Various Facets of Indian Consumer Markets - 2
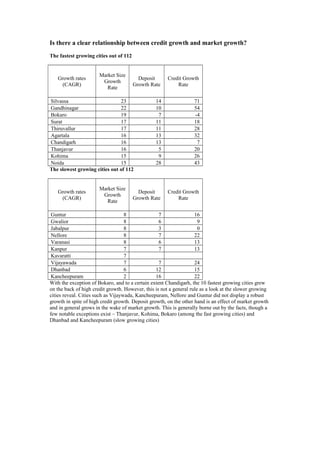
- 1. Is there a clear relationship between credit growth and market growth? The fastest growing cities out of 112 Growth rates (CAGR) Market Size Growth Rate Deposit Growth Rate Credit Growth Rate Silvassa 23 14 71 Gandhinagar 22 10 54 Bokaro 19 7 -4 Surat 17 11 18 Thiruvallur 17 11 28 Agartala 16 13 32 Chandigarh 16 13 7 Thanjavur 16 5 20 Kohima 15 9 26 Noida 15 28 43 The slowest growing cities out of 112 Growth rates (CAGR) Market Size Growth Rate Deposit Growth Rate Credit Growth Rate Guntur 8 7 16 Gwalior 8 6 9 Jabalpur 8 3 0 Nellore 8 7 22 Varanasi 8 6 13 Kanpur 7 7 13 Kavaratti 7 Vijayawada 7 7 24 Dhanbad 6 12 15 Kancheepuram 2 16 22 With the exception of Bokaro, and to a certain extent Chandigarh, the 10 fastest growing cities grew on the back of high credit growth. However, this is not a general rule as a look at the slower growing cities reveal. Cities such as Vijaywada, Kancheepuram, Nellore and Guntur did not display a robust growth in spite of high credit growth. Deposit growth, on the other hand is an effect of market growth and in general grows in the wake of market growth. This is generally borne out by the facts, though a few notable exceptions exist – Thanjavur, Kohima, Bokaro (among the fast growing cities) and Dhanbad and Kancheepuram (slow growing cities)
- 2. Insights into the Financial landscape of the country Indian Financial Scape provides insights into the financial landscape of the country. It presents nearly 250 different variables at district level. The product helps enhance a professional’s understanding of the markets. A few samples of unusual insights are presented below. There are many more interesting ones available in the product. Fastest growing districts in terms of Personal Loans (Personal loans, as defined by RBI includes all loans taken by individuals – secured and unsecured) Unit % Year 2001-02 to 2007-08 Personal loans - growth rate of SCB`s credit State District Karnataka Bangalore Rural 77 Meghalaya West Garo Hills 74 Arunachal Pradesh Changlang 72 Arunachal Pradesh East Siang 72 Arunachal Pradesh Papum Pare 72 Arunachal Pradesh West Kameng 72 Bihar Katihar 72 Uttar Pradesh Sant Kabir Nagar 71 Haryana Jhajjar 70 Assam Hailakandi 69 Gujarat Narmada 69 Haryana Panipat 68 Haryana Rohtak 67 Haryana Sonipat 67 Haryana Faridabad 62 Jammu & Kashmir Pulwama 62 Mizoram Champhai 60 Bihar Araria 57 Chhattisgarh Rajnandgaon 57 Uttar Pradesh Baghpat 56 Arunachal Pradesh is an unusual place. Not much is known about it and it has a small base. Yet, on a sustained basis, over a 6 year period, four of its districts have figured among the top 6 districts in India in terms of growth in personal credit. Haryana is another place which has seen a boom with four of its districts figuring in the top 15. Fastest growing districts in terms of Professional and other Services credit Unit % % Year 2001-02 to 2007-08 2001-02 to 2007-08 Professional & other Services - growth rate of SCB`s credit Personal loans - growth rate of SCB`s credit State District Gujarat Rajkot 51 26 Chhattisgarh Korba 47 34 Punjab Bathinda 47 50
