Mais conteúdo relacionado Semelhante a Trigonometry (20) 2. The word ‘trigonometry’ is derived from the Greek words
‘tri’(meaning three), ‘gon’ (meaning sides) and ‘metron’
(meaning measure).
Trigonometry is the study of relationships between
the sides and angles of a triangle.
Early astronomers used it to find out the distances of the
stars and planets from the Earth.
Even today, most of the technologically advanced methods
used in Engineering and Physical Sciences are based on
trigonometrical concepts.
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
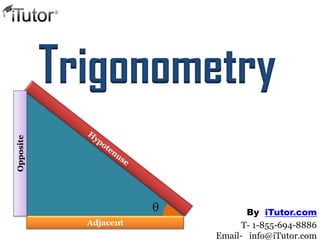
3. A triangle in which one angle is
equal to 90 is called right
triangle.
The side opposite to the right
angle is known as hypotenuse.
AC is the hypotenuse
The other two sides are known
as legs.
AB and BC are the legs
Trigonometry deals with Right Triangles
A
CB
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
4. In any right triangle, the area of the square whose side is
the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of areas of the squares
whose sides are the two legs.
A
CB
(Hypotenuse)2 = (Perpendicular)2 + (Base)2
AC2 = BC2 + AB2
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
5. Pythagoras Theorem Proof:
Given: Δ ABC is a right angled triangle where B = 900
And AB = P, BC= b and AC = h.
To Prove: h2 = p2 + b2
Construction : Draw a BD from
B to AC , where AD = x and CB = h-x ,
Proof : In Δ ABC and Δ ABD,
Δ ABC Δ ABD --------(AA)
In Δ ABC and Δ BDC both are similar
So by these similarity,
p
b
h
A
B
C
6. Or P2 = x × h And b2 = h (h – x)
Adding both L.H.S. and R.H. S. Then
p2 + b2 = (x × h) + h (h – x)
Or p2 + b2 = xh + h2 – hx
Hence the Pythagoras theorem
p2 + b2 = h2
b
xh
h
b
p
x
h
p
And
p
b
h
A
B
C
7. Let us take a right triangle ABC
Here, ∠ ACB ( ) is an acute angle.
The position of the side AB with
respect to angle . We call it the
side opposite to angle .
AC is the hypotenuse of the right
triangle and the side BC is a part of
. So, we call it the side
adjacent to angle .
A
CB
Sideoppositetoangle
Side adjacent to angle ‘ ’
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
8. The trigonometric ratios of
the angle C in right ABC as
follows :
Sine of C =
=
Cosine of C=
=
A
CB
Sideoppositetoangle
Side adjacent to angle ‘ ’
Side opposite to C
Hypotenuse
AB
AC
Side adjacent to C
Hypotenuse
BC
AC
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
9. Tangent of C =
=
Cosecant of C=
=
Secant of C =
A
CB
Sideoppositetoangle
Side adjacent to angle ‘ ’
Side opposite to C
Side adjacent to C
AB
BC
Side adjacent to C
Hypotenuse
Side opposite to C
Hypotenuse
AC
AB
AC
AB
=
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
10. Cotangent of C
Above Trigonometric Ratio
arbitrates as sin C, cos C, tan C
, cosec C , sec C, Cot C .
If the measure of angle C is ‘ ’
then the ratios are :
sin , cos , tan , cosec , sec
and cot
A
CB
Sideoppositetoangle
Side adjacent to angle ‘ ’
Side opposite to C
Side adjacent to C
AB
BC= =
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
11. Tan =
Cosec = 1 / Sin
Sec = 1 / Cos
Cot = Cos / Sin
= 1 / Tan
A
CB
p
b
h
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
cos
sin
12. 1. Sin = p / h
2. Cos = b / h
3. Tan = p / b
4. Cosec = h / p
5. Sec = h / b
6. Cot = b / p
A
CB
p
b
h
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
13. Trigonometric Ratios of 45°
In Δ ABC, right-angled at B,
if one angle is 45°, then
the other angle is also 45°,
i.e., ∠ A = ∠ C = 45°
So, BC = AB
Now, Suppose BC = AB = a.
