Review 6 _earthquakes___crustal_activity_sc
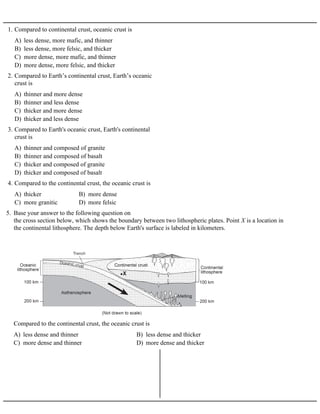
- 1. A) less dense, more mafic, and thinner B) less dense, more felsic, and thicker C) more dense, more mafic, and thinner D) more dense, more felsic, and thicker 1. Compared to continental crust, oceanic crust is A) thinner and more dense B) thinner and less dense C) thicker and more dense D) thicker and less dense 2. Compared to Earth’s continental crust, Earth’s oceanic crust is A) thinner and composed of granite B) thinner and composed of basalt C) thicker and composed of granite D) thicker and composed of basalt 3. Compared to Earth's oceanic crust, Earth's continental crust is A) thicker B) more dense C) more granitic D) more felsic 4. Compared to the continental crust, the oceanic crust is 5. Base your answer to the following question on the cross section below, which shows the boundary between two lithospheric plates. Point X is a location in the continental lithosphere. The depth below Earth's surface is labeled in kilometers. A) less dense and thinner B) less dense and thicker C) more dense and thinner D) more dense and thicker Compared to the continental crust, the oceanic crust is
- 2. A) low density and is mafic B) low density and is felsic C) high density and is mafic D) high density and is felsic 6. When two tectonic plates collide, oceanic crust usually subducts beneath continental crust because oceanic crust is primarily composed of igneous rock that has A) continental crust B) oceanic crust C) plastic mantle D) rigid mantle 7. In which part of the Earth are felsic rocks most likely to be found? A) nitrogen B) oxygen C) silicon D) iron 8. Which element is most abundant by mass in the Earth's crust? A) oxygen, potassium, sodium, and calcium B) hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and potassium C) aluminum, iron, silicon, and magnesium D) aluminum, calcium, hydrogen, and iron 9. What are the four most abundant elements, by volume, in the Earth's crust? 10. The diagram below represents a cross section of a portion of the Earth's crust where no overturning of the rock layers has occurred. Two rock layers are labeled A and B. A) Deposition occurred before folding or faulting. B) Faulting occurred before folding of the rock layers. C) Faulting occurred before the formation of rock layer A. D) Folding occurred before the formation of rock layer B. Which statement describes the most likely sequence of events? 11. Base your answer on the geologic cross section below. A) folding at A B) the intrusion at B C) faulting at C D) the unconformity at D Which geologic event occurred most recently? 12. The diagram below shows a cross section of a portion of Earth's crust. A) bedrock folding B) bedrock faulting C) stream erosion D) volcanic activity The hills of this area were formed primarily by 13. The diagram below shows the bedrock structure beneath a series of hills. A) folding B) faulting C) deposition D) vulcanism Which process was primarily responsible for forming the hills?
- 3. 14. The diagram below represents a geologic cross section of a portion of Earth's crust. A) Gayle shale B) Freeport sandstone C) Erie coal, but before formation of Freeport sandstone D) Dunbar limestone, but before formation of Erie coal Folding and erosion occurred after the formation of the 15. Base your answer to the following question on the geologic cross section below in which overturning has not occurred. Letters A through H represent rock layers. A) folding ® uplift ® erosion ® deposition B) intrusion ® erosion ® folding ® uplift C) erosion ® folding ® deposition ® intrusion D) deposition ® uplift ® erosion ® folding Which sequence of events most likely caused the unconformity shown at the bottom of rock layer B?
