NGT handouts
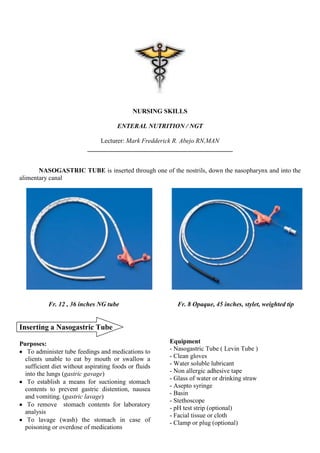
- 1. NURSING SKILLS ENTERAL NUTRITION / NGT Lecturer: Mark Fredderick R. Abejo RN,MAN _____________________________________________ NASOGASTRIC TUBE is inserted through one of the nostrils, down the nasopharynx and into the alimentary canal Fr. 12 , 36 inches NG tube Fr. 8 Opaque, 45 inches, stylet, weighted tip Inserting a Nasogastric Tube Purposes: Equipment To administer tube feedings and medications to - Nasogastric Tube ( Levin Tube ) clients unable to eat by mouth or swallow a - Clean gloves sufficient diet without aspirating foods or fluids - Water soluble lubricant into the lungs (gastric gavage) - Non allergic adhesive tape - Glass of water or drinking straw To establish a means for suctioning stomach - Asepto syringe contents to prevent gastric distention, nausea - Basin and vomiting. (gastric lavage) - Stethoscope To remove stomach contents for laboratory - pH test strip (optional) analysis - Facial tissue or cloth To lavage (wash) the stomach in case of - Clamp or plug (optional) poisoning or overdose of medications
- 2. Lecture Notes on Enteral Nutrition ( Nasogastric Tube ) Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, M.A.N Clinical Instructor Assessment: Mark this length with This length Check the patency of nares and intactness of adhesive tape if the tube approximates the nasal tissue: does not have markings. distance from the nares to the - Ask the client to hyperextend the head, using stomach flashlight, observe the intactness of the tissue of Insert the tube the nostrils. Put on gloves Lubricate the tip with To reduce friction - Ask the client to breath through one nostril while water-soluble lubricant. occluding the other, select the nostril that has Hyperextend the neck, Hyperextension of greater airflow. gently advance the tube the neck reduces toward the nasopharynx the curvature of the Determine presence of gag reflex Note: nasopharyngeal Ability to cooperate with the procedure If the tube meets resistance, junction. withdraw it, relubricate it, and insert to the other To prevent injury Steps / Procedure Rationale nostril Identify and inform the client and explain To allay anxiety the procedure. Assist the client to a high fowler’s It is often easier to position if his/her swallow in this position health condition and gravity helps the permits, support head passage of tube with pillow. Measure the length NEX technique ( nose- of NGT to be inserted ear-xiphoid) Tilt the client’s head Tilting the head forward once the tube forward facilitates reaches the throat and passage of tube into ask the client to the esophagus swallow or drink water rather than into as the tube advances. larynx. Swallowing moves the epiglottis cover the opening to the larynx Pass the tube 5-10 cm with each swallow, until the indicated length is inserted. Checking the patency Aspirate stomach Testing pH is a Measuring the appropriate length to insert the contents and check the reliable way to NGT ( NEX technique ) pH, which should be determine location acidic of a feeding tube.
- 3. Lecture Notes on Enteral Nutrition ( Nasogastric Tube ) Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, M.A.N Clinical Instructor Introduce 10-30 ml of Tape the tube to the area between the end air into the NGT and Note: of the nares and the upper lip as well as to the auscultate at the Gastric contents cheek. epigastric area, gurgling must be re-instill to sound is heard. the stomach to Ask the client to speak prevent electrolyte Administering Tube Feeding or hum imbalances (NGT Feeding , Gastric Gavage) Observe the client for coughing and choking Difficulty in Purposes: speaking and client To restore or maintain nutritional status. Note: is choking and To administer medications The most accurate method continuously cough, of assessing the placement tube is possibly in Equipment: of NGT is X-ray study the lungs - Correct amount of feeding solution - Asepto syringe Secure the NGT by This prevents the - Measuring container or cup tapping it to the bridge of tube from pressing - Emesis basis the client’s nose. against and - Clean gloves irritating the edge - Stethoscope of the nostril - pH test strip (optional) - Facial tissue or cloth Special Considerations: - Water Inserting a NGT to Infants and Young Assessment: Children: Assess for any signs of malnutrition or dehydration. Restraints may be necessary during tube Check for allergies to any food in the feeding. insertion and throughout therapy. Restraints Assess for the presence of bowel sounds will prevent accidental dislodging of the tube. Note any problems that suggest lack of Place the infant in an infant seat or tolerance of previous feedings (e.g delayed position the infant with a rolled towel or gastric emptying, abdominal distention, pillow under the head and shoulders. dumping syndrome, constipation or dehydration) When assessing the nares, obstruct one of the infant’s and feel for air passage from the Steps / Procedure Rationale other. If the nasal passageway is very small or is obstructed, an orogastric tube may be more Identify and inform appropriate. the client and To allay anxiety explain, why it is Measure appropriate NGT length from the necessary and how nose to the tip of the earlobe and then to the he/she can cooperate point midway between the umbilicus and Assist the client to a xiphoid process. fowler’s position in This positions enhance If an orogastric tube is used, measure from bed or a sitting the gravitational flow of the tip of the earlobe to the corner of the position in chair, if the solution and prevent mouth to the xiphoid process. his/her health aspiration of fluid into condition permits. the lungs Do not hyperextend or hyperflex an Wash hands and infant’s neck. Hyperextension or hyperflexion observe appropriate of the neck could occlude the airway. infection control and provide privacy
- 4. Lecture Notes on Enteral Nutrition ( Nasogastric Tube ) Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, M.A.N Clinical Instructor Check the patency of Through A Syringe the tube: (open system) - Aspirate stomach - Introduce feeding contents and check the slowly To prevent flatulence, pH, which should be - Height of feeding is cramps , and reflex acidic 12 inches above the vomiting point of insertion. - Introduce 10-30 ml of - Instill 60- 100 ml of air into the NGT and water to NGT after To cleanse the lumen of auscultate at the the tube epigastric area, gurgling - Clamp the cover of sound is heard. the feeding before all To prevent leakage and Assess residual water is instilled air from entering the feeding contents. To tube. assess absorption of Note: the last feeding, if 50 Gastric contents must Ensure client comfort ml or more, verify if be re-instill to the and safety : the feeding will be stomach to prevent given. electrolyte imbalances - Pin the tubing to the Minimizes pulling of the client’s gown tube thus preventing Note: discomfort If the client is on continuous feeding, - Ask the client to This facilitate digestion check the gastric remain in position for at and prevent potential residual 4-6 hours least 30 min. aspiration. Administer the feeding Monitor patient for Check the feeding, Spoiled feeding cause possible problem and time it was diarrhea and complications on prepared, its abdominal pain to the tube feedings expiration client. Make relevant Warm the feeding at Excessively cold documentation room temperature feeding may cause cramps Feeding Through a Syringe Through A Feeding Bag - Hang the bag from an infusion pole about 12 inches above the point of insertion. - Clamp the tubing and add the formula to the bag. - Open the clamp, run the formula to the tube, to prevent instillation of air to the client’s stomach. - Attach the bag to the NGT and regulate the drip.
- 5. Lecture Notes on Enteral Nutrition ( Nasogastric Tube ) Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, M.A.N Clinical Instructor Special Considerations: apparatus if connected - Unpin the tube to the Administering a Tube Feeding to: client’s gown Infants - Remove the adhesive tape securing the tube Feeding tubes may be reinserted at each to the nose feeding to prevent irritation of the mucous Remove the Tube membrane, nasal airway obstruction and Wear gloves stomach perforation. (optional) Instill 50 This clears the tube of Children ml of air into the any gastric contents Position a small child or infant in your lap, tube provide a pacifier, and hold and cuddle the Ask the client to This closes glottis, child during feedings. This promotes comfort, take deep breath preventing aspiration of supports the normal sucking instinct of the and hold it gastric contents infant and facilitates digestion Pinch the tube with This prevent gastric Elders he gloved hand contents inside the tube Quickly and from draining into the Decreased gastric emptying may smoothly, withdraw clients throat necessitate checking frequently fir gastric the tube. residual. Dispose the tube To prevent possible Diarrhea from administering the feeding immediately transfer of too fast or at too high concentration may cause microorganism dehydration Provide oral care if desired If feeding has a high concentration of Assist the client to To remove accumulated glucose, assess hyperglycemia blow the nose secretions Document relevant information Removing a Nasogastric Tube Equipment: Common Problems of Tube Feedings - Disposable pad 1. Vomiting - Clean gloves 2. Aspiration - 50 ml syringe (optional) 3. Diarrhea - Disposable bag 4. Constipation 5. Hyperglycemia 6. Abdominal Distention Steps / Procedure Rationale Confirm the physician’s order. Identify and inform the client and explain To allay anxiety the procedure. Assist the client into a sitting position if health permits Place the disposable To collect any spillage pad across the of mucous and gastric client’s chest secretions from the tube Wash hands Detach the tube: - Disconnect to suction
- 6. Lecture Notes on Enteral Nutrition ( Nasogastric Tube ) Prepared By: Mark Fredderick R Abejo R.N, M.A.N Clinical Instructor After feeding, remain in sitting position or Administering a Gastrostomy or slightly elevated right lateral position for at least 30 mins. To prevent gastric reflux and Jejunostomy Feeding possible aspiration. Assess status of peristomal skin for signs and symptoms of infection. Gastrostomy Tube Feeding Make relevant documentation Total Parenteral Nutrition (TPN) Intravenous Hyperalimentation (IVH) TPN or IVH, is provided when the gastrointestinal tract is nonfunctional because of an interruption in its continuity or because its absorptive capacity is impaired. Parenteral Nutrition, is administered intravenously such as through a central venous catheter into the superior vena cava. Because TPN solutions are hypertonic ( highly concentrated in comparison to the solute concentration of blood), they are injected only into high – flow central veins, where they are diluted by the client’s blood Clients suggestive for TPN Severe malnutrition Severe burns Procedure: Bowel disease disorders Acute renal failure Assess and prepare the client Hepatic failure Insert a feeding tube into the ostomy opening Metastatic cancer 10-15 cm (4-6 inches) if one is not already in Major surgeries ( where NPO is taken for more place. Lubricate with water soluble lubricant than 5 days) before insertion to prevent friction. Check the patency of a tube suture in place. Pour 15-30 ml of water into the syringe and allow water to flow into the tube. Check the residual formula. If 50mls or more, verify if the feeding will be administered. Administer feeding slowly. Hold the syringe 7-15 cm (3-6 inches) above the ostomy opening. To prevent flatulence, crampy pain and reflex vomiting Flush the tube with 30 ml. Flushing the tube preserves its patency.
