COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING: track costs and revenues
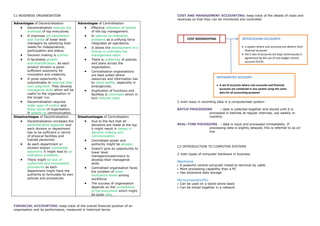
- 1. C1-BUSINESS ORGANISATION COST AND MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING: keep track of the details of costs and revenues so that they can be monitored and controlled Advantages of Decentralisation Advantages of Centralisation Decentralisation reduces the Effective utilisation of talents workload of top executives. of the top management. It improves job satisfaction It reduces co-ordination and morale of lower level problems as a unifying force COST BOOKKEEPING INTERLOCKING ACCOUNTS: managers by satisfying their integrates all operations. needs for independence, It allows the development of a a system where cost accounts are distinct from participation and status. strong co-ordinates top financial accounts Decision making is quicker. management team. the 2 sets of accounts are kept continuously in agreement by the use of cost ledger control It facilitates growth There is uniformity of policies account (CLCA) and diversification. As each and plans across the product division is given organisation. sufficient autonomy for Centralisation organisations innovation and creativity. are best suited where It gives opportunity to resources and information has INTERGRATED ACCOUNT: subordinates to exercise their to move swiftly, especially in own judgment. They develop emergencies. A set of accounts where cost accounts and financial managerial skills which will be accounts are combined in one system using the same Duplication of functions and useful to the organisation in data for all accounting purposes facilities is minimised which in the longer run. turn reduces costs. Decentralisation requires 2 main ways in recording data in a computerised system: wider span of control and fewer levels of organisation. BATCH PROCESSING : data is collected together and stored until it is It speeds up communication. processed in batches at regular intervals, say weekly or Disadvantages of Decentralisation Disadvantages of Centralisation monthly Decentralisation increases the Due to the fact that all administrative expenses and decisions are made at the top REAL-TIME POCESSING : data is input and processed immediately. If each division or department it might result in delays in processing data is slightly delayed, this is referred to as on- has to be sufficient in terms decision-making and line of physical facilities and communication. trained personnel. Centralised power and As each department or authority might be abused. division enjoys substantial C2-INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SYSTEMS Doesn‟t give an opportunity to autonomy it might lead to co- lower level ordination problems. 2 main types of computer hardware in business managers/supervisors to There might be lack of develop their managerial Mainframe uniformity and inconsistent skills. A powerful central computer linked to terminal by cable procedures as each Centralised organisation faces More processing capability than a PC department might have the the problem of lower Has extensive data storage authority to formulate its own motivation levels among policies and procedures. workforce. Microcomputers/PCs The success of organisation Can be used on a stand-alone basis depends on the competence Can be linked together in a network of top executives which might be quite risky. FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING: keep track of the overall financial position of an organisation and its performance, measured in historical terms
- 2. Different types of computer software: STORING INFORMATION SECURELY Operating system Interface between hardware, other software and user Backing up : copying essential files onto another computer or storage medium Typical function: handles initial set-up of computer, calling up files from storage, Archiving : the process of moving data away from the primary storage area file management and communication between user and hardware onto another storage medium for long-term storage E.g.: Microsoft Windows, Novell Netware, the Mac OS system. Unix and Linux Document retention Utilities software Perform basic tasks concerned with general operation of computer system such as performing back-up PREVENTION OF COMPUTER FRAUD Off-the-shelf application packages Confidentiality and hacking Software released to the market and can be used immediately in the form of sold How to prevent? without any further programming needed Physical security E.g.: Microsoft Word and Excel, Sage products, database Passwords Database: organise operational data to allow different users to access the same Data encryption files for their data processing requirements System logs Audit trails Advantage: Segregation of duties - Thoroughly tested Random checks - Cheaper than writing programs from scratch Firewall - Legislative changes may be incorporated automatically - Can benefit from the experiences of other user of same application Viruses: a program that can attach itself to other programs and modify or destroy them Bespoke applications How to prevent? Designed to meet the needs of business Install anti-virus software Expensive than