Lecture 8.1- Ionic vs. Covalent
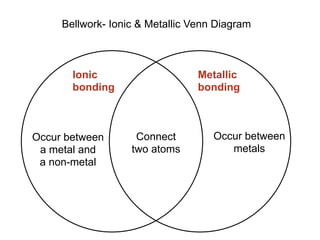
- 1. Bellwork- Ionic & Metallic Venn Diagram Ionic Metallic bonding bonding Occur between Connect Occur between a metal and two atoms metals a non-metal
- 2. Noble gases don’t bond! In nature, matter takes many forms. The noble gases, including helium and neon, are monatomic (means they exist as single atoms).
- 3. ionic vs. covalent Ionic compounds transfer electrons to form ions, which are held together by their opposite charges.
- 4. ionic vs. covalent Ionic compounds transfer electrons to form ions, which are held together by their opposite charges. IONIC = transfer of electrons COVALENT = sharing of electrons
- 5. Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals. Non-metals need to gain electrons in order to get eight =THE OCTET RULE Cl
- 6. Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals. Non-metals need to gain electrons in order to get eight =THE OCTET RULE Cl Cl
- 7. Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals. Non-metals need to gain electrons in order to get eight =THE OCTET RULE Cl Cl Both get eight by sharing!
- 8. Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals. Non-metals need to gain electrons in order to get eight =THE OCTET RULE Cl Cl Covalent bond Both get eight by sharing! Cl–Cl
- 9. A molecule is a neutral group of atoms joined together by covalent bonds. Air contains oxygen molecules. A diatomic molecule contains two atoms. An oxygen molecule is a diatomic molecule.
- 10. Using covalent bonds, atoms can be arranged in different ways to make an unlimited variety of molecules.
- 11. A compound composed of molecules is called a molecular compound. Water and carbon monoxide are molecular compounds. Covalent bonding makes molecules
- 12. Molecular compounds tend to have relatively lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds. They can be gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature.
- 14. A molecular formula is the chemical formula of a molecular compound. A molecular formula shows how many atoms of each element a molecule contains.
- 15. Ethane, a component of natural gas, is a molecular compound. C2H6 Each ethane molecule contains two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms
- 16. Molecular Formulas H 2O Type of # of Type of If blank- atom is atoms is atom is there is hydrogen two oxygen only one
- 17. Formulas of Some Molecular Compounds
- 19. BOND = a force that holds groups of atoms together TO BOND = when two atoms become held together
- 20. A bond can be an ionic bond or covalent bond… …or somewhere in between.
- 21. Let’s focus on the two extreme cases of a completely ionic bond and a completely covalent bond. Then we will learn about the bonds that are somewhere in between these two.
- 22. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND Between a metal and Between 2 non-metals a non-metal
- 23. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND Between a metal and Between 2 non-metals a non-metal A transfer of electrons A sharing of electrons
- 24. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND Between a metal and Between 2 non-metals a non-metal A transfer of electrons A sharing of electrons Conducts electricity Does not conduct when melted or electricity dissolved
- 25. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND Between a metal and Between 2 non-metals a non-metal A transfer of electrons A sharing of electrons Conducts electricity Does not conduct when melted or electricity dissolved Crystal solids Solid, liquid or gas (made of ions) (made of molecules)
- 26. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND
- 27. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND Compounds have Compounds have high boiling and low boiling and melting points melting points
- 28. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND Compounds have Compounds have high boiling and low boiling and melting points melting points Many dissolve in 100% covalent water. They do not molecules will dissolve dissolve in oils. in oil, but not in water.
- 29. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND
- 30. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND Compounds are Compounds are crystal lattices of distinct and separate positive and units called negative ions molecules.
- 31. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND Compounds are Compounds are crystal lattices of distinct and separate positive and units called negative ions molecules. Chemical formula is Chemical formula can the formula unit (the be called a molecular formula that repeats) formula
- 32. IONIC BOND COVALENT BOND Compounds are Compounds are crystal lattices of distinct and separate positive and units called negative ions molecules. Chemical formula is Chemical formula can the formula unit (the be called a molecular formula that repeats) formula Inorganic Organic (biological) compounds are molecules are covalent often ionic.
- 33. 8.1 Section Quiz. 1. Compared to ionic compounds, molecular compounds tend to have relatively a. low melting points and high boiling points. b. low melting points and low boiling points. c. high melting points and high boiling points. d. high melting points and low boiling points. Slide of 18 © Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
- 34. 8.1 Section Quiz. 1. Compared to ionic compounds, molecular compounds tend to have relatively a. low melting points and high boiling points. b. low melting points and low boiling points. c. high melting points and high boiling points. d. high melting points and low boiling points. Slide of 18 © Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
- 35. 8.1 Section Quiz 2. A molecular compound usually consists of a. two metal atoms and a nonmetal atom. b. two nonmetal atoms and a metal atom. c. two or more metal atoms. d. two or more nonmetal atoms. Slide of 18 © Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
- 36. 8.1 Section Quiz 2. A molecular compound usually consists of a. two metal atoms and a nonmetal atom. b. two nonmetal atoms and a metal atom. c. two or more metal atoms. d. two or more nonmetal atoms. Slide of 18 © Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
- 37. 8.1 Section Quiz 3. A molecular formula shows a. how many atoms of each element a molecule contains. b. a molecule's structure. c. which atoms are bonded together. d. how atoms are arranged in space. Slide of 18 © Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
- 38. 8.1 Section Quiz 3. A molecular formula shows a. how many atoms of each element a molecule contains. b. a molecule's structure. c. which atoms are bonded together. d. how atoms are arranged in space. Slide of 18 © Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall