Address resolution protocol and internet control message protocol
- 1. Address Resolution Protocol - ARP IP over Ethernet 1
- 2. Address Resolution Finding hardware address for protocol address is called Address Resolution Data link layer resolves protocol address to hardware address Resolution is local to a network Network component only resolves address for other components on same network 2
- 3. Address Resolution (continued) A resolves protocol address for B for protocol messages from an application on A sent to an application on B A does not resolve a protocol address for F Through the internet layer, A delivers to F by routing through R1 and R2 A resolves R1 hardware address Network layer on A passes packet containing destination protocol address F for delivery to R1 Host A Host C Host E Network 1 Router 1 Network 2 Router 2 Network 3 Host B Host D Host F 3
- 4. Address Resolution Techniques Association between a protocol address and a hardware address is called a binding. Three techniques: Table lookup - Bindings stored in memory with protocol address as key - data link layer looks up protocol address to find hardware address Closed-form computation - Protocol address based on hardware address - Data link layer derives hardware address from protocol address Dynamic - Network messages used for "just-in- time" resolution - Data link layer sends message requesting hardware address; destination responds 4
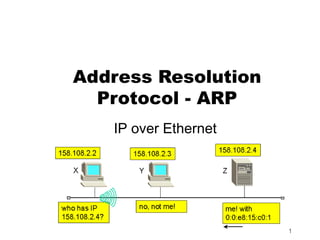
- 5. Address Resolution Protocol - ARP IP uses dynamic distributed resolution technique Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) - part of TCP/IP protocol suite RFC 826 - Address Resolution Protocol Two-part protocol: Request from source asking for hardware address Reply from destination carrying hardware address 5
- 6. ARP Message Exchange ARP request message dropped into a hardware frame and broadcast Sender inserts IP address into message and broadcast Every other computer examines request 6
- 7. ARP Message Exchange (cont’d) Computer whose IP address is in the request responds Puts its own hardware address in the response Unicasts the response to the sender Original requester can then extract hardware address and send IP packet to destination using recently acquired hardware address 7
- 8. ARP Message Format 8
- 9. ARP Message Contents HARDWARE ADDRESS TYPE = 1 for Ethernet PROTOCOL ADDRESS TYPE = 0x0800 for IP OPERATION = 1 for request, 2 for response Contains both target and sender mappings from protocol address to hardware address Request sets hardware address of target to 0 Target can extract hardware address of 9
- 10. Processing the ARP Messages Receiver extracts sender's hardware address and updates local ARP table Receiver checks operation - request or response Response: Adds sender's address to local cache Sends pending IP packet(s) Request: If receiver is target, forms response Unicasts to sender Adds sender's address to local cache Note: Target likely to respond "soon" Computers have finite storage for ARP cache Only target adds sender to cache; others only update if target already in cache 10
- 11. 11
- 12. ARP, Bridging and Routing ARP is transparent to bridging, since bridging will propagate ARP broadcasts like any other Ethernet broadcast, and will transparently bridge the replies. A router does not propagate Ethernet broadcasts, because the router is a Network Level device, and Ethernet is a Data Link Level protocol. Therefore, an Internet host must use its routing protocols to select an appropriate router, that can be reached via Ethernet ARPs. After ARPing for the IP address of the router, the packet (targeted at some other Destination Address) is transmitted to the Ethernet address of the12router.
