Skin Problems & Treatments Health Center
- 1. Skin Anatomy and burn Classes Dr. Bassem Alaa El-
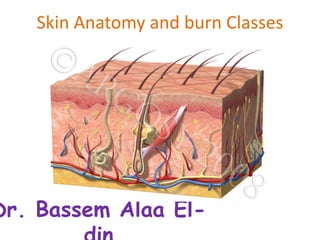
- 2. Skin • The skin is the largest organ of the body, with a total area of about 20 square feet. The skin protects us from microbes and the elements, helps regulate body temperature, and permits the sensations of touch, heat, and cold. • Skin has three layers: • The epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone. • The dermis, beneath the epidermis, contains tough connective tissue, hair follicles, and sweat glands. • The deeper subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis) is made of fat and connective tissue. • The skin’s color is created by special cells called melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin. Melanocytes are located in the epidermis.
- 5. Skin Burns • First-degree burns are red and painful. They swell a little and turn white when you press on them. The skin over the burn may peel off in a day or two. These are the least severe type of burn, affecting only the outer layer of skin. • Causes: Sunburn and hot liquids
- 7. First degree burn • Healing time: 3 to 6 days; the superficial skin layer over the burn may peel off in 1 or 2 days.
- 8. Second Degree Burns • A second degree (partial thickness) burn damages the top layers of the skin & • causes blistering. It can result in scarring and may require a skin graft.
- 9. Second Degree Burns • Second degree burns can result from: • Hot liquids • Flame Injury • Scalding liquids
- 10. Second Degree Burns • Signs and symptoms: Blisters, severe pain, and redness. The blisters sometimes • break open and the area is wet looking with a bright pink to cherry red color.
- 13. Third Degree Burn • A third degree (full thickness) burn destroys all layers of the skin. Skin grafting is • necessary to repair the skin • Third degree burns can result from: • Prolonged flame (house fire) • Steam or scalding liquids • Chemical or electrical injury
- 14. Third Degree Burn • Signs and symptoms: • The surface is dry and can look waxy white, leathery, brown, or charred. • There may be little or no pain or the area may feel numb at first because of nerve damage.
- 16. Fourth Degree Burns • A fourth degree (full thickness) burn destroys all layers of the skin and involves tendons and muscles. As a result, there is no sensation in the burn area.
- 17. Fourth Degree Burns • Fourth degree burns can result from • Prolonged flame contact • High voltage electrical injury
- 19. TISSUE-HEALING AGENTS • MEBO is of natural and herbal edible origin. It is composed of ß-sitosterol 0.25% as the main active ingredient. The base of the ointment is composed of sesame oil and beeswax. In addition to that, MEBO includes in its formula 18 amino acids, 4 major fatty acids, vitamins, and polysaccharides.
