Plant tissues & organs
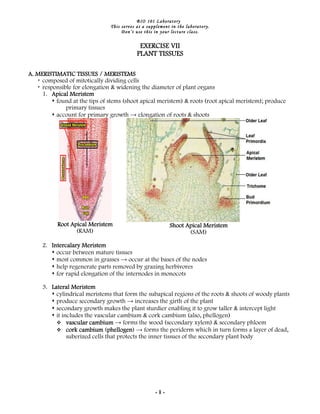
- 1. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. EXERCISE VII PLANT TISSUES A. MERISTIMATIC TISSUES / MERISTEMS composed of mitotically dividing cells responsible for elongation & widening the diameter of plant organs 1. Apical Meristem found at the tips of stems (shoot apical meristem) & roots (root apical meristem); produce primary tissues account for primary growth → elongation of roots & shoots Root Apical Meristem Shoot Apical Meristem (RAM) (SAM) 2. Intercalary Meristem occur between mature tissues most common in grasses → occur at the bases of the nodes help regenerate parts removed by grazing herbivores for rapid elongation of the internodes in monocots 3. Lateral Meristem cylindrical meristems that form the subapical regions of the roots & shoots of woody plants produce secondary growth → increases the girth of the plant secondary growth makes the plant sturdier enabling it to grow taller & intercept light it includes the vascular cambium & cork cambium (also, phellogen) vascular cambium → forms the wood (secondary xylem) & secondary phloem cork cambium (phellogen → forms the periderm which in turn forms a layer of dead, phellogen) phellogen suberized cells that protects the inner tissues of the secondary plant body -1-
- 2. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. Intercalary Meristem Lateral Meristem (found only in monocots) (Vascular cambium & Cork Cambium) B. PROTECTIVE TISSUES / DERMAL TISSUES comprise the outermost layer of the plants 1. Epidermis dermal tissue that covers the primary body of the plant, protecting the underlying tissues regulates the movement of gases between the plant and the atmosphere sheet of cutinized cells covering the plants to protect it against rapid water loss & mechanical injury modified epidermal cells: Guard Cells kidney-shaped in dicots dumbbell-shaped in monocots Trichomes single-celled or multicellular outgrowths of epidermal cells found in leaves, stems, flowers, & fruits e.g.: cotton fibers → from the epidermis of cotton seeds 2. Cork the outermost part of the periderm secondary tissue produced by the cork cambium Epidermis with Guard Cells & Trichomes Cork Stomata Stomata -2-
- 3. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. C. FUNDAMENTAL/ GROUND TISSUES more variable in function & type it constitute the mesophyll in leaves & the cortex & pith in stems & roots 1. Parenchyma isodiametric or polyhedral cells with prominent protoplast & thin walls common examples are: Chlorenchyma – contains chloroplasts Aerenchyma – cells with prominent intercellular spaces 2. Collenchyma consists of cells with unevenly thickened cell walls functions for support 3. Sclerenchyma consists of cells which are devoid of protoplast upon maturity but has thick lignified walls two types of cells: Sclerids – short & polygonal e.g.: stone cells in pears gives it a gritty texture (rough) Fibers – long and with tapering ends e.g.: hemp fibers for making ropes Parenchyma Collenchyma Sclerenchyma Distinguishing made up of made up of collenchyma made up of fibers (long Features parenchyma cells → cells → elongated in slender cells typically usually many sided shape occurring in strands) & sclerids (variable shape, shorter than fibers) Cell Wall primary or secondary; unevenly thickened primary & thick secondary; may be lignified, primary cell wall only; usually lignified suberized, or cutinized not lignified alive at maturity alive at maturity maybe alive or dead at maturity Location on Throughout the plant beneath the epidermis in Fibers: usually associated the Plant Body body young elongating stems with xylem & phloem; in often seen as a cylinder leaves in monocots; of tissue or only in sometimes in cortex of patches in ribs along stems veins in some leaves Sclerids: throughout the plant Function for metabolic processes support in primary plant Fibers → for support such as respiration & body Sclerids → for protection & photosynthesis; storage mechanical support & conduction; wound healing & regeneration -3-