- 13. Proxy ARP Proxy ARP is a technique that is can be used by routers to handle traffic between hosts that don't expect to use a router as described above. Probably the most common case of its use would be the gradual subnetting of a larger network. Those hosts not yet converted to the new system would expect to transmit directly to hosts now placed behind a router. A router using Proxy ARP recognizes ARP requests for hosts on the "other side" of the router that can't reply for themselves. The router answers for those addresses with an ARP reply matching the remote IP address with the router's Ethernet address (in essence, a lie). 13
- 14. Proxy ARP Use Host A Host B "Old" IP Routing Router IP Subnet Routing and Modified ARP 14
- 15. Proxy ARP - Problems Proxy ARP is best thought of as a temporary transition mechanism, and its use should not be encouraged as part of a stable solution. There are a number of potential problems with its use, including the inability of hosts to fall back on alternate routers if a network component fails, and the possibility of race conditions and bizarre traffic patterns if the bridged and routed network segments are not clearly delineated. 15
- 16. Proxy ARP Use When host A wants to send an IP datagram to host B, it first has to determine the physical network address of host B through the use of the ARP protocol. As host A cannot differentiate between the physical networks, his IP routing algorithm thinks that host B is on the local physical network and sends out a broadcast ARP request. Host B doesn't receive this broadcast, but router R does. Router R understands subnets, that is, it runs the ``subnet'' version of the IP routing algorithm and it will be able to see that the destination of the ARP request (from the target protocol address field) is on another physical network. If router R's routing tables specify that the next hop to that other network is through a different physical device, it will reply to the ARP as if it were host B, saying that the network address of host B is that of the router R itself. 16
- 17. Proxy ARP Use Host A receives this ARP reply, puts it in his cache and will send future IP packets for host B to the router R. The router will forward such packets to the correct subnet. The result is transparent subnetting. Normal hosts (such as A and B) don't know about subnetting, so they use the “old” IP routing algorithm. The routers between subnets have to: Use the “subnet” IP algorithm. Use a modified ARP module, which can reply on behalf of other hosts. 17
- 18. Reverse ARP - RARP Sometimes, it is also necessary to find out the IP-address associated with a given Ethernet address. This happens when a diskless machine wants to boot from a server on the network, which is quite a common situation on local area networks. A diskless client, however, has virtually no information about itself-- except for its Ethernet address! So what it basically does is broadcast a message containing a plea for boot servers to tell it its IP-address. There's another protocol for this, named Reverse Address Resolution Protocol, or RARP. Along with the BOOTP protocol, it serves to define a procedure for bootstrapping diskless clients over the network. 18
- 19. Internet Control Message Protocol ICMP The Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a control protocol that is considered to be an integral part of IP, although it is architecturally layered upon IP - it uses IP to carry its data end-to-end. ICMP provides error reporting, congestion reporting, and first-hop router redirection. 19
- 20. IP and ICMP 20
- 21. ICMP Features ICMP uses IP as if ICMP were a higher- level protocol (that is, ICMP messages are encapsulated in IP datagrams). However, ICMP is an integral part of IP and must be implemented by every IP module. ICMP is used to report some errors, not to make IP reliable. Datagrams may still be undelivered without any report on their loss. Reliability must be implemented by the higher-level protocols that use IP. 21
- 22. ICMP Features ICMP can report errors on any IP datagram with the exception of ICMP messages, to avoid infinite repetitions. For fragmented IP datagrams, ICMP messages are only sent about errors on fragment zero. That is, ICMP messages never refer to an IP datagram with a non- zero fragment offset field. 22
- 23. ICMP Features ICMP has rules regarding error message generation to prevent broadcast storms ICMP messages are never sent in response to datagrams with a destination IP address that is a broadcast or a multicast address. ICMP messages are never sent in response to a datagram which does not have a source IP address which represents a unique host. That is, the source address cannot be zero, a loopback address, a broadcast address or a multicast address. 23