- 3. Andhra Pradesh Krishna 46 18 Rajasthan Ajmer 46 31 Rajasthan Kota 44 25 Madhya Pradesh Katni 44 12 Chhattisgarh Kanker 44 34 Rajasthan Ganganagar 43 31 Sikkim South Sikkim 42 26 Sikkim North Sikkim 42 53 Arunachal Pradesh Lohit 42 -16 Rajasthan Jodhpur 42 36 West Bengal Haora 42 17 Sikkim East Sikkim 42 16 Rajasthan Sikar 41 51 Orissa Sambalpur 41 34 Haryana Rewari 40 -11 Andhra Pradesh Nalgonda 40 21 Haryana Mahendragarh 40 33 The growth in credit in this category has been much lower than in the personal credit category. The districts that have grown fastest are those that are not in the top pecking order, yet they are not very small either. Lohit, in Arunachal Pradesh is unusual because it shows a negative growth in personal credit. Its possible that personal credit were routed through Professional credit in reality. Rewari is another standout – high growth in Professional combining with a negative growth in personal credit. Fastest growing districts in terms of Trade Credit Unit % Year 2001-02 to 2007-08 Trade Credit - growth rate of SCB`s credit State District Tamil nadu Nagapattinam 49 Chhattisgarh Rajnandgaon 47 Meghalaya Jaintia Hills 44 Haryana Jhajjar 40 Karnataka Bangalore Rural 40 Uttar Pradesh Mahoba 40 Gujarat Kheda 39 Orissa Ganjam 39 Haryana Gurgaon 38 Himachal Pradesh Kinnaur 38 Uttar Pradesh Gautam Buddha Nagar 38 Sikkim East Sikkim 37 Jammu & Kashmir Leh (Ladakh) 37 Bihar Madhubani 37 Arunachal Pradesh West Kameng 36 Uttaranchal Rudraprayag 35 West Bengal Medinipur 35
- 4. Andhra Pradesh Medak 35 Haryana Panchkula 34 Nagaland Mon 34 Economic Risk The Economic Risk Index is an important variable to consider while doing business. In case of financial products, it is important for marketers to consider the risks involved in addition to market size, growth and demography. Indian Financial Scape is a product which has introduced an Economic Risk index and rated districts based on variables such as economic offences, credit penetration, and credit overdue per credit of district central cooperative banks, Gross domestic product, GDP Growth, No. of Industrial Disputes (All strikes & Lockouts) and Maydays Lost Due to Industrial, Disputes per worker.. The top ranking districts in terms of economic risk State District Dadra & Nagar Haveli Dadra & Nagar Haveli Daman & Diu Daman Daman & Diu Diu Lakshadweep Lakshadweep Madhya Pradesh Neemuch Madhya Pradesh Jhabua Rajasthan Ganganagar Himachal Pradesh Kinnaur Madhya Pradesh Shajapur Madhya Pradesh Satna The worst districts in terms of economic risk State District Pondicherry Mahe Pondicherry Yanam Pondicherry Pondicherry West Bengal Kolkata West Bengal Koch Bihar West Bengal North 24 Parganas West Bengal South 24 Parganas Jharkhand Dumka Arunachal Pradesh Tirap West Bengal Puruliya How are some of the top business centres ranked (out of nearly 600 districts of India)? District Rank Hyderabad 177 Delhi 104 Ahmadabad 35 Surat 33 Bangalore 110 Mumbai 72 Mumbai (Suburban) 70 Pune 74 Chennai 111 Coimbatore 112 Kolkata 581
- 5. Most of the major centres are ranked within the top 30%. However, there are wide differences. The Western region (Mumbai, Ahmadabad, etc.) are clearly the safest. Kolkata stands out with a very poor ranking.