- 4. 16. The block diagram below shows a part of the eastern coastline of North America. Points A, B, and C are reference points along the coast. A) A — folding; B — subduction; C — crosscutting B) A — weathering; B — erosion; C — deposition C) A — faulting; B — conduction; C — mass movement D) A — precipitation; B — infiltration; C — evaporation Which list best represents the primary processes occurring along the coastline at points A, B, and C? 17. The diagram below shows a cross section of the Earth's crust. Line XY is a fault. A) B) C) D) Which sequence of events, from oldest to youngest, has occurred in this outcrop?
- 5. 18. The diagrams below show geologic cross sections of the same part of the Earth's crust at different times in the geologic past. A) A ® B ® C ® D B) C ® D ® A ® B C) C ® A ® D ® B D) A ® C ® B ® D Which sequence shows the order in which this part of the crust probably formed? 19. Base your answer to the following question on the diagrams below which represent two rock outcrops found several miles apart in New York State. Individual rock layers are lettered, and fossils and rock types are indicated. A) F, B, E, D B) C, A, F, D C) F, E, C, A D) C, E, D, A In which sequence are the rock layers listed in order from oldest to youngest? A) shale schist phyllite slate gneiss B) shale slate phyllite schist gneiss C) shale gneiss phyllite slate schist D) shale gneiss phyllite schist slate 20. Which sequence of change in rock type occurs as shale is subjected to increasing heat and pressure? 21. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below shows a geologic cross section. Letters A through D represent different rock units. A) A ® B ® C ®D B) C ® D ® A ®B C) D ® B ®A ®C D) D ® C ® B ®A Which sequence correctly shows the age of the lettered rock units, from oldest to youngest?
- 6. 22. Base your answer to the following question on The cross section below shows rock layers A, B, C, D, and fault F. The rock layers have not been overturned. A) D C B A F B) A B C D F C) F D C B A D) F A B C D Which sequence places the rock layers and fault in order from oldest to youngest? 23. Base your answer to the following question on The cross section below shows a rock sequence that has not been overturned. A) Shale was deposited. B) Glacial till was deposited. C) Basaltic lava flows solidified. D) Glossopteris flourished and then became extinct. Which event occurred last at this location?
- 7. 24. Base your answer to the following question on the example of a seismogram and set of instructions for determining the Richter magnitude of an earthquake below. The example shows the Richter magnitude of an earthquake 210 kilometers from a seismic station. Instructions for determining Richter magnitude: • Determine the distance to the epicenter of the earthquake. (The distance in the example is 210 kilometers.) • Measure the maximum wave height of the S-wave recorded on the seismogram. (The height in the example is 23 millimeters.) • Place a straightedge between the distance to the epicenter (210 kilometers) and the height of the largest S -wave (23 millimeters) on the appropriate scales. Draw a line connecting these two points. The magnitude of the earthquake is determined by where the line intersects the Richter magnitude scale. (The magnitude of this example is 5.0.)
- 8. Using the set of instructions and the seismogram and scales below, determine the Richter magnitude of an earthquake that was located 500 kilometers from this seismic station.
- 9. 25. Base your answer to the following question on The seismogram below shows P-wave and S-wave arrival times at a seismic station following an earthquake. A) 1,600 km B) 3,200 km C) 4,400 km D) 5,600 km The distance from this seismic station to the epicenter of teh earthquake is approximately 26. The seismogram below shows the arrival times of an earthquake's P-wave and S-wave recorded at a seismic station in Portland, Oregon. A) 1800 km B) 2500 km C) 3200 km D) 4100 km What was the distance from Portland to the earthquake's epicenter?
- 10. 27. An earthquake recorded by seismic stations around the world created the pattern of seismic wave recordings shown in the diagram below A) Some seismic waves cannot travel through oceans to reach every location on Earth. B) S-waves are too weak to travel very far from the earthquake focus. C) Mountain ranges and tectonic plate boundaries absorb or bend seismic waves. D) Layers with different properties inside Earth absorb or bend seismic waves. Which statement best explains this pattern of wave recordings? 28. The seismogram below shows the time that an earthquake P-wave arrived at a seismic station. A) 1,900 km B) 3,200 km C) 4,000 km D) 5,200 km If the earthquake occurred at exactly 10:00 p.m., approximately how far from the earthquake epicenter from the seismic station?