off-the-shelf Cannot be implemented until designed and tested LEGISLATION RELATED Computer Misuse Act 1990 Programming tools Specialist program designed to help programmers produce computer programs DATA PROTECTION LEGISLATION Data Protection Act 1998 Computer network: a group of computers, printers, and other devices that are Protect the privacy of individuals and applies to both manual and computer connected together with cables or wireless connections systems Does not apply to criminal records of individuals nor to the personal tax HEALTH AND SAFETY LEGISLATION information Health and Safety (Display Screen) Equipment Regulations 1992 C3-COMPUTER SYSTEM CONFIDENTIALITY AND SECURITY C4-INTRODUCTION TO MANAGEMENT INFORMATION COMPUTER SYSTEM ACCESS CONTROLS PURPOSE OF MANAGEMENT INFORMATION Physical access controls Decision making Security guards outside office hours, locks (card entry, keypad systems, intruder Long-term and short term decisions alarms), fingerprint recognition system Planning Expressed in financial terms in the organisation‟s budget User name and passwords Control Regular comparison of actual costs and income with those that were anticipated in the budget for the period enables managers to identify where control action may be required
- 3. FEATURES OF EEFFECTIVE MANAGEMENT INFORMATION C5-CLASSIFICATION OF COSTS AND COST BEHAVIOUR Relevant Reliable CLASSIFICATION OF COST : analysing costs into logical groups so that they can be Understandable summarised into meaningful information for management Complete use or for preparing external financial reports Accurate Timely Product cost : the cost of making, or buying an item of inventory. E.g.: Clear material and labour costs Consistent Cost effective Period cost : cost charged in the income statement for the period that is not directly related to the production of goods. Most are fixed costs. DIFFERENCE Direct cost : expenditure that can be directly identified with a specific FINANCIAL ACCOUNT MANAGEMENT ACCOUNT cost centre or cost unit Limited companies are required by law Records are not mandatory to prepare them Indirect cost/overhead : expenditure that cannot be directly identified with a Cost of record-keeping is a necessity Cost of record-keeping need to be specific cost centre or cost unit. It is jointly incurred and justified must be shared out on an equitable basis Objectives and uses are not defined by Objectives and uses can be laid down management by management FIXED COST Mainly an historical record Regularly concerned with future results as well as historical data Total FC is always constant Information must be compiled prudently Information should be compiled as FC/unit is decreasing and in accordance with legal and management requires, the key accounting requirements criterion being relevance Prepared for external reporting Prepared for internal use only RESPONSIBILITY CENTRE Cost centre : a production or service location, function, activity or item of equipment for which costs can be determined Profit centre : a production or service location, function or activity for which costs and revenues and therefore profits can be determined Investment centre : a production or service location, function or activity for which costs, revenues and net assets can be determined VARIABLE COST WHAT IS COST UNIT? Total VC is increasing or decreasing relating to level of activity or production per output A unit of product or service in relation to which costs are ascertained, i.e. it is the VC/unit is constant basic unit of output of the business Data : raw facts and statistics before they have been processed Information : data which has been processed into a useful form
- 4. STEPPED COST E.g.: supervisors‟ salaries SEMI-FIXED COST E.g.: telephone bills OTHER SEMI-VARIABLE COST C7-MATERIALS COST - Classified into direct and indirect materials STORES DEPARTMENT Responsible for: - Receipt of goods - Storage of materials - Issue of materials - Recording of receipts and issues
- 5. MATERIALS CONTROL CYCLE Bin card: Control of purchasing necessary to ensure: o maintained by stores department o Only necessary items are purchased o written up from goods received note, materials requisition note and goods o Orders are placed with the most appropriate supplier after considering price and returned note delivery details o shows quantity of goods held in stores o The goods that are actually received are the goods that were ordered and in the correct quantity Materials inventory account: records the quantity and value of receipts, issues and o The price paid for the goods is correct the current balance of each item of inventory. This would cover both direct and indirect material held in inventory. Summary of documents used: Purchase requisitions: Free inventory: inventory that is in stores or on order from a supplier which has not o Filled out by stores yet been requisitioned for a specific use o Authorised o Sent to purchasing department Free inventory = inventory in stores + inventory on order from supplier - inventory already requisitioned for use Purchase order: o Filled out by purchasing department o Supplier chosen by purchasing department C8-LABOUR COST o Price of goods calculated from price list