- 6. Demand for Housing The Housing Skyline of India estimates the demand for housing units in the top 30 cities to grow by 6.36 million units during the next 7 years leading up to 2015. The current stock of housing units in these 30 cities is estimated to be 25 million units, which implies a growth in housing stock of over 25% within 7 years. Demand between 2008 and 2015 Total Demand for Housing Demand for Plinth Area Less than 500 Sq ft Demand for Plinth Area Between 500- 1000 Sq ft Demand for Plinth Area More than 1000 Sq ft Top 10 cities (alpha) 3,548,000 1,212,000 1,151,00 0 1,186,0 00 Next 20 cities (beta) 2,815,000 930,000 921,00 0 965,0 00 Top 30 cities (alpha + beta) 6,363,000 2,142,000 2,072,00 0 2,151,0 00 Current Stock Current Housing Stock Current Housing Stock - Plinth Area Less than 500 Sq ft Current Housing Stock - Plinth Area Between 500-1000 Sq ft Current Housing Stock - Plinth Area More than 1000 Sq ft Top 10 14,624,000 5,829,000 4,337,00 0 4,458,0 00 Next 20 10,413,000 4,179,000 3,145,00 0 3,089,0 00 Top 30 25,037,000 10,008,000 7,482,000 7,547,000 Whereas most of the attention of the building industry is on the upper segment, it is middle and lower middle India which is driving demand - • The demand for housing of size less than 1000 sq ft is 4.2 million units over 7 years, which is 2/3rd of the demand • The anticipated growth in percentage terms in the lower segments (24% combined) is only marginally lower than the upper segment (28.5%) • The pattern is similar for the alpha (top 10) and beta (the next 20) cities, implying a uniform demand for affordable housing. The above pattern indicates that a renewed focus on affordable housing is in order. There is plenty of demand out there; supply is more likely to be the constraint. Alpha cities are - Hyderabad, Delhi, Ahmadabad, Surat, Bangalore, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, Coimbatore, Kolkata Beta cities are – Asansol, Bhopal, Faridabad, Indore, Jaipur, Jamshedpur, Kancheepuram, Kanniyakumari, Kanpur, Kochi, Lucknow, Ludhiana, Madurai, Nagpur, Patna, Salem, Thiruvallur, Urban Areas in North 24 Parganas, Urban Areas in Thane, Vadodara The estimation process involved the following steps: • Demographic parameters such as population across age-groups, change in household sizes, and family structures were estimated using data from census and various large scale data surveys. • This data was used with large scale survey data on housing conditions (NSSO 49th and 58th rounds) to establish the relationship between housing demand and demographic parameters. • Independently the relationship between ownership and income was established. Estimates of current income and growth from “The Market Skyline of India” were used to estimate households across income levels for the two time periods. • One of the major drivers of housing demand is the current and future rental markets. This in turn is driven by growth in economy, employment and migration trends. Estimates of GDP, employment growth and migration were used from “The District Level GDP 2006-07” to define the relationship with housing demand.
- 7. • Another relationship established was the ease and extent of availability of finance and housing demand. Data from RBI on housing loans for the last ten years were used to determine the function. • All these aspects were then combined to estimate the net demand in housing during the period 2008-15. They were also used to determine the demand for housing across various segments including income categories, plinth area, room size, etc. • The entire exercise was validated at various stages using a primary survey of households on income, demography, financial habits and housing conditions conducted in July 2008. Secondary data such as housing stock estimates from NHB, proposed construction data from various housing boards, etc. were also used to cross check estimates at various intermediate steps.