- 11. 29. Base your answer to question 43 on the seismogram below. The seismogram was recorded at a seismic station and shows the arrival times of the first P-wave and S-wave from an earthquake. A) P-wave arrival time, only B) S-wave arrival time, only C) difference in the arrival time of the P-wave and S-wave D) difference in the height of the P-wave and S-wave Which part of this seismogram is used to find the distance to the epicenter of the earthquake? 30. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents three seismograms showing the same earthquake as it was recorded at three different seismic stations, A, B, and C. A) A is closest to the epicenter, and C is farthest from the epicenter. B) B is closest to the epicenter, and C is farthest from the epicenter. C) C is closest to the epicenter, and A is farthest from the epicenter. D) A is the closest to the epicenter, and B is the farthest from the epicenter. Which statement correctly describes the distance between the earthquake epicenter and these seismic stations?
- 12. A) 7 minutes 20 seconds B) 5 minutes 10 seconds C) 3 minutes 20 seconds D) 4 minutes 10 seconds 31. A seismic station is 2,000 kilometers from an earthquake epicenter. How long does it take an S-wave to travel from the epicenter to the station? A) 4:24 p.m. B) 4:29 p.m. C) 4:36 p.m. D) 4:56 p.m. 32. If a seismograph recording station located 5,700 kilometers from an epicenter receives a P-wave at 4:45 p.m., at which time did the earthquake actually occur at the epicenter? 33. Base your answer to the following question on the map below which shows epicenters of some of the earthquakes that occurred in North America during a 2-week period. Five epicenters are labeled A through E. Denver and New York City are also indicated. A) 1 min 20 sec B) 5 min 40 sec C) 7 min 30 sec D) 10 min 00 sec The distance from epicenter E to New York City is 3,000 kilometers. What was the approximate travel time for the P-waves from this epicenter to New York City?
- 13. A) 11 min 15 sec B) 9 min 35 sec C) 5 min 20 sec D) 4 min 20 sec 34. The epicenter of an earthquake is located 2,800 kilometers from a seismic station. Approximately how long did the S-wave take to travel from the epicenter to the station? A) 6 mm 40 sec B) 9 mm 40 sec C) 15 mm 00 sec D) 19 mm 00 sec 35. A P-wave takes 8 minutes and 20 seconds to travel from the epicenter of an earthquake to a seismic station. Approximately how long will an S-wave take to travel from the epicenter of the same earthquake to this seismic station? A) When the P-waves and S-waves are near the epicenter, they both travel at the same speed. B) The velocity of P-waves and S-waves is constant, regardless of the distance traveled. C) P-waves always travel faster than S-waves, regardless of the distance traveled. D) S-waves always travel about twice as fast as P -waves. 36. Which generalization about earthquake S-waves and P -waves is correct? 37. The seismogram below shows the arrival times of P- and S-waves at a seismic station in hours, minutes, and seconds. A) 1,650 km B) 1,900 km C) 2,200 km D) 4,100 km Approximately how far from the earthquake epicenter is this seismic station? 38. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram of the Earth below showing the observed pattern of waves recorded after an earthquake. A) crust in zone 1 B) mantle in zone 2 C) crust in zone 3 D) core of the Earth The location of the epicenter of the earthquake that produced the observed wave pattern most likely is in the