Then by Pythagoras Theorem,
AC2 = BC2 + AB2 = a2 + a2
AC2 = 2a2 , or AC = a 2
A
CB
450
a
a
450
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
14. Sin 450 = = = = 1/ 2
Cos 450 = = = = 1/ 2
Tan 450 = = = = 1
Cosec 450 = 1 / sin 450 = 1 / 1/ 2 = 2
Sec 450 = 1 / cos 450 = 1 / 1/ 2 = 2
Cot 450 = 1 / tan 450 = 1 / 1 = 1
Side opposite to 450
Hypotenuse
AB
AC
a
a 2
Side adjacent to 450
Hypotenuse
BC
AC
a
Side opposite to 450
Side adjacent to 450
AB
BC
a
a
a 2
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
15. Consider an equilateral triangle ABC.
Since each angle in an equilateral triangle is
60°, therefore,
∠ A = ∠ B = ∠ C = 60°.
Draw the perpendicular AD from A
to the side BC,
Now Δ ABD ≅ Δ ACD --------- (S. A. S)
Therefore, BD = DC
and ∠ BAD = ∠ CAD -----------(CPCT)
Now observe that:
Δ ABD is a right triangle, right-angled at D with ∠ BAD =
30° and ∠ ABD = 60°
600
300
A
B D C
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
16. As you know, for finding the trigonometric ratios, we
need to know the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
So, let us suppose that AB = 2a.
BD = ½ BC = a
AD2 = AB2 – BD2 = (2a)2 - (a)2 = 3a2
AD = a 3
Now Trigonometric ratios
Sin 300 = =
= = ½
600
300
A
B D C
2a
2a
2a
a aSide opposite to 300
Hypotenuse
BD
AB
a
2a
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
17. Cos 300 = = = 3 / 2
Tan 300 = = = 1 / 3
Cosec 300 = 1 / sin 300 = 1 / ½ = 2
Sec 300 = 1 / cos 300 = 1 / 3/2 = 2 / 3
Cot 300 = 1 / tan 300 = 1 / 1/ 3 = 3
Now trigonometric ratios of 600
AD
AB
a 3
2a
BD
AD
a
a 3
300
A
B D C
2a
2a
2a
a a
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
18. Sin 600 = = = 3 / 2
Cos 600 = = = ½
Tan 600 = = = 3
Cosec 600 = 1 / Sin 600 = 1 / 3 / 2 = 2 / 3
Sec 600 = 1 / cos 600 = 1 / ½ = 2
Cot 600 = 1 / tan 600 = 1 / 3
AD
AB
a 3
2a
BD
AB
a
2a
AD
BD
a 3
a
600
A
B D C
2a
2a
2a
a a
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
19. T. Ratios 0 30 45 60 90
Sine 0 ½ 1/ 2 3/2 1
Cosine 1 3/2 1/ 2 ½ 0
Tangent
0 1/ 3 1 3
Not
defined
Cosecant Not
defined
2 2 2/ 3 1
Secant
1 2/ 3 2 2
Not
defined
Cotangent Not
defined
3 1 1/ 3 0
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
20. Relation of with Sin when 00 900
The greater the value of ‘ ’, the greater is the value of
Sin .
Smallest value of Sin = 0
Greatest value of Sin = 1
Relation of with Cos when 00 900
The greater the value of ‘ ’, the smaller is the value of
Cos .
Smallest value of Cos = 0
Greatest value of Cos = 1
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
21. Relation of with tan when 00 900
Tan increases as ‘ ’ increases
But ,tan is not defined at ‘ ’ = 900
Smallest value of tan = 0
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
22. If 00 900
1. Sin(900- ) = Cos
2. Cos(900- ) = Sin
If 00< 900
1. Tan(900- ) = Cot
2. Sec(900- ) = Cosec
If 00 < 900
1. Cot(900- )= Tan
2. Cosec(900- ) = Sec
A
CB
p
b
h
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
23. Sin2 +Cos2 = 1
Sec2 -Tan2 = 1
Cosec2 - Cot2 = 1
© iTutor. 2000-2013. All Rights Reserved
24. The End
Call us for more
information:
www.iTutor.com
1-855-694-8886
Visit