Gestalt Psychology
- 2. Gestalt (pronounced ge-SHTALT) is a German word that means roughly means “shape”, “form”, “essence”, or “whole”. Gestalt is a psychology term which means "unified whole". It refers to theories of visual perception developed by German psychologists in the 1920s One of the most important theories of perception is the Gestalt Theory. Gestalt Theory “The Whole is different from the sum of its part”. It was developed about 1910by Max Wertheimer and carry on by Wolfgang Kohler and Kurt Koffka at Frankfurt University.
- 3. Born April 15, 1880 Died Oct 12, 1943 Born in Prague, Czech Republic Psychologist Father of Gestalt psychology
- 4. Born in Jan 21, 1887 Died in June 11, 1967 Born in Reval (now Tallinn), Estonia Psychologist and phenomenologist Another of the founders of Gestalt psychology
- 5. Born March 18, 1886 Died Nov 22, 1941 Born in Berlin, Germany Psychologist Another of the founders of Gestalt psychology Learning theorist
- 6. Max Wertheimer,Wolfgang Kohler and Kurt Koffka concluded that learners were not Passive,but rather active.They suggested that learners do not just collect information as is but they actively process and restructure data in order to understand it.This is the Perceptual Process,Certain factors impact on this perceptual process.Factors like past experiences,needs,attitudes and one’s present situation can affect his perception.
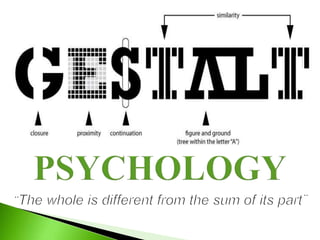
- 7. Law of Proximity Law of Similarity Law of Closure Law of Good Continuation Law of Good Pragnanz Law of Figure/Ground
- 8. The law of proximity states that when objects appear close to one another they tend to be perceived as a group.
- 10. The law of similarity captures the idea that when we look at objects that are similar to each other, we tend to group them together. We are prone to notice matching shapes, colors, and forms (as opposed to looking for what isn’t similar). Our brains quickly identify patterns faster than the separate parts of the pattern.
- 12. The law of closure captures the idea that when we see incomplete elements in a visual, our brains tend to fill in the gaps and see it as a whole.
- 15. The mind continous visual patterns. The eye continues in the direction it is going. The principle of continuity predicts the preference for continous figures.
- 17. The word pragnanz is a German term meaning "good figure." The law of Pragnanz is sometimes referred to as the law of good figure or the law of simplicity. This law holds that objects in the environment are seen in a way that makes them appear as simple as possible.
- 21. Figure–ground organization is a type of perceptual grouping which is a vital necessity for recognizing objects through vision.
- 23. Wolfgang kohler was the first psychologist who developed the insight learning in which he described an experiment with apes that could use boxes and sticks as tools to solve the problem.
- 24. In his experiment, Kohler hung a piece of fruit just out of the reach of each chimp. He then provided the chimps with either two sticks or three boxes, then waited and watched. Kohler noticed that after the chimps realized they could not simply reach or jump up to retrieve the fruit, they stopped, had a seat, and thought about how they might solve the problem. Then after a few moments, the chimps stood up and proceeded to solve the problem.
- 25. In the first scenario, the problem was solved by placing the smaller stick into the longer stick to create one very long stick which could be used to knock the hanging fruit down.
- 26. In the second scenario, the chimps would solve the problem by stacking the boxes on top of each other, which allowed them to climb to the top of the stack of boxes and reach the fruit.
- 27. The important aspect of learning was not reinforcement,but the coordination of thinking to create new organizations. Kohler referred to this behavior as insight or discovery learning. Insight learning is the abrupt realization of a problem's solution. Insight learning is not the result of trial and error, responding to an environmental stimulus, or the result of observing someone else attempt the problem. It is a completely cognitive experience, which requires the ability to visualize the problem and the solution internally, in the mind's eye so to speak, before initialing a behavioral response.
- 28. 1. Law of Proximity Related concepts or lessons should be taught aligned or closely to each other.This is the reason why subtraction is taught after addition,multiplication after subtraction then division after multiplication. Imagine teaching addition then jumping directly to polygons.
- 29. 2. Law of Similarity Similar lessons or contents should be grouped together to make learners develop understanding more efficiently and effectively.This is the reason why lessons are grouped into units: Unit I is for human body, Unit II is for energy and motion,so on and so forth.
- 30. 3. Law of Closure When a concept or topic is incomplete thus isn't "closed", incomplete information may make learners want to discover what’s missing, rather than concentrating on the given instruction. If students find a math algorithm confusing because a certain question is left unanswered or a step isn't clear, they will tend to concentrate on that confused part of the process rather than the total process as a whole. This is why students get "lost".Thus,make the lesson complete.Present it clearly,simply and always be ready for students' clarifications.
- 31. 4. Law of Good Continuation Lessons should be presented in such a way that learners will see these as connected and continuous. Now you know why we have the "Review" part of the lesson plan.This way, students will realize that their new lesson actually has continuity and is related to what they already know or to the previous lesson.
- 32. 5. Law of Pragnanz Pragnanz states that when things are grasped as wholes, the minimal amount of energy is exerted in thinking. In short, make your lesson holistic, complete and most of all simple.
- 33. 6. Law of Figure/Ground For a figure to be perceived, it must stand out from the background.Emphasis should be done on important aspects of the lesson. For example,teachers should vary the tone of their voice or write boldly or underline the important key words of the lesson.