- 14. 39. Base your answer to the following question on the data table below, which gives information collected at seismic stations W, X, Y, and Z for the same earthquake. Some of the data have been omitted. A) W B) X C) Y D) Z Which seismic station was farthest from the earthquake epicenter? A) 1,000 km B) 1,500 km C) 2,000 km D) 2,500 km 40. A seismograph indicates the difference between the arrival of S-waves and P-waves to be 4 minutes. The distance of the seismograph station from the earthquake's epicenter is about A) 5:04:30 a.m. B) 5:05:40 a.m. C) 5:10:12 a.m. D) 6:15:00 a. m. 41. An earthquake occurred at 5:00:00 a.m. At what time would the P-wave reach a seismic station 3,000 kilometers from the epicenter? A) an iron-rich solid B) an iron-rich liquid C) a silicate-rich solid D) a silicate-rich liquid 42. The rock between 2,900 kilometers and 5,200 kilometers below the Earth's surface is inferred to be A) 6,500ºC B) 4,200ºC C) 3,500ºC D) 1,800ºC 43. At a depth of 2,000 kilometers, the temperature of the stiffer mantle is inferred to be A) analyzing worldwide seismic data B) measuring crustal temperature ranges C) determining crustal density differences D) observing rock samples from surface bedrock 44. The structure of the Earth's interior is best inferred by A) an iron-rich solid B) an iron-rich liquid C) a silicate-rich solid D) a silicate-rich liquid 45. The rock between 2,900 kilometers and 5,200 kilometers below the Earth's surface is inferred to be 46. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows a cutaway view of Earth in which the interior layers are visible. The paths of earthquake waves generated at point X are shown. A, B, C, and D are locations of seismic stations on Earth's surface, and point E is located in Earth's interior. A) 1,500ºC B) 2,900ºC C) 5,000ºC D) 6,200ºC The actual rock temperature at point E is inferred to be approximately
- 15. A) liquid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm3 B) liquid, with an average density of approximately 11 g/cm3 C) solid, with an average density of approximately 4 g/cm3 D) solid, with an average density of approximately 11 g/cm3 47. Earth’s outer core is best inferred to be A) liquid B) solid C) composed of a high percentage of iron D) under the same pressure 48. Earth’s outer core and inner core are both inferred to be A) the Moon’s interior B) the Moon’s composition C) Earth’s surface features D) Earth’s seismic data 49. Scientists have inferred the structure of Earth’s interior mainly by analyzing A) seismic waves B) crustal rocks C) radioactive decay rates D) magnetic pole reversals 50. Earth’s inner core is inferred to be solid based on the analysis of A) 1000°C B) 2500°C C) 4500°C D) 5000°C 51. The inferred temperature at the interface between the stiffer mantle and the asthenosphere is closest to A) 3500°C and 0.4 million atmospheres B) 3500°C and 2.0 million atmospheres C) 5500°C and 0.4 million atmospheres D) 5500°C and 2.0 million atmospheres 52. Which combination of temperature and pressure is inferred to occur within Earth’s stiffer mantle? A) crust B) mantle C) outer core D) inner core 53. A part of which zone of the Earth's interior is inferred to have a density of 10.0 grams per cubic centimeter? A) 1 million atmospheres B) 2 million atmospheres C) 3 million atmospheres D) 4 million atmospheres 54. The pressure at the interface between the inner core and outer core of the Earth is inferred to be approximately 55. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below which represents Earth's interior zones. A) crust B) mantle C) outer core D) inner core In which layer of Earth's interior is the inferred temperature 6,000°C? A) continents moved due to changes in the Earth's orbital velocity B) continents moved due to the Coriolis effect caused by the Earth's rotation C) present-day continents of South America and Africa are moving toward each other D) present-day continents of South America and Africa once fit together like puzzle parts 56. The theory of continental drift suggests that the A) Basaltic rock is found to be progressively younger at increasing distances from a mid-ocean ridge. B) Marine fossils are often found in deep-well drill cores. C) The present continents appear to fit together as pieces of a larger landmass. D) Areas of shallow-water seas tend to accumulate sediment, which gradually sinks. 57. Which statement best supports the theory of continental drift?
