and outside the cell (“osmotic balance”) Osmosis
- 20. 60% H2O 90% H2O
- 21. Water will move out of to the left across the membrane until osmotic balance has been reached
- 23. 100% H2O 80% H2O
- 24. 90% H2O 90% H2O
- 25. 75% H2O 90% H2O Water leaves the cell and it shrinks. This is called plasmolysis in plant cells
- 27. Facilitated Diffusion Involves carrier or channel proteins to transport substances that otherwise could not pass the phospholipid bilayer (because of their polarity or charge, like ions)
- 28. Active Transport and ATP Powered Pumps Animal cells contain membrane vesicles called lysosomes, filled with enzymes that can degrade proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules. These enzymes are most effective at acid pH, and it can be experimentally shown that the pH inside lysosomes is about 5.0, whereas the pH of the cell cytoplasm is close to 7.0. The diagram (at right) illustrates one lysosome inside a cell.