- 8. Financial Asset Penetration On an average, only 16% of Indian households have taken loans from institutional agencies. On the other hand, 22% of the households have taken loans from non institutional agencies. There are two clear indications here – a) the bulk of the population is financially underserved and rely on informal lending and b) the non institutional agencies have together achieved a much higher penetration than the institutional agencies. If we look at another indicator of financial inclusion, namely percentage of households who hold stocks and debentures, we find that the penetration is just 5%. There is no doubt that financial inclusion is extremely poor and financial institutions need to focus more on expanding the market rather than flog the existing markets. Here are the top districts in terms of penetration of institutional loans. These districts have penetrations ranging from 37% to 68%. As many as 14 of these 20 are from Kerala. The districts are Kottayam, Kannur, Idukki, Ernakulam, Pathanamthitta, Kasaragod, Wayanad, Palakkad, Kollam, Thrissur, Kozhikode, Malappuram, Alappuzha and Thiruvananthapuram from Kerala and Mahe, Udupi, Satara, Kolhapur, Wardha, Shajapur (MP). The bottom twenty districts (all less than 1% penetration) are mainly from the hill districts (Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Mehghalaya and J&K - Changlang, East Kameng, Lohit, Lower Subansiri, Tirap, Dhubri, Kupwara, Bishnupur, Chandel, Churachandpur, Senapati, Tamenglong, Thoubal, Ukhrul, East Garo Hills, Jaintia Hills, Ri Bhoi, South Garo Hills, West Garo Hills The picture changes substantially when one looks at the penetration of non institutional loans. The top 24 districts have penetration ranging from 50-53%. These are - Tiruchirappalli, Nagapattinam, Thiruvarur, Thanjavur, Karur, Pudukkottai and Perambalur from Tamil Nadu, Mahe, Karaikal, Pondicherry, Yanam from Pondicherry, and Prakasam, Srikakulam, West Godavari, Krishna, Nellore, Guntur, Visakhapatnam, Vizianagaram, East Godavari, Chittoor, Cuddapah, Anantapur and Kurnool from Andhra Pradesh indicating a clear geographic pattern. The bottom districts are again from the hill states. In fact of the bottom 64 (up to 7% penetration) - 2 are from Andaman and Nicobar, 13 are from Arunachal, 14 are from J&K, 7 from Meghalaya, 8 from Mizoram, 4 from Sikkim, 13 from Uttaranchal, and 3 from West Bengal. At a broader level there is a clear need for enhanced services in the hill states. However, even among the relatively well off districts, it is interesting to note that TN and Andhra seem to have a very high penetration of non institutional loans as compared to institutional loans – clearly an area for capturing the low hanging fruits for the formal sector.
- 9. How many people invest in stocks and shares? We all know that penetration of shares and debentures is extremely low in India. Just how low is it? The various data thrown around suggest around 30 million demat accounts. This however does not account for multiple accounts of investors. In our product, Indian Financial Scape, we have estimated the number of households (not individuals) who own shares and debentures at district level. This is based on large scale household surveys at various points in time conducted by Census of India, NSSO, and others. Some of the top line results are as follows: • Less than 5% of the households, about 12 million in number own shares and debentures (note: this can translate into anywhere between 20-25 million individuals and 30-40 million demat accounts) • Region wise the penetration of shares and debentures (% of households) are – West 5.25%, North 4.52%, South 8.17%, and East 3.2%. • West is dragged down by Rajasthan (3.6%) and MP (3.2%). The other states in the West are Maharashtra (8.4%), Gujarat (6.1%) and the combined Goa, Daman and Diu, Dadra Nagar Haveli (8.2%) • At state level, the highest penetrations are in: Delhi Kerala Karnataka Maharashtra Goa, Daman, Dadra Tamil Nadu Punjab Haryana 13.00 10.50 8.96 8.37 8.20 7.97 7.00 6.95 • The leading districts in terms of penetration are: Maharashtra Karnataka Maharashtra Maharashtra Haryana Mumbai Udupi Mumbai (Suburban) Thane Panchkula 27 24 23 20 19 Chandigarh West Bengal Goa Karnataka Kerala Chandigarh Kolkata North Goa Bangalore Ernakulam 19 19 18 18 18 Kerala Tamil Nadu Maharashtra Karnataka Karnataka Thrissur Chennai Kolhapur Dakshina Kannada Dharwad 18 18 17 17 17 Andhra Pradesh Karnataka Kerala Gujarat Madhya Pradesh Hyderabad Uttara Kannada Kottayam Ahmadabad Indore 15 15 15 14 14 • The bottom 41 districts in terms of penetration are all from the East • The bottom 249 districts (42% of the districts) are from the East, hill states or MP, Rajasthan and UP. In fact, if we ignore the backward areas of Vidarbha and Panchmahals, then we actually see that the bottom 50% (about 290 districts) are all from the East, hill states or MP, Rajasthan and UP, clearly indicating an East-West divide in penetration.