- 16. A) the seafloor is spreading B) the ocean basins are older than the continents C) the mid-ocean ridges are higher than the nearby plains D) Earth's rate of rotation has changed 58. Magnetic readings taken across mid-ocean ridges provide evidence that A) African plate and Antarctic plate B) Nazca plate and South American plate C) China plate and Philippine plate D) Australian plate and Eurasian plate 59. Seafloor spreading is occurring at the boundary between the A) The bedrock of the ridge and nearby seafloor is igneous rock. B) The ridge is the location of irregular volcanic eruptions. C) Several faults cut across the ridge and nearby seafloor. D) Seafloor bedrock is younger near the ridge and older farther away. 60. Which observation about the Mid-Atlantic Ridge region provides the best evidence that the seafloor has been spreading for millions of years? A) crust B) asthenosphere C) outer core D) inner core 61. In which Earth layer are most convection currents that cause seafloor spreading thought to be located? Base your answers to questions 62 through 64 on the diagram below which shows the magnetic orientation of igneous rock on the seafloor on the east (right) side of a mid-ocean ridge. The pattern on the west (left) side of the ridge has been omitted. The age of the igneous rock and its distance from the ridge center are shown. A) The orientation of the Earth's magnetic field has reversed with time. B) The size of the continents has changed with time. C) The elevation of sea level has changed with time. D) The amount of fossil material preserved in the igneous rock has changed with time. 62. Which inference can best be made from the diagram? A) B) C) D) 63. Which diagram below best represents the pattern of magnetic orientation in the seafloor on the west (left) side of the ocean ridge? A) destruction of oceanic crust B) destruction of continental crust C) existence of ancestral mountains D) existence of rising mantle convection currents 64. The occurrence of high-heat floors at the ridge center provides evidence of the
- 17. 65. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below shows the interaction of two tectonic plates. A) Antarctic Plate and the African Plate B) Antarctic Plate and the Indian-Australian Plate C) South American Plate and the Nazca Plate D) South American Plate and the African Plate The type of plate boundary represented in the diagram most likely exists between the A) at a convergent plate boundary B) above a mantle hot spot C) above a mid-ocean ridge D) near the center of a large plate 66. According to tectonic plate maps, New York State is presently located 67. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the boundary between two tectonic plates. A) divergent B) convergent C) transform D) complex Which type of plate boundary is shown?
- 18. 68. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows an incomplete concept map identifying the types of plate boundaries. Information in the boxes labeled A, B, C, D,and E has been deliberately omitted. On the geographic map shown above, write the letters D and E on the plate boundary locations where the indicated movements are occurring. Write the letters approximately the same size as shown on the concept map and locate the letters directly on the plate boundary.
- 19. 69. Base your answer to the following question on the world map shown below. Letters A through H represent locations on Earth’s surface. Explain why location A has a greater probability of experiencing a major earthquake than location D. A) the mid-Atlantic ridge B) the Aleutian trench C) the Atlantic-Indian ridge D) the Pacific/North American plate boundary 70. Which of the following locations is the site of a convergent plate boundary? A) B) C) D) 71. Which diagram best shows the type of plate boundary found between the China Plate and the Philippine Plate? A) Southwest Indian Ridge B) Iceland Hotspot C) Marianas Trench D) Sandwich Plate 72. Which of the following is located at a converging plate boundary? A) convergent B) transform C) divergent D) complex 73. What type of plate boundary exists between the African Plate and the Antartic Plate?
- 20. 74. Base your answer to the following question on The map below shows the northern section of the boundary between the Arabian Plate and theAfrican Plate. Arrows show the relative direction of plate motion. A) divergent B) subduction C) convergent D) transform Which type of plate boundary is located at the Jordan Fault? A) Nazca Plate and Antarctic Plate B) Pacific Plate and Indian-Australian Plate C) Indian-Australian Plate and Antarctic Plate D) Nazca Plate and Pacific Plate 75. At which plate boundary is one lithospheric plate sliding under another?