- 4. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. Parenchyma Cells Chollenchyma Cells Sclerenchyma Cells Sclerenchyma (Fiber Cells) Sclerenchyma (Stone Cells) D. Vascular / Conducting Tissues Vascular tissues are complex → i.e. composed of four types of cells 1. Xylem for transport of water & dissolved minerals absorbed by the roots from the soil composed of fibers, parenchyma cells, vessels (large), & tracheids (small, devoid of protoplast) Vessels & Tracheids main water-conducting elements exhibit secondary wall thickenings which can be annular, spiral, scalariform, reticulate, or pitted Xylem showing vessel elements & tracheids -4-
- 5. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. in longitudinal (left) and transverse (right) sections. 2. Phloem for transport of food materials from the leaves to all plant parts in woody stems, phloem tissues constitute the greater bulk of the bark consists of fibers, parenchyma cells, & sieve tube cells (devoid of protoplast) Sieve Tube Cells main food-conducting elements thick-walled & provided at both ends with perforated sieve plates companion cells → associated with sieve tube cells Phloem showing sieve tube members & companion cells in longitudinal (left) & transverse (right) sections. -5-
- 6. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. PLANT ORGANS Vegetative Plant Organs: 1. Roots 2. Stems 3. Leaves Reproductive Plant Organs: 1. Flowers 2. Fruits 3. Seeds A. ROOTS Root System -6-
- 7. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. Monocot Root Young Eudicot Root 1. Epidermis – uncutinized cells with root hairs (to facilitate absorption) 2. Cortex – multi-layered parenchyma cells: Endodermis = inner most layer (endodermal cells) Casparian strip = suberized Passage cells = for water transport 3. Stele – innermost cylinder Pericycle – made up of parenchyma cells; gives rise to the vascular cambium & secondary/lateral roots Xylem – 3-4 radial rows of thick walled cells alternating with thin phloem cells Vascular cambium – meristimatic zone between phloem & xylem Phloem – thin-walled; food conducting cells alternating with xylem rays Pith – if present, composed of parenchyma cells -7-
- 8. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. B. Stems Morphology Monocot stem (cross section) -8-
- 9. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. C. Leaf Morphology Venation Monocot Eudicot (Parallel) (Netted/Reticulated) Monocot Eudicot Simple Leaf Pinnately Compound Leaf Palmately Compound Leaf -9-
- 10. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. Leaf Arrangement Whorled Alternate Opposite Monocot: Eudicot: - 10 -
- 11. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. D. Flower Morphology Complete Flower – has all 4 parts (sepals, petals, pistil, stamen) Incomplete – lacks one or more of the 4 parts Perfect Flower (bisexual) – has both stamens & carpels/ovary Imperfect Flower (unisexual)– has stamen or carpel but not both Imperfect flower = Incomplete Flower Monoecious – male & female reproductive parts in separate flowers (e.g.: corn) Dioecious – male & female reproductive parts in separate plants (e.g.: papaya) Inflorescence - 11 -
- 12. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. E. Fruit matured / ripened ovary holds & protects seeds Simple Fruit – developed from a single ovary Aggregate – several ovaries of a flower (sugar apple) Multiple – several ovaries of several flowers (pineapple) TERMS: Pericarp - the fruit wall (derived from the ovary of the pistil) which is composed of the exocarp, mesocarp and endocarp (the three layers are not always recognizable, ex. dry fruit) Endocarp - the innermost layer of the pericarp (often hard, stony or papery) Mesocarp - the middle layer of the pericarp (often fleshy) Exocarp - the outermost layer of the pericarp (often like a skin or peel). (peach) - 12 -
- 13. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. Types of Fruits Fleshy - 13 -
- 14. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. Dry Fruits Dry Dehiscent Dry Indehiscent - 14 -
- 15. BIO 101 Laboratory This serves as a supplement in the laboratory. Don’t use this in your lecture class. F. Seed Albuminous (Endospermic) Seed : (Non- Exalbuminous (Non-endospermic) Seed - 15 -