- 10. Housing Stock and Demand The Housing Skyline of India estimates the demand for housing units in the top 112 cities to be 10.5 million units during the next 7 years leading up to 2015. The current stock of housing units in these cities is estimated to be 41.8 million units, which implies a growth in housing stock of over 25% within 7 years Of these 112, the top 30 cities will account for 60% of the demand and are expected to add 6.36 million units during the next 7. The current stock of housing units in these 30 cities is estimated to be 25 million units. The top 112 Cities Figures in millions Households with Plinth Area Less than 500 Sq ft 17.0 Households with Plinth Area Between 500-1000 Sq ft 12.5 Households with Plinth Area More than 1000 Sq ft 12.3 Demand for units (2008-2015) for Plinth Area Less than 500 Sq ft 3.5 Demand for units (2008-2015) for Plinth Area Between 500-1000 Sq ft 3.4 Demand for units (2008-2015) for Plinth Area More than 1000 Sq ft 3.7 The top 30 Cities Figures in millions Households with Plinth Area Less than 500 Sq ft 10.01 Households with Plinth Area Between 500-1000 Sq ft 7.48 Households with Plinth Area More than 1000 Sq ft 7.55 Current stock of houses with plinth area > 1000 sq feet (figures in ‘000s)
- 11. Demand for units (2008-2015) for Plinth Area Less than 500 Sq ft 2.14 Demand for units (2008-2015) for Plinth Area Between 500-1000 Sq ft 2.07 Demand for units (2008-2015) for Plinth Area More than 1000 Sq ft 2.15 Whereas most of the attention of the building industry is on the upper segment, it is middle and lower middle India which is driving demand - • The demand for housing of size less than 1000 sq ft is 6.2 million units over 7 years, which is 2/3rd of the demand • The anticipated growth in percentage terms in the lower segments (23% combined) is lower than the upper segment (30%), but on a base which is nearly two and a half times. • The pattern is similar for the alpha (top 10) and beta (the next 20) cities, implying a uniform demand for affordable housing. The above pattern indicates that a renewed focus on affordable housing is in order. There is plenty of demand out there; supply is more likely to be the constraint.
- 12. Demography – Age profile of the top 112 cities of India The age profile of the top 112 cities (which account for a population of 200 million) does not show too much variation. 69% are between the age of 18 and 60 and the proportions do not vary much across different cities. The proportion of the aged in the larger cities is higher but only marginally. In sheer numbers, about 36 million people in the top 112 cities are above 60 years of age and the alpha cities account for 35% of them. The under 18 population is significantly smaller at about 26 million under 18 years 18-35 years 35-60 years > 60 years Alpha (top 10) 12.4% 34.3% 34.7% 18.6% Beta (11th to 30th) 13.0% 34.7% 34.2% 18.1% Gamma (31st to 50th) 14.1% 35.9% 32.7% 17.3% Delta (51st to 112th) 14.3% 36.7% 31.6% 17.3% Total (112 cities) 13.3% 35.3% 33.5% 17.9% under 18 years 18-35 years 35-60 years > 60 years Alpha (top 10) 8,306,888 23,052,698 23,318,890 12,456,128 Beta (11th to 30th) 6,714,661 17,926,723 17,642,448 9,352,400 Gamma (31st to 50th) 4,390,776 11,161,258 10,161,636 5,388,436 Delta (51st to 112th) 7,211,062 18,473,936 15,894,690 8,708,917 Total (112 cities) 26,623,387 70,614,615 67,017,664 35,905,881 8,306,888 6,714,661 4,390,776 7,211,062 23,052,698 17,926,723 11,161,258 18,473,936 23,318,890 17,642,448 10,161,636 15,894,690 12,456,128 9,352,400 5,388,436 8,708,917 Alpha (top 10) Beta (11th to 30th) Gamma (31st to 50th) Delta (51st to 112th) under 18 years 18-35 years 35-60 years > 60 years
- 13. 12.4% 13.0% 14.1% 14.3% 34.3% 34.7% 35.9% 36.7% 34.7% 34.2% 32.7% 31.6% 18.6% 18.1% 17.3% 17.3% Alpha (top 10) Beta (11th to 30th) Gamma (31st to 50th) Delta (51st to 112th) under 18 years 18-35 years 35-60 years > 60 years
- 14. Income and Savings in Urban India The top 112 cities account for about 200 million Indians which is more than 60% of urban India. These cities constitute a market of consumers whose combined annual incomes are Rs 13.26 billion. Their combined savings are Rs 3.5 billion which is about 26.5% of income. However there is considerable heterogeneity in the income and savings pattern across these cities. If we look at four classes of cities (by size), we get the following picture: Total Income (Rs billions) Total Savings (Rs billions) Savings/ Income Ratio Alpha (Top 10) 5,912 1,296 21.9% Beta (11th to 30th) 2,887 931 32.2% Gamma (31st to 50th) 1,774 519 29.3% Delta (The balance 62) 2,688 771 28.7% Top 112 cities 13,261 3,516 26.5% The large cities have a significantly lower savings rate. The top 10 cities have a savings rate of under 22%, whereas the gamma and delta cities (82 in number) have savings rate around 29%. Clearly the EMI culture hasn’t percolated down to too many cities in India. An interesting piece of statistics is that the 2nd rung of cities are the biggest savers – the beta cities save as much as 32% of their income and reinforce the old adage that savings and investment are the route to growth. If we look at the same set of data through the regional prism, we get the following picture: Total Income (Rs billions) Total Savings (Rs billions) Savings/ Income Ratio East 2,011 522 25.9% West 5,167 1,191 23.0% North 2,849 797 28.0% South 3,233 1,007 31.1% The Southerners are by far the largest savers with a savings rate of over 31%. The West (it includes Rajasthan and MP) has the lowest savings rate of just 23%. Within West, Gujarat is a high saver with 27% savings rate whereas Maharashtra saves only 18%. Madhya Pradesh is a very high saver with savings rate of 38%. Contrary to popular wisdom, the North is not exactly spendthrift, they are second only to the South in savings rate. What do the figures look like for some of the major cities? Total Income (Rs billions) Total Savings (Rs billions) Savings/ Income Ratio Mumbai 1,608 216 13.4% Delhi 1,264 289 22.8% Bangalore 602 192 31.9% Urban Areas in Thane 569 132 23.2% Pune 446 111 24.9% Ahmadabad 429 109 25.3% Chennai 393 88 22.2% Kolkata 350 68 19.3% Surat 318 82 25.8% Hyderabad 295 87 29.3% Mumbai has the lowest savings rate. Delhi, Kolkata and Mumbai’s neighbours are also low savers. Bangalore and Hyderabad are high savers, much higher than average. The heterogeneity of India is well reflected in the savings patterns. There are no clear regional patterns. However, it is evident that the economically vibrant cities are lower in savings rate as compared to their regional brethrens which reinforces the theory that consumerism is one of the key pivots of the recent surge in economic growth and erosion in consumer confidence will impact economic growth negatively.