- 21. 76. Base your answer to the following question on Arrows in the block diagram below show the relative movement along a tectonic plate boundary. A) Nazca Plate and South American Plate B) Eurasian Plate and Indian-Australian Plate C) North American Plate and Eurasian Plate D) Pacific Plate and North American Plate Between which two tectonic plates does this type of plate boundary exist?
- 22. Base your answers to questions 77 and 78 on the world map in your answer booklet and on your knowledge of Earth science. The map shows major earthquakes and volcanic activity occurring from 1996 through 2000. Letter A represents a volcano on a crustal plate boundary. 77. Identify the type of plate movement responsible for the presence of the volcano at location A. 78. Place an X on the map to show the location of the Nazca Plate.
- 23. 79. The diagram below shows a tectonic plate boundary. A) Hawaii Hot Spot B) Yellowstone Hot Spot C) Galapagos Hot Spot D) Canary Hot Spot Which mantle hot spot is at a plate boundary like the one shown in this diagram?
- 24. 80. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows a tectonic plate boundary. Points A and B represent locations on Earth’s surface. A) B) C) D) Which graph best shows the depths of most major earthquakes whose epicenters lie between A and B?
- 25. 81. Base your answer to the following question on the map below, which shows the depths of selected earthquakes along the crustal plate boundary near the west coast of South America. Letters A, B, C, and D are epicenter locations along a west-to-east line at the surface. The relative depth of each earthquake is indicated. A) B) C) D) Which graph best shows the depth of earthquakes beneath epicenters A, B, C, and D?
- 26. 82. Base your answer to the following question on the block diagram below. The diagram shows the tectonic plate boundary between Africa and North America 300 million years ago, as these two continents united into a single landmass. The arrows at letters A, B, C, and D represent relative crustal movements. Letter X shows the eruption of a volcano at that time. Identify the type of tectonic plate motion represented by the arrow shown at D. A) Mid-Atlantic Ridge B) Yellowstone Hot Spot C) San Andreas Fault D) Peru-Chile Trench 83. Alternating parallel bands of normal and reversed magnetic polarity are found in the basaltic bedrock on either side of the A) Parallel strips of igneous rocks on each side of the ridge show matching reversals of magnetic polarity. B) The fossils found on one side of the ridge are younger than the fossils found on the other side. C) The age of the rocks decreases as the distance from the ridge increases. D) Seafloor temperatures increase as the distance from the ridge increases. 84. Which statement provides evidence that the seafloor is spreading out from both sides of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge? A) younger B) thicker C) less dense D) more felsic 85. Compared to the continental crust of central North America, the oceanic crust of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge is 86. Which map best represents the general pattern of magnetism in the oceanic bedrock near the mid-Atlantic Ridge? A) B) C) D)
- 27. 87. Base your answer to the following question on The diagram below represents the pattern of normal and reversed magnetic polarity and the relative age of the igneous bedrock composing the ocean floor on the east side of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The magnetic polarity of the bedrock on the west side of the ridge has been deliberately left blank. A) B) C) D) Which diagram best shows the magnetic pattern and relative age of the igneous bedrock on the west side of the ridge?
- 28. 88. The scale below shows the age of rocks in relation to their distance from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. A) 1.8 million years ago B) 2.0 million years ago C) 3.0 million years ago D) 45.0 million years ago Some igneous rocks that originally formed at the Mid-Atlantic Ridge are now 37 kilometers from the ridge. Approximately how long ago did these rocks form? 89. Base your answer to the following question on the map of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge shown below. Points A through D are locations on the ocean floor. Line XY connects locations in North America and Africa. A) B) C) D) In which cross section do the arrows best show the convection occurring within the asthenosphere beneath line XY?
- 29. 90. Base your answer to the following question on table below, which lists the location of some earthquakes, their Richter magnitude, and their year of occurrence. Identify the process in Earth’s asthenosphere that is inferred to be the cause of tectonic plate motion.
