Jewellrgb
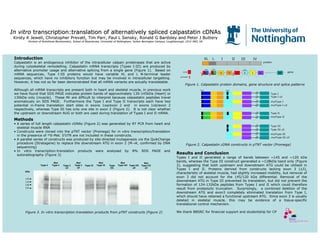
- 1. In vitroIn vitro transcription:translation of alternatively spliced calpastatintranscription:translation of alternatively spliced calpastatin cDNAscDNAs KirstyKirsty K Jewell, ChristopherK Jewell, Christopher PrevattPrevatt, Tim Parr, Paul L, Tim Parr, Paul L SenskySensky, Ronald G Bardsley and Peter J Buttery, Ronald G Bardsley and Peter J Buttery Division of Nutritional Biochemistry, School of Biosciences, UniDivision of Nutritional Biochemistry, School of Biosciences, University of Nottingham, Suttonversity of Nottingham, Sutton BoningtonBonington Campus, Loughborough, LE12 5RD, UKCampus, Loughborough, LE12 5RD, UK IntroductionIntroduction Calpastatin is an endogenous inhibitor of the intracellular calpain proteinases that are active during cytoskeletal remodelling. Calpastatin mRNA transcripts (Types I-III) are produced by alternative promoter usage and alternative splicing from a single gene (Figure 1). Based on mRNA sequences, Type I-III proteins would have variable XL and L N-terminal leader sequences, which have no inhibitory function but may be involved in intracellular targetting. However, it has not so far been demonstrated that all mRNA variants are actually translatable. Although all mRNA transcripts are present both in heart and skeletal muscle, in previous work we have found that SDS PAGE indicates protein bands of approximately 130-145kDa (heart) or 130kDa only (muscle). These Mr are difficult to interpret because calpastatin peptides travel anomalously on SDS PAGE. Furthermore the Type I and Type II transcripts each have two potential in-frame translation start sites in exons 1xa/exon 2 and in exons 1xb/exon 2 respectively, whereas Type III has only one site in exon 2 (Figure 2). It is not clear whether the upstream or downstream AUG or both are used during translation of Types I and II mRNA. Figure 1. Calpastatin protein domains, gene structure and splice patterns MethodsMethods • A series of full length calpastatin cDNAs (Figure 2) was generated by RT PCR from heart and skeletal muscle RNA • Constructs were cloned into the pTNT vector (Promega) for in vitro transcription/translation in the presence of 35S-Met. 5’UTR are not included in these constructs. • A parallel series of constructs was produced by site-directed mutagenesis via the QuikChange procedure (Stratagene) to replace the downstream ATG in exon 2 (M→K, confirmed by DNA sequencing) • In vitro transcription:translation products were analysed by 8% SDS PAGE and autoradiography (Figure 3) Results and ConclusionResults and Conclusion Types I and II generated a range of bands between ~145 and ~120 kDa bands, whereas the Type III construct generated a ~128kDa band only (Figure 2), suggesting that both upstream and downstream ATG could be utilised in Types I and II. Proteins derived from constructs lacking exon 3 (∆3), characteristic of skeletal muscle, had slightly increased mobility, but removal of exon 3 did not account for the 145/120 kDa differential. Removal of the downstream ATG in Type III prevented its translation, but did not prevent the formation of 124-132kDa peptides from Types I and II which could therefore result from proteolytic truncation. Surprisingly, a combined deletion of the downstream ATG and exon3 completely eliminated translation from Type I, which should have retained a functional upstream ATG. Since exon 3 is usually deleted in skeletal muscle, this may be evidence of a tissue-specific translational control mechanism. We thank BBSRC for financial support and studentship for CP Type I Type II Type III Type III ∆3 Type I ∆3 promoter 1u 3 4 30+ XL L II III IVI protein gene Figure 2. Calpastatin cDNA constructs in pTNT vector (Promega) mutType I mutType I ∆3 mutType III mutType III ∆3 mutType II ATG ATG Type I Type I ∆∆∆∆3 Mut Type I Mut Type I ∆∆∆∆3 Mut Type II Type III Type III ∆∆∆∆3 Mut Type III Mut Type III ∆∆∆∆3 142 132 130 124 Figure 3. In vitro transcription:translation products from pTNT constructs (Figure 2) kDa 1y 1z ATG ATG ATG Type II 5’UTR 1xa 1xb 2