Membranes and osmosis
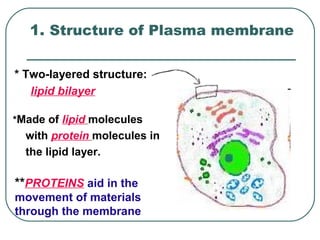
- 1. 1. Structure of Plasma membrane * Two-layered structure: lipid bilayer *Made of lipid molecules with protein molecules in the lipid layer. **PROTEINS aid in the movement of materials through the membrane
- 2. extracellular fluid (watery environment) phospholipid hydrophilic heads hydrophobic tails bilayer hydrophilic heads cytoplasm (watery environment)
- 3. Polar Head Non-Polar Tails tails (hydrophobic) head (hydrophilic)
- 4. * Bilayer can be considered a liquid FLUID MOSAIC MODEL: plasma membrane : made up of molecules that are free to flow among one another. Kinds and arrangements of proteins + lipids vary from one membrane to another and give each type of membrane specific permeability properties.
- 5. Polar heads Fluid Mosaic Model love water & of the cell dissolve. membrane Non-polar Membrane movement tails hide animation from water. Carbohydrate cell markers Proteins
- 6. Structure of the Cell Membrane Outside of cell Carbohydrate Proteins chains Lipid Bilayer Transport Protein Phospholipids Animations of membrane Inside of cell structure (cytoplasm) Go to Section:
- 7. 1. Maintaining a BALANCE in a CELL Cells Maintain HOMEOSTASIS : internal balance Selective permeability : allows some materials to pass through membrane while rejecting others.
- 8. Diffusion Movement of molecules high concentration to lower concentration Example: skunk, perfume, night after a dinner at Taco Bell!
- 9. 2 Dye molecules diffuse into the 3 Both dye molecules 1 A drop of dye is water; water and water molecules placed in water. molecules diffuse are evenly dispersed. into the dye. drop of dye pure water Diffusion animation
- 10. Osmosis The diffusion of Water from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration Animation: How Osmosis Works
- 11. Transport across membranes Passive transport of water by Osmosis • a. Isotonic • b. Hypertonic • c. Hypotonic
- 12. Isotonic Solution: Solution concentration of water (solvent) outside of the cell is the same as concentration inside the cell (Animal cell normal / plant flaccid)
- 13. Hypotonic Solution: concentration of water (solvent) outside the cell is higher than concentration inside the cell. Water rushes into the cell! Turgor pressure: Pressure that builds in a plant cell as a result of osmosis. Makes a plant cell firm. (Turgid) Plant cells are healthiest in a hypotonic environment. Lysed: pressure builds in animal cell (burst)
- 14. Hypertonic Solution: concentration of water (solvent) outside cell is lower than concentration inside the cell. Water rushes out of the cell! Plasmolysis: loss of water from within a plant cell, causing cytoplasm to shrink, pulling inner plasma membrane away from cell wall. (wilting of plants) Crenation: (crenates: shrinks) animal cell loses water and it shrinks (collapses)
- 16. What type of solution are these cells in? A B C Hypertonic Isotonic Hypotonic
- 17. 10 micrometers (a) isotonic solution (b) hypertonic solution (c) hypotonic solution equal movement of water net water movement net water movement into and out of cells out of cells into cells
- 18. 5. PASSIVE TRANSPORT: No energy required for this to happen Passive transport : movement of substances across plasma membranes without additional energy Facilitated diffusion: diffusion of materials across a plasma membrane by transport (channel) proteins.
- 19. 6. ACTIVE TRANSPORT: Requires energy in the form of ATP Active Transport : gradient from low to high. Energy is required. Proteins throughout the membrane are “carriers” used for this purpose.
- 20. Sodium-potassium pump Na out K in ACTIVE TRANSPORT = ATP Na+ ions: moved out of cell K+ ions: moved by the same carrier into the cell (This process is important in nerve and muscle function.)
- 21. 7. TRANSPORT of LARGE PARTICLES • Endocytosis (Endo = In): cell surrounds and takes in material from environment. Material does not pass through the membrane; instead, it is engulfed and closed by a portion of membrane and cytoplasm. Pinocytosis: water Phagocytosis: food/ minerals/ large particles • Exocytosis (Exo = Out): transport of materials out of cell across cell membrane.
- 22. Exocytosis
- 23. (a) Animated Review of Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis and Receptor Mediated pinocytosis (extracellular fluid) Endocytosis. Click on Active Transport, watch the brief overview of Active Transport and 1 then click on Endocytosis in the bar below the animation 3 2 vesicle containing extracellular (cytoplasm) fluid cell (b) phagocytosis food particle pseudopod 1 2 3 particle enclosed in vesicle
Notas do Editor
- Figure: 03-00UN02 Title: Phospholipid bilayer. Caption: Phospholipid bilayer.
- Figure: 03-00UN01 Title: A phospholipid. Caption: A phospholipid has a polar hydrophic head and a pair of nonpolar hydrophobic tails.
- Figure: 03-02 Title: Diffusion of a dye in water. Caption: Diffusion of a dye in water.
- Figure: 03-05 Title: The effects of osmosis. Caption: Red blood cells are normally suspended in the fluid environment of the blood. (a) If red blood cells are immersed in an isotonic salt solution, which has the same concentration of dissolved substances as the blood cells do, there is no net movement of water across the plasma membrane. The red blood cells keep their characteristic dimpled disk shape. (b) A hypertonic solution, with too much salt, causes water to leave the cells, shriveling them up. (c) A hypotonic solution, with less salt than is in the cells, causes water to enter, and the cells swell.
- Figure: 03-07 Title: Two types of endocytosis. Caption: (a) To capture drops of liquid, a dimple in the plasma membrane deepens and eventually pinches off as a fluid-filled vesicle, which contains a random sampling of the extracellular fluid. (b) Pseudopodia encircle an extracellular particle. The ends of the pseudopodia fuse, forming a large vesicle that contains the engulfed particle.