- 30. Base your answers to questions 91 through 93 on the Earth Science Reference Tables and the diagram below. The diagram is a model which represents one possible interpretation of the movements of the Earth's rock surfaces according to the theory of plate tectonics (continental drift and sea floor spreading). According to this interpretation, the Earth's lithosphere consists of several large "plates" which are moving in relationship to one another. The arrows in the diagram show some of this relative motion of the "plates." The diagram shows the age of formation of the igneous rocks that make up the oceanic crust of the northern section of the Pacific Plate. A) North America and South America are moving toward each other. B) The India Plate is moving away from the Eurasia Plate. C) The Africa Plate and Eurasia Plate are moving away from the America Plate. D) The Antarctica Plate is moving away from the America Plate. 91. Which statement is best supported by the relative movement shown by the arrows in the diagram? A) thick continental crust B) thick layers of sediment C) mid-ocean ridge D) granitic igneous rock 92. Which geologic structure is represented by the double line separating the America Plate from the Africa and Eurasia Plates? A) convection currents in the mantle B) faulting of the lithosphere C) the spin of the Earth on its axis D) prevailing wind belts of the troposphere 93. Which provides the best explanation of the mechanism that causes these "plates" to move across the Earth's surface? A) convection currents exist in the asthenosphere B) meteor craters are found beneath the oceans C) climate change has melted huge glaciers D) marine fossils have been uplifted to high elevations 94. Hot springs on the ocean floor near the midocean ridges provide evidence that A) differences in densities of earth materials B) subsidence of the crust C) occurrence of earthquakes D) rotation of the Earth 95. The primary cause of convection currents in the Earth's mantle is believed to be the
- 31. 96. Base your answer to the following question on the information below. A camper takes a 100-gram piece of basalt rock from a campfire and places it in a cup holding 250 milliliters of water. The temperature of the rock is 300ºC and the temperature of the water is 20ºC. Air temperature also is 20ºC. A) B) C) D) Which diagram best represents the convection currents in the cup of water after the warm piece of basalt was placed in it? A) B) C) D) 97. Which diagram best represents the convection currents in a container of water when the bottom of the container is heated at the center? A) B) C) D) 98. Which diagram best represents the direction of convection currents around the burning wood of a campfire? A) rigid mantle B) asthenosphere C) outer core D) inner core 99. Which part of Earth’s interior is inferred to have convection currents that cause tectonic plates to move? A) B) C) D) 100. Which cross-sectional diagram of Earth’s asthenosphere best shows the convection currents that would cause crustal plate X to drift away from crustal plate Y? 101. Which cross-sectional diagram of a portion of the crust and mantle best shows the pattern of mantle convection currents that are believed to cause the formation of a mid-ocean ridge? A) B) C) D) A) 50° N, 120° W B) 25° N, 158° E C) 25° N, 158° W D) 25° S, 158° E 102. Approximately what are the coordinates of the Hawaii Hot Spot? A) 32° S 18° W B) 32° S 18° E C) 32° N 18° W D) 32° N 18° E 103. What is the approximate location of the Canary Islands hot spot? A) South American B) Antarctic C) Nazca D) Pacific 104. On which plate is the Hawaii Hot Spot located?
- 32. 105. The cross section below shows the direction of movement of an oceanic plate over a mantle hot spot, resulting in the formation of a chain of volcanoes labeled A, B, C, and D. The geologic age of volcano C is shown. A) B is 5 million years old and D is 12 million years old. B) B is 2 million years old and D is 6 million years old. C) B is 9 million years old and D is 9 million years old. D) B is 10 million years old and D is 4 million years old. What are the most likely geologic ages of volcanoes B and D?
- 33. 106. Base your answer to the following question on The block diagram below shows the bedrock age as measured by radioactive dating and the present location of part of the Hawaiian Island chain. These volcanic islands may have formed as the Pacific Plate moved over a mantle hot spot. A) south B) east C) southwest D) northwest This diagram provides evidence that the Pacific Crustal Plate was moving toward the