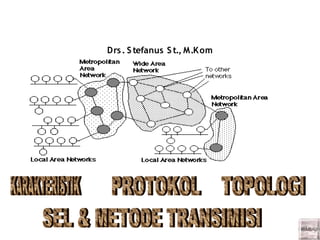
4 Metropolitan Area Network
- 1. Drs . S tefanus S t., M.K om
- 2. KARAKTERISTIK • A MAN is a relatively new class of network, it serves a role similar to an ISP, but for corporate users with large LANs [FAIR,2001]. • • MAN dapat berupa jaringan antarkantor organisasi atau jaringan kota, atau suatu daerah (pertambangan, pabrik, industri besar) yang dapat dimanfaatkan untuk keperluan suatu organisasi / umum, misal televisi kabel dan Internet Service Provider (ISP). • Terdapat 3 kategori :
- 3. • The network size falls intermediate between LANs and WANs. A MAN typically covers an area of between 5 and 50 km diameter. Many MANs cover an area the size of a city, although in some cases MANs may be as small as a group of buildings or as large as the North of Scotland. • A MAN (like a WAN) is not generally owned by a single organisation. The MAN, its communications links and equipment are generally owned by either a consortium of users or by a single network provider who sells the service to the users. This level of service provided to each user must therefore be negotiated with the MAN operator, and some performance guarantees are normally specified. • A MAN often acts as a high speed network to allow sharing of regional resources (similar to a large LAN). It is also frequently used to provide a shared connection to other networks
- 4. PR OTOK OL • Protokol dan teknologi pada MAN hampir sama dengan LAN. Perbedaan terbesar terletak pada ukurannya yang lebih besar sehingga dapat dikatakan MAN merupakan LAN yang berukuran besar [TANE,1997]. • Standar yang sedang dikembangkan adalah Distributed Queue Dual Bus (DQDB) yang ditetapkan oleh IEEE dengan nomor kode 802.6. DQDB terdiri dari dua bus (kabel) unidirectional dalam sebuah kota tempat semua stasiun terhubung. DQDB dapat beroperasi sampai 160 km pada kecepatan 44,736 Mbps [TANE,1997]
- 5. TOPOLOG I BUS A HEAD END SIMPUL SIMPUL SIMPUL BUS B HEAD END
- 6. SEL & METODE TRANSMISI • Setiap bus mempunyai sebuah head end yang menghasilkan sebuah sel ukuran 53 byte dg payload sebesar 44 byte. Setiap sel juga memegang dua buah bit protokol ‘busy’ yang mengindikasikan sel sedang dipakai dan ‘request’ yang dapat diset ketika stasiun akan menggunakan bus. • Setiap sel akan memperoleh gilirannya secara First in Fisrt Out (FIFO) sesuai urutan pemesanan penggunaan bus. Tidak ada stasiun pusat yang mengatur antrian ini. Transmisi ke arah kanan stasiun menggunakan bus A sebaliknya pengiriman data ke arah kiri stasiun menggunakan bus B. Penyisipan data dengan rangkaian OR