o Authorised CALCULATING GROSS PAY o Sent to supplier Time related pay employees paid for the hours that they spend at work Delivery note: employees under this method are split into salaried employees and hourly rate o Provided by supplier with delivery employees o Received together with goods by stores department o Compared to actual goods e.g.: o Goods checked and counted An employee‟s basic week is 40 hours at a rate pay of $10 per hour. Overtime is o Delivery note and goods checked to purchase order paid at „time and a half‟. The employee works a 45-hour week. Calculate the gross pay of the employee. Distinguish between the overtime payment and overtime Goods received note: premium for the week. o Produced by stores department for their own use o Goods checked and counted o Written up and signed $ o Matched with delivery note and purchase order Basic pay (40 x $10) 400 o Sent to accounts to await purchase invoice Overtime hours (5 x ($10 x 1.5) 75 Gross pay 475 Purchase invoice: Or o Received from supplier Basic pay (45 x $10) 450 o Checked to purchase order, delivery note and goods received note Overtime premium (5 x ($10 x 0.5) 25 o Authorised for payment Gross pay 475 o Payment made Overtime premium is the additional amount over the basic rate of pay that is paid Materials requisition note: for the overtime hours rather than the total payment made for the overtime hours o Filled out by user department o Authorised Output related pay o Sent to stores fixed amount is paid per unit of output achieved irrespective of the time spent Materials returned note: e.g.: o filled out by returning department If the amount paid to an employee is $3/unit produced and that employee produces o actual goods checked against goods returned note by stores 80 units in a week, how much would his gross pay be? o signed as evidence of receipt 80 x $3= $240
- 6. Piece rate with guarantee give employee some security if employer does not provide enough work in a Bonus= (TA-TT) x rate paid particular period 2 if employee‟s earnings for the amount of units is lower than the guaranteed amount then the guaranteed amount is paid instead Rowan scheme proportion of the time saving paid to the employee could be based on the ratio e.g.: of time taken to time allowed Pam is paid $6 per unit she produces but she has a guaranteed wage of $50 per eight-hour day. In a particular week she produces as follows: Bonus= TT x TS x rate paid Monday 12 units TA Tuesday 14 units Wednesday 8 units TA time allowed Calculate Pam‟s wage. TT time taken A: $206 TS time saved Differential piecework Group bonus scheme piece rate increases as successive targets for a period are achieved and exceeded e.g.: Bonus percentage = 50% x excess units Payment by results rates for an organisation is as follows: Standard units Up to 99 units/week $1.25/unit Bonus rate = bonus percentage x rate paid 100 to 119 units/week $1.50/unit 120 or more units/week $1.75/unit PAYROLL If an employee produces 102 units in a week, how much will he be paid? $ A: $128.25 Employee‟s gross pay X Less: PAYE X CALCULATING BONUSSES Less: NIC X Net pay X For Salaried Employees Flat rate bonus/common rate bonus PRODUCTIVTIY same amount of bonus to all employees Amount of output produced per labour hour e.g.: Time related pay and productivity A small business made a profit of $100 000 in the previous quarter and the if employee is paid on a time basis then labour cost per unit will fall if productivity managing director decided to pay out $20 000 as a flat rate bonus to each increase employee. The business has 50 employees including the MD. The MD earns a salary of $48 000 per annum and Pam his secretary earns $18000 per annum. How much e.g.: is their bonus? Natalie is paid $6/hour for a 38-hour week. In week 1 output/hour was 15 units. A: $400 This increased to 17 units/hour in week 2. Show the impact on unit labour costs. Solution: Week 1- unit labour cost is $6/15= $0.40/unit Percentage bonus Week 2- unit labour cost is $6/17= $0.35/unit bonus is a set percentage of employee‟s annual salary The unit labour cost has fallen from $0.40 to $0.35. Managers may share some of e.g.: *using previous example. However the bonus is set at 1.6% of the business this gain with employees in the form of bonus. employees‟ salaries. A: MG $768 Output related pay and productivity Pam $288 if employee is paid on an output basis then increasing productivity will have no effect on unit labour cost as a fixed rate is paid for each output unit, provided For Time Rate Employees differential piecework system is not used. This is because the system will increase Bonus scheme unit labour cost. benefit individual workers according to their own result additional profit earned by the individual employee is split between employer and employee in some agreed manner