- 24. Error Message Generation Rules ICMP errors messages are not generated in response to an ICMP error message datagrams destined to an IP broadcast address datagrams sent as a link-layer broadcast a fragment other than the first a datagram whose source address does not define a single host 24
- 25. ICMP Message Format ICMP messages are described in RFC 792 and RFC 950, belong to STD 5 and are mandatory. ICMP messages are sent in IP datagrams. The IP header will always have a Protocol number of 1, indicating ICMP and a type of service of zero (routine). The IP data field will contain the actual ICMP message in the format shown in the figure below: 25
- 26. ICMP Message Transport ICMP encapsulated in IP But ... how can that work? ICMP messages sent in response to incoming datagrams with problems ICMP message not sent for ICMP message 26
- 27. Error Detection Internet layer can detect a variety of errors: Checksum (header only!) TTL expires No route to destination network Can't deliver to destination host (e.g., no ARP reply) Internet layer discards datagrams with problems Some - e.g., checksum error - can't trigger error messages 27
- 28. Types of Messages ICMP defines two types of messages: error and informational messages Error messages: Source quench Time exceeded Destination unreachable Redirect Fragmentation required Informational messages: Echo request/reply Address mask request/reply Router discovery 28
- 29. ICMP: Message Types Type Message 0 Echo reply 3 Destination unreachable 4 Source quench 5 Redirect 8 Echo request 11 Time exceeded 12 Parameter unintelligible 13 Time-stamp request 14 Time-stamp reply 15 Information request 16 Information reply 17 Address mask request 18 Address mask reply 29
- 30. ICMP Message Types Type Code Description Query Error Type Code Description Query Error 0 0 Echo reply • 5 Redirect 3 Destination unreachable: 0 Redirect for network • 0 Network unreachable • 1 Redirect for host • 1 Host unreachable • 2 Redirect for TOS and Net • 2 Protocol unreachable 3 Redirect for TOS and Host • • 3 Port unreachable • 8 0 Echo request • 4 Fragmentation needed • 9 0 Router advertisement • 5 Source route failed • 10 0 Router solicitation • 6 Destination network unknown 11 Time exceeded • 7 Destination host unknown 0 TTL equals 0 during transit • • 8 Source host isolated 1 TTL equals 0 during reassembly • 9 Destination net prohibited • 12 Parameter problem 10 Destination host prohibited • 0 IP header bad • 11 Network unreachable for TOS • 1 Required option missing • 12 Host unreachable for TOS • 13 0 Timestamp request • 13 Communication prohibited • 14 0 Timestamp reply • 14 Host precedence violation • 15 0 Information request • 15 Precedence cutoff in effect • 16 0 Information reply • 4 0 Source quench • 17 0 Address mask request • 18 0 Address mask reply • 30
- 31. ICMP and Reachability An internet host, A, is reachable from another host, B, if datagrams can be delivered from A to B ping program tests reachability - sends datagram from B to A that A echoes back to B Uses ICMP echo request and echo reply messages Internet layer includes code to reply to incoming ICMP echo request messages 31
- 32. Destination Unreachable Codes Code Meaning 0 Network unreachable 1 Host unreachable 2 Protocol unreachable 3 Port unreachable 4 Fragmentation need and don’t fragment bit set 5 Source route failed 6 Destination network unknown 7 Destination host unknown 8 Source host isolated 9 Communication with dest net administratively prohibited 10 Communication with dest host administratively prohibited 11 Network unreachable for type of service 12 Host unreachable for type of service 32
- 33. ICMP and Path MTU Discovery Fragmentation should be avoided How can source configure outgoing datagrams to avoid fragmentation? Source determines path MTU - smallest network MTU on path from source to destination Source probes path using IP datagrams with don't fragment flag Router responds with ICMP fragmentation required message Source sends smaller probes until destination reached 33
- 34. Information Request/Reply: This request is intended for a diskless system to obtain its subnet mask Set source and destination addresses to 0 in the request and broadcast Server replies back with your IP address (Not used. Replaced by RARP and BOOTP) Address Mask Request/Reply: What is the subnet mask on this net? Replied by “Address mask agent” type (17 or 18) code (0) 16-bit checksum identifier (can be set to anything) sequence (can be set to anything) 32-bit subnet mask 34
- 35. ICMP Summary Internet layer provides best-effort delivery service May choose to report errors for some problems ICMP provides error message service ICMP is the control sibling of IP ICMP is used by IP and uses IP as network layer protocol - Encapsulated in IP datagram - Not reliable Feedback about problems e.g. time to live expired ICMP is used for ping, traceroute, and path MTU discovery Transfer of (control) messages from routers and hosts to hosts 35