- 7. e.g.: C9-EXPENSES AND ABSORPTION OF OVERHEADS A differential piecework scheme specifies the following rates of pay per unit produced. OVERHEAD ABSORPTION Up to 50 units/day $2/unit A process by which overheads are included in the total cost of a product 51-75 units/day $2.20/unit “The charging of overheads to cost units by means of rates separately calculated 76 units or more per day $2.40/unit for each cost centre, in most cases the rates are pre-determined.” (CIMA) Only additional units qualify for the higher rate. Calculate the unit labour cost if production/day is: O.A.R for a cost centre= Total overheads of cost centre a) 45 units Total no. of units of absorption b) 80 units base applicable to cost centre A: a) $2/unit b) $2.09 Cost Centre “A location, function or items of equipment in respect of which costs may be Labour turnover ascertained and related to cost units for control purposes.” (CIMA) -rate at which employees leave a company e.g.: plating shop, sales office -should be kept as low as possible -divided into 2: Preventative and replacement cost Bases of absorption e.g.: data relating to Machine Shop for October 19X7 Reasons: Total overhead £6 000 -illness and accidents Total direct labour hours 800 hours -a family move away from locality Total direct wages £1 600 -marriage, pregnancy or difficulties with child care provision Total direct material used £3 000 -retirement or death Total machine hours 1 200 hours Total units produced 45 units Rate= replacements x 100% Average no. of employees in period Overhead Absorption Bases Direct labour hour OAR Replacement costs (hiring new employees) = £6 000 = £7.50/direct labour hour -cost of selection and placement 800 hours -inefficiency of new labour; productivity will be lower Direct Wages OAR -costs of training = £6 000 = £3.75/ £ of wages or 375% of wages -loss of output due to delay in new labour becoming available £1 600 -increased wastage and spoilage due to lack of expertise among new staff Direct material OAR -the possibility of more frequent accidents at work = £6 000 = £2.00/ £ of materials or 200% of -costs of tool and machine breakages £3 000 materials Prime cost OAR Preventative costs (prevent employees leaving) = £6 000 = £1.30/ £ of prime cost or 130% of -cost of personnel administration to maintain good relationships £4 600 prime cost -cost of medical services Machine hour OAR -cost of welfare services = £6 000 = £5.00/machine hours -pension schemes 1 200 hours -cost of providing training and offering career progression Cost unit OAR = £6 000 = £133/unit produced Prevention of high labour turnover 45 units -paying satisfactorily wages -offering satisfactory hours and conditions at work -creating good relations between employers and subordinates Using the calculated OAR -offering good training schemes including promotion ladder e.g.: -improving content of jobs to create job satisfaction Unit X in machine shop -proper planning to avoid redundancies Direct materials used £23.00 -investigating the cost of high labour turnover rates Direct wages £27.50 Direct labour hours 12 hours Machine hours 17 hours To calculate full manufacturing cost of unit X a direct labour hour OAR:
- 8. £ It is better to predetermine the OAR to avoid delays in the preparation of Direct labour 27.50 management information Direct materials 23.00 Prime cost 50.50 Under/Over absorption Overheads Absorbed o/H > actual = over 12 hours @ 90.00 Absorbed o/H < actual = under £7.50/hour Full manufacturing 140.50 Determination of o/Hs cost Allocation Apportionment Comparison of alternative bases Absorption Absorption OAR Cost data Calculation o/H absorbed per base unit D. labour hour £7.50 12 hours 12 x £7.50 £90.00 C10-MARGINAL COSTING AND ABSORPTION COSTING D. wages 375% £27.50 3.75 x £27.50 £103.13 D. material 200% £23.00 2 x £23.00 £46.00 CONTRIBUTION o = sales – variable cost Prime cost 130% £50.50 1.3 x £50.50 £65.65 o = fixed cost + profit Machine hour £5.00 17 hours 17 x £5.00 £85.00 o Contribution/unit = selling price – variable cost/unit Cost unit £133.00 1 unit 1 x £133.00 £133.00 o Profit= contribution – fixed cost o Used in marginal costing Choosing the appropriate absorption base Absorption costing : cost accounting system that charges both fixed and variable Direct labour basis production o/Hs to cost units Suitable in a labour intensive cost centre which has good time recording system Marginal costing : an accounting system in which variable costs are charged to Machine hour basis cost units and fixed costs are not absorbed into cost units but Suitable in mechanised cost centre. A lot of o/Hs will relate to the use of written off as period costs in the income statement for the machinery. E.g.: power, repairs, depreciation etc. period to which they relate Direct wages Same as direct labour basis. Only suitable where there are uniform wages rates, in INVENTORY VALUATION which case it will give the same amount of o/H as direct labour basis Direct material e.g.: Only likely to be useful for absorbing material handling expenses. For other Company A produces a single product with the following budget: manufacturing o/Hs the value of the material is unlikely to relate to the time spent Selling price $10/unit in the cost centre D. material $3/unit Prime cost D. wages $2/unit As this is a combination of direct wages and direct materials it is unlikely to be Variable o/H $1/unit suitable The fixed production OAR is $10000 and is based on a production level of 5000 Cost unit units/month. The actual production is 6000 by which 4800 units sold and 1200 This allocates the same amount of o/H to each unit. Thus, it is only to be suitable units left in closing inventory. Prepare profit statement for the month. where all the units produced are identical Absorption costing - fixed production o/H costs are also include in inventory Predetermined overhead rates valuations using predetermined absorption rate = Budgeted T. o/Hs for cost centre Budgeted T. no. of units of Predetermined OAR = $10000/5000 units = $2/unit Absorption base Full production cost/unit for the absorption costing statement = $6 variable cost + e.g.: $2 fixed production o/Hs = $8/unit Budgeted o/H £12 600 Budgeted machine hours 840 hours Machine hour OAR = £12 600 840 hours = £15/hour
- 9. $ F. production o/H absorbed (6000 units x $2) 12000 C11-BASIC BUDGETING F. production o/H incurred 10000 Over-absorbed F. production o/H 2000 Production budget $ $ Budgeted production = c/stocks – o/stocks + budgeted sales Sales 48000 Cost of sales: Raw materials Production (6000 x $8) 48000 Budgeted raw materials purchases = c/stocks of raw materials – o/stocks of raw Closing inventory (1200 x $8) 9600 38400 materials + budgeted raw materials usage Operating margin 9600 Over-absorbed F. production o/H 2000 C12-COMPARISON OF INFORMATION AND PERFORMANCE INDICATOR Operating profit 11600 Efficiency ratio = expected hours to make actual output x 100% Over-absorbed o/H is added back to the profit at the end of the operating AH statement in order to determine the absorption costing operating profit for the period. If there would have been under-absorption, then it will be deducted indeed. Capacity utilisation ratio = AH x 100% BH Marginal costing - inventory is valued at variable production cost Production volume ratio = expected hours to make actual output x 100% $ $ BH Sales 48000 Variable costs: Profit margin = profit x 100% Production costs (6000 x $6) 36000 Sales Closing inventory (1200 x $6) 7200 28800 19200 ROCE = profit before interest and tax x 100% Fixed costs 10000 Capital employed Operating profit 9200 Relation Changes in inventory levels ROCE = profit margin x asset turnover Increase = absorption costing profit is higher C13-STANDARD COSTING AND VARIANCES Decrease = marginal costing profit is higher Direct Materials Variances: BREAK-EVEN POINT AND MARGIN OF SAFETY Materials purchase price variance Formula: B/Ept = fixed cost (quantity) Materials purchase price variance = (Actual quantity purchased × Actual price) – Cn/unit (Actual quantity purchased × Standard price) = fixed cost (value-$) Materials price usage variance formula C/S ratio Materials price usage variance = (Actual quantity used × Actual price) – (Actual quantity used × Standard price) C/S ratio is always constant provided there is no change in selling price and variable cost per unit Materials quantity / usage variance formula Materials price usage variance = (Actual quantity used × Standard price) – Margin of safety= current sales – B/Ept (Standard quantity allowed × Standard price) Margin of safety x 100% (in percentage) Materials mix variance formula Expected sales (Actual quantities at individual standard materials costs) – (Actual quantities at weighted average of standard materials costs)
- 10. Materials yield variance formula Factory overhead yield variance formula: (Actual quantities at weighted average of standard materials costs) – (Actual (Standard hours allowed for expected output × Standard overhead rate) – output quantity at standard materials cost) (Standard hours allowed for actual output × Standard overhead rate) Direct Labour Variances: *Fixed overhead budgeted + Standard hours allowed × Standard variable overhead rate Direct labour rate / price variance formula: (Actual hours worked × Actual rate) – (Actual hours worked × Standard rate) **Standard hours allowed for actual production × Standard overhead rate Direct labour efficiency / usage / quantity formula: (Actual hours worked × Standard rate) – (Standard hours allowed × Standard rate) ***Fixed overhead budgeted + Actual hours worked × Standard variable overhead rate Direct labour yield variance formula: (Standard hours allowed for expected output × Standard labour rate) – (Standard hours allowed for actual output × Standard labour rate) Factory Overhead Variances: Factory overhead controllable variance formula: (Actual factory overhead) – (Budgeted allowance based on standard hours allowed*) Factory overhead volume variance: (Budgeted allowance based on standard hours allowed*) – (Factory overhead applied or charged to production**) Factory overhead spending variance: (Actual factory overhead) – (Budgeted allowance based on actual hours worked***) Factory overhead idle capacity variance formula: (Budgeted allowance based on actual hours worked***) – (Actual hours worked × Standard overhead rate) Factory overhead efficiency variance formula: (Actual hours worked × Standard overhead rate) – (Standard hours allowed for expected output × Standard overhead rate) Variable overhead efficiency variance formula: (Actual hours worked × Standard variable overhead rate) – (Standard hours allowed × Standard variable overhead rate) Variable overhead efficiency variance formula: (Actual hours worked × Fixed overhead rate) – (Standard hours allowed × Fixed overhead